- Definition: a common degenerative disorder of GI vessels (mostly venous) that can cause GI bleeding
- Epidemiology: predominantly seen in individuals > 60 years of age
- Etiology: associated with von Willebrand disease, aortic stenosis (e.g., Heyde syndrome), and end-stage renal disease (ESRD)
- Clinical features
- Manifests with episodic bleeding (hematochezia) , fatigue, weakness, dizziness, shortness of breath, and, potentially, hematemesis
- Physical examination: tachycardia, pallor
- Diagnostics
- Laboratory studies
- Positive fecal occult blood test
- CBC and iron studies to evaluate for anemia
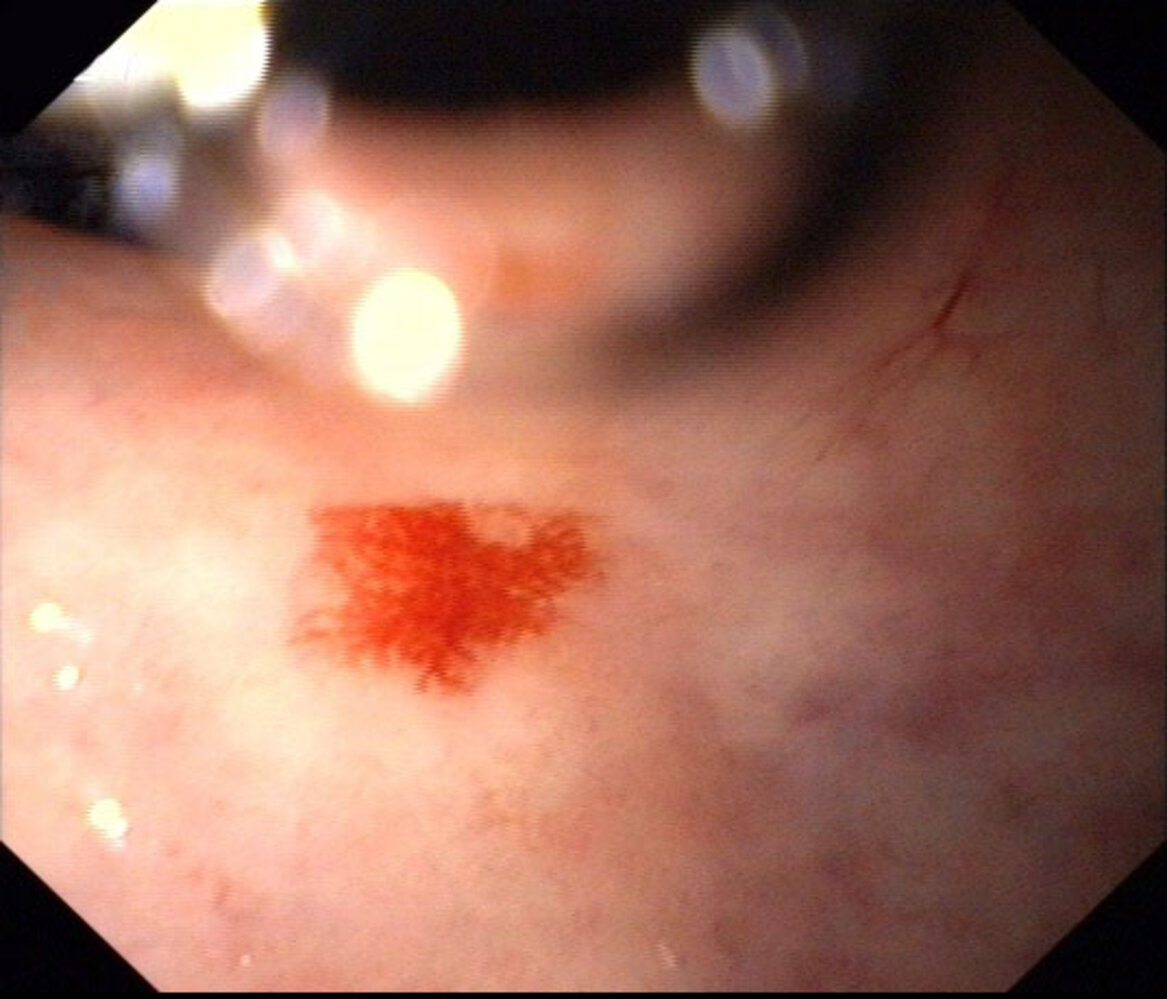
- Endoscopy: the preferred method for establishing diagnosis
- Findings
- Lesions are usually multiple tortuous dilated vessels, most commonly located in the right-sided colon
- Angiography
- Gold standard
- Indication: recurrent bleeding with inconclusive endoscopy
