Venous congestion of the head, neck, and upper extremities resulting from impaired venous flow through the superior vena cava (SVC) to the right atrium.
Epidemiology
Etiology
- Malignant SVC syndrome (most common) (extravascular)
- The following entities account for > 80% of all SVC syndrome cases:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
- Less common: metastatic cancer (usually breast cancer), germ cell tumors, thymoma, mesothelioma
- The following entities account for > 80% of all SVC syndrome cases:
- Nonmalignant SVC syndrome (intravascular)
- Most commonly caused by thrombosis associated with an intravascular device (e.g., dialysis catheter, pacemaker wire)
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
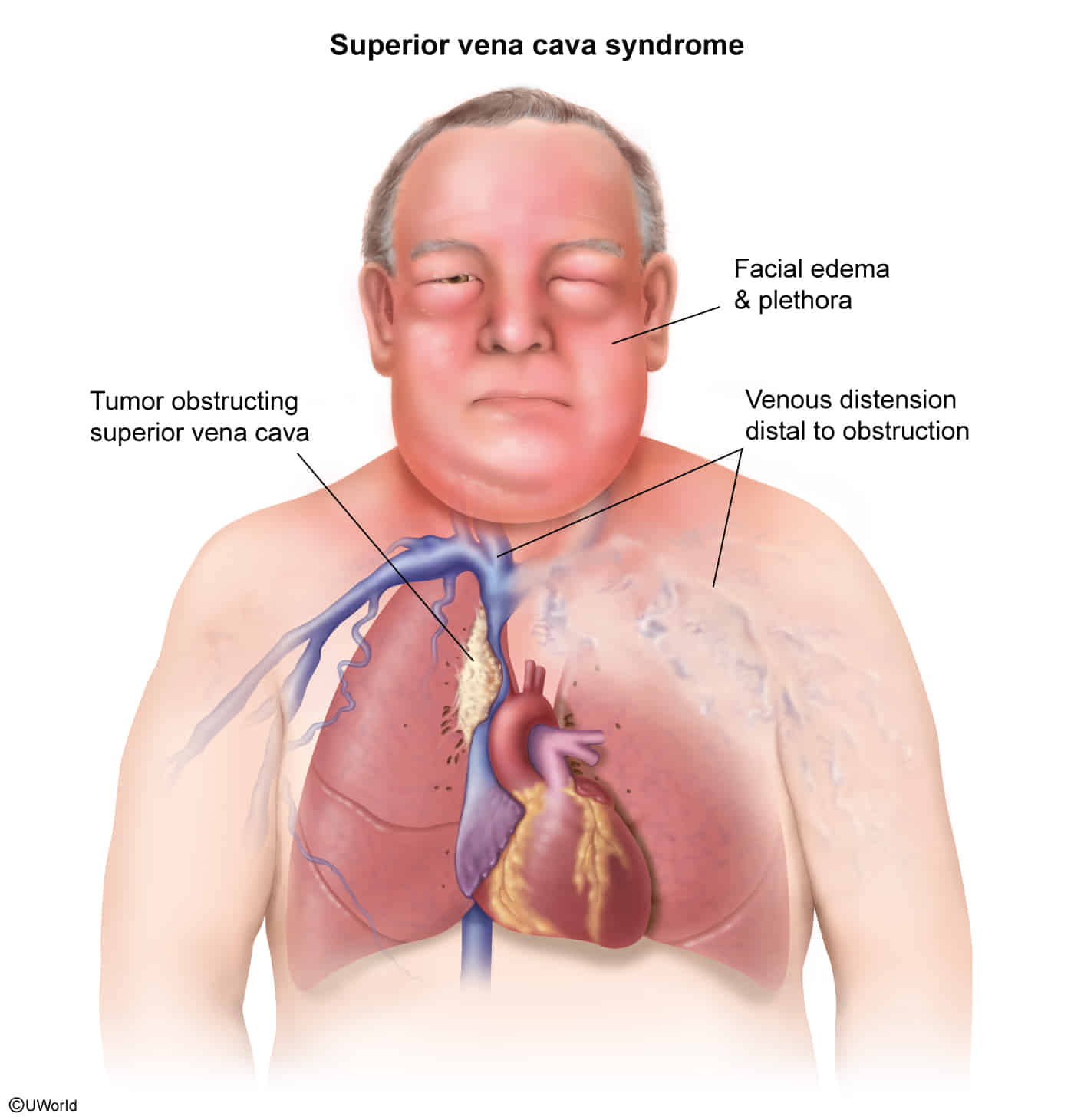
- Hemodynamic symptoms
- Edema of the upper extremities and face (facial plethora)
- Prominent venous pattern on the chest, face, and upper extremities
- Jugular venous distension
- Symptoms and signs of congestion of the neck
- Dyspnea
- Cough and hoarseness
- Neurological symptoms
- Headache
- Dizziness
Warning
Evaluate frequently for signs of laryngeal edema, hemodynamic instability, and ↑ ICP.