Pathophysiology
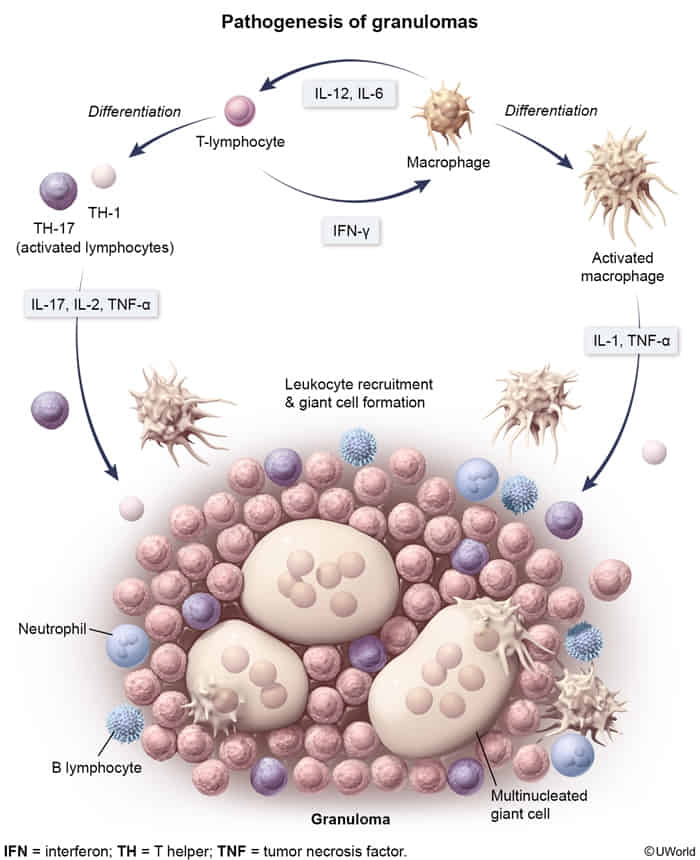
- Antigen-presenting cells present antigens to CD4+ Th cells and secrete IL-12 → stimulation of Th cell differentiation into Th1 cells
- Th1 cells activate macrophages by secreting IFN-γ → cytokine release from macrophages (e.g., TNF) → formation of epithelioid macrophages and giant cells
- Epithelioid cells secrete TNF-α, which serves to maintain the granuloma.
- This is the reason why anti-TNF therapy can promote sequestration of granulomas and cause disseminated disease.
- Therefore, every individual considered for anti-TNF therapy has to be tested for latent TB beforehand.
- Macrophages within the granuloma cause ↑ calcitriol activation due to ↑ 1α-hydroxylase activity → hypercalcemia
