| Malignancy | Usually benign. Malignant transformation is rare, but possible (most commonly to squamous cell carcinoma). | Often malignant, can metastasize. |
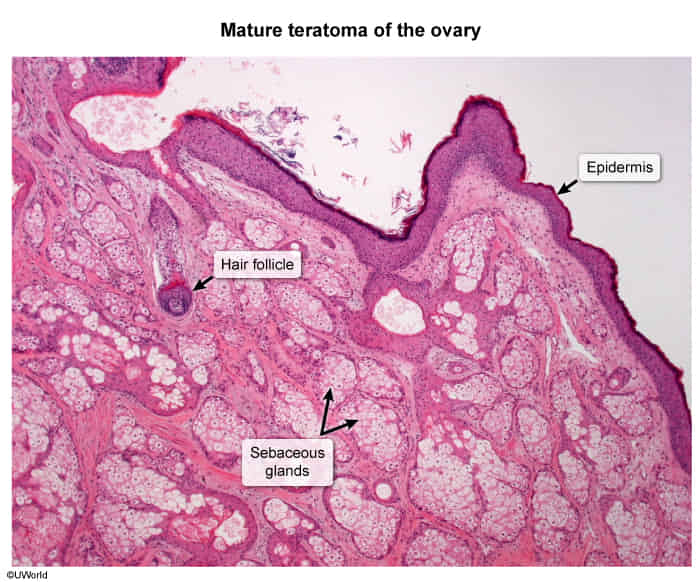
| Differentiation | Well-differentiated, containing mature tissues from all three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm). Often contains skin, hair, teeth, bone, muscle, and even complex parts. | Contains immature or embryonic tissues, most commonly neuroectoderm (immature neural tissue). May also have immature cartilage and skeletal muscle. |
| Age of Onset | Can occur at any age, but they’re most common during reproductive years. | Most frequently in the first two decades of life, rare after menopause. |
| Common Locations | Most common in ovaries (dermoid cysts) in females and testes in males. Can occur in other midline locations. | Ovaries and testes are common sites, can be found in other locations. |
| Appearance | Often cystic, containing a variety of mature tissues. The predominant type is cystic (Mature Cystic Teratoma or MCT) and it always contains skin, hair, and neural tissues, along with sebaceous materials. | Typically larger and more solid, with heterogeneous areas, often including coarse calcifications and small foci of fat. |
| Prognosis | Generally good due to benign nature. | Depends on grade and stage, generally poorer than mature teratomas. |
| Genetic | Usually a diploid, normal 46, XX karyotype | May have a variety of karyotypes |