Condition in which the fetal vessels are located in the membranes near the internal os of the cervix, putting them at risk of injury if the membranes rupture
Epidemiology
Etiology
- Placental anomalies, such as:
- Velamentous umbilical cord insertion
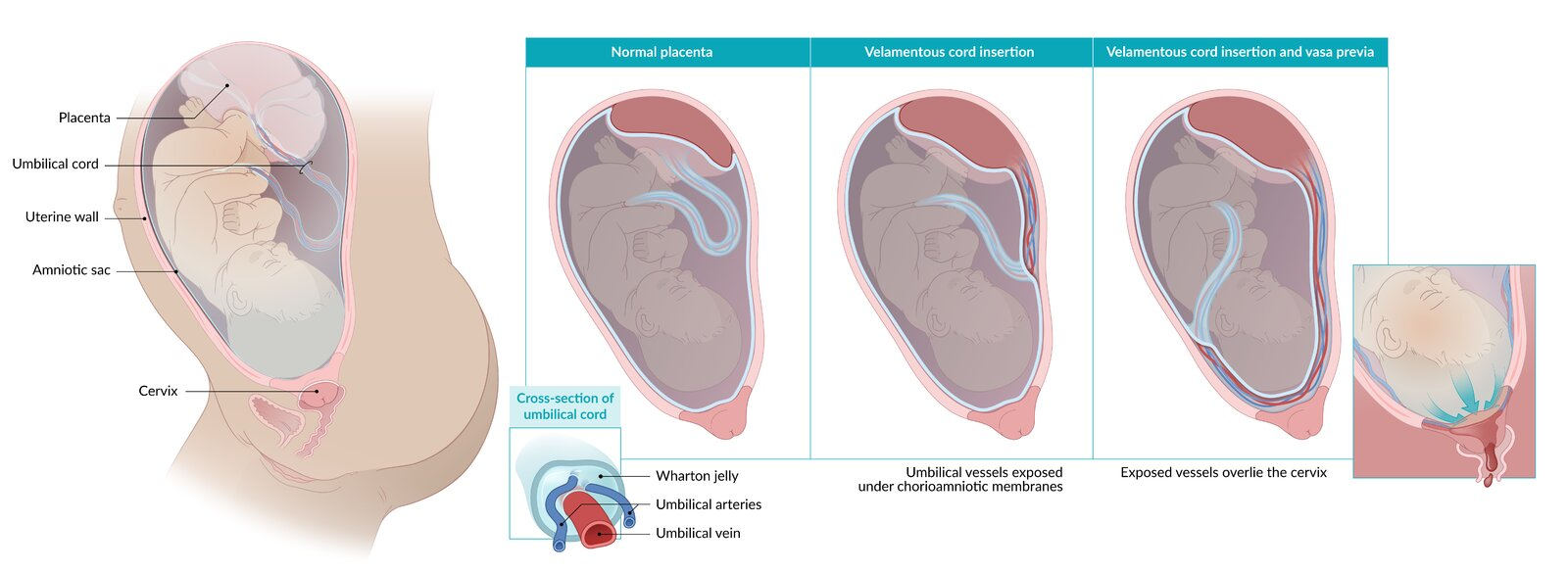
- Inserts in chorioamniotic membrane rather than placenta → fetal vessels travel to placenta unprotected by Wharton jelly
- Bilobate or succenturiate placenta
- Variation of the placental morphology with one or more accessory lobes developing separately from the main placental body
- Velamentous umbilical cord insertion
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Painless vaginal bleeding (fetal blood) that occurs suddenly after rupture of membranes
- Fetal distress (e.g., fetal bradycardia; decelerations or sinusoidal pattern on fetal heart tracings)
- Fetal death can occur quickly through exsanguination or asphyxiation if fetal vessels are compressed during labor.