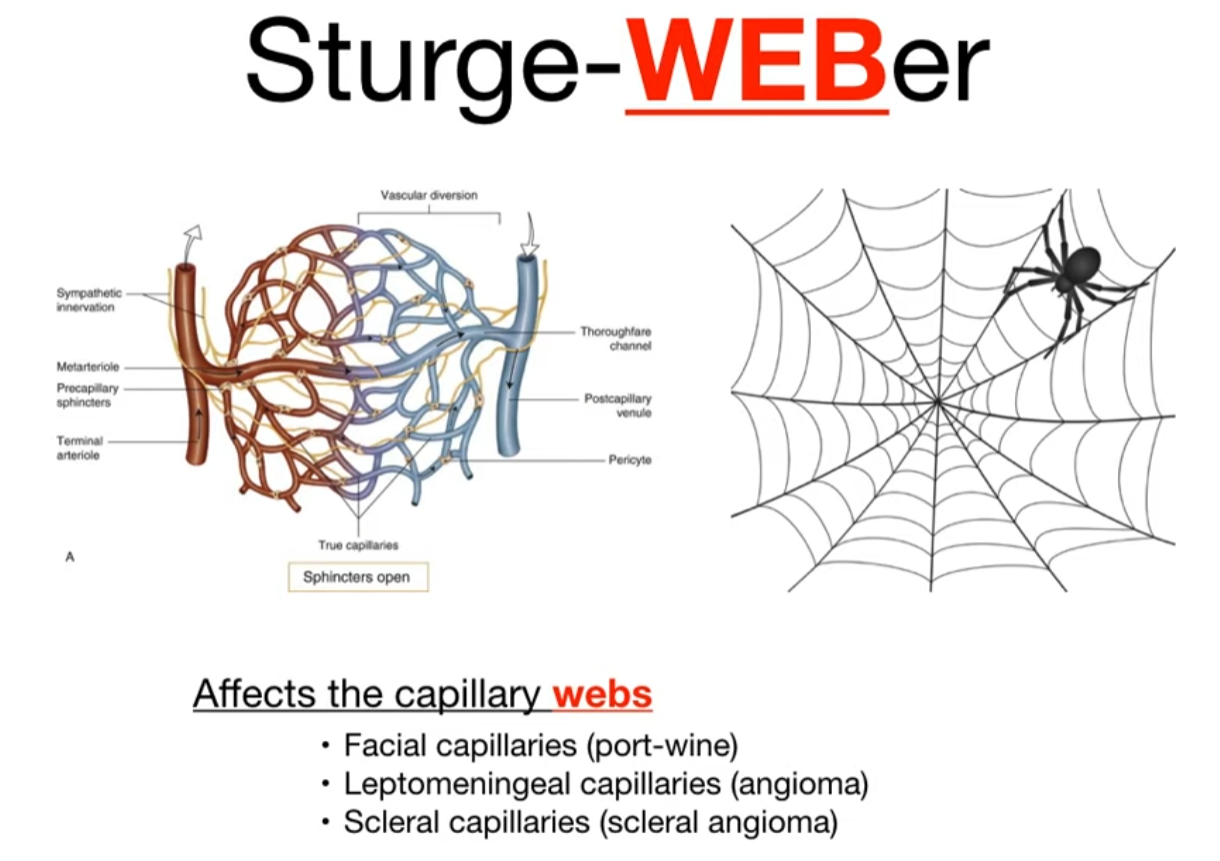
Sturge-Weber syndrome
- Somatic mosaic mutation of GNAQ gene → malformation of capillaries
Tuberous sclerosis
- Mutation of tumor suppressor genes (variable expression) → loss of function → unchecked cell growth → tumor development
- Tumor suppressor genes
- TSC1 gene on chromosome 9 encodes hamartin protein
- TSC2 gene on chromosome 16 encodes tuberin protein
- Clinical features
- Intellectual disability (caused by brain lesions)
- Seizures
- Skin manifestations
- Adenoma sebaceum (facial angiofibroma): benign tumor composed of blood vessels and fibrous connective tissue
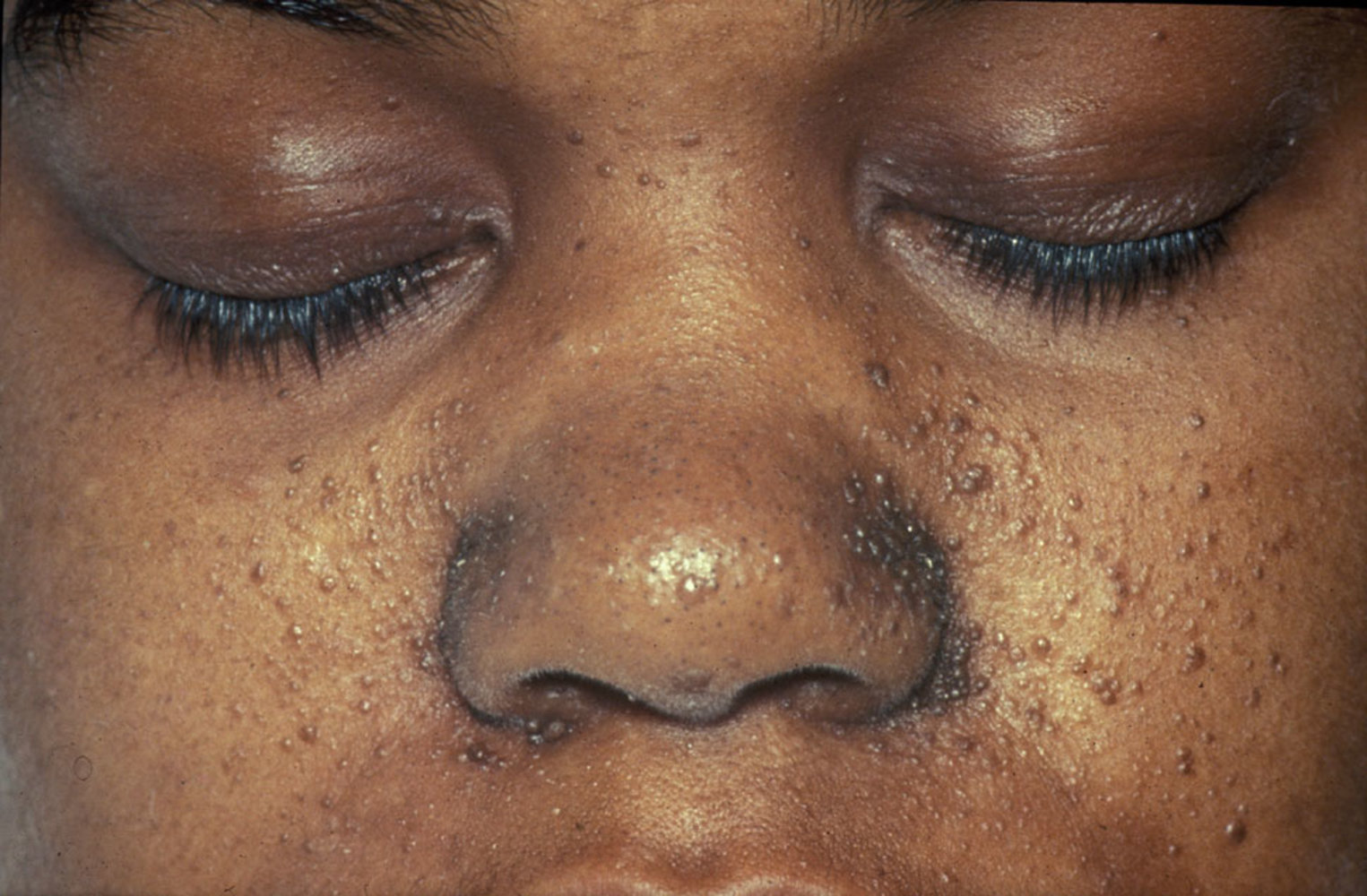
- Mostly located around the nose and cheeks
- Distribution resembles a butterfly shape
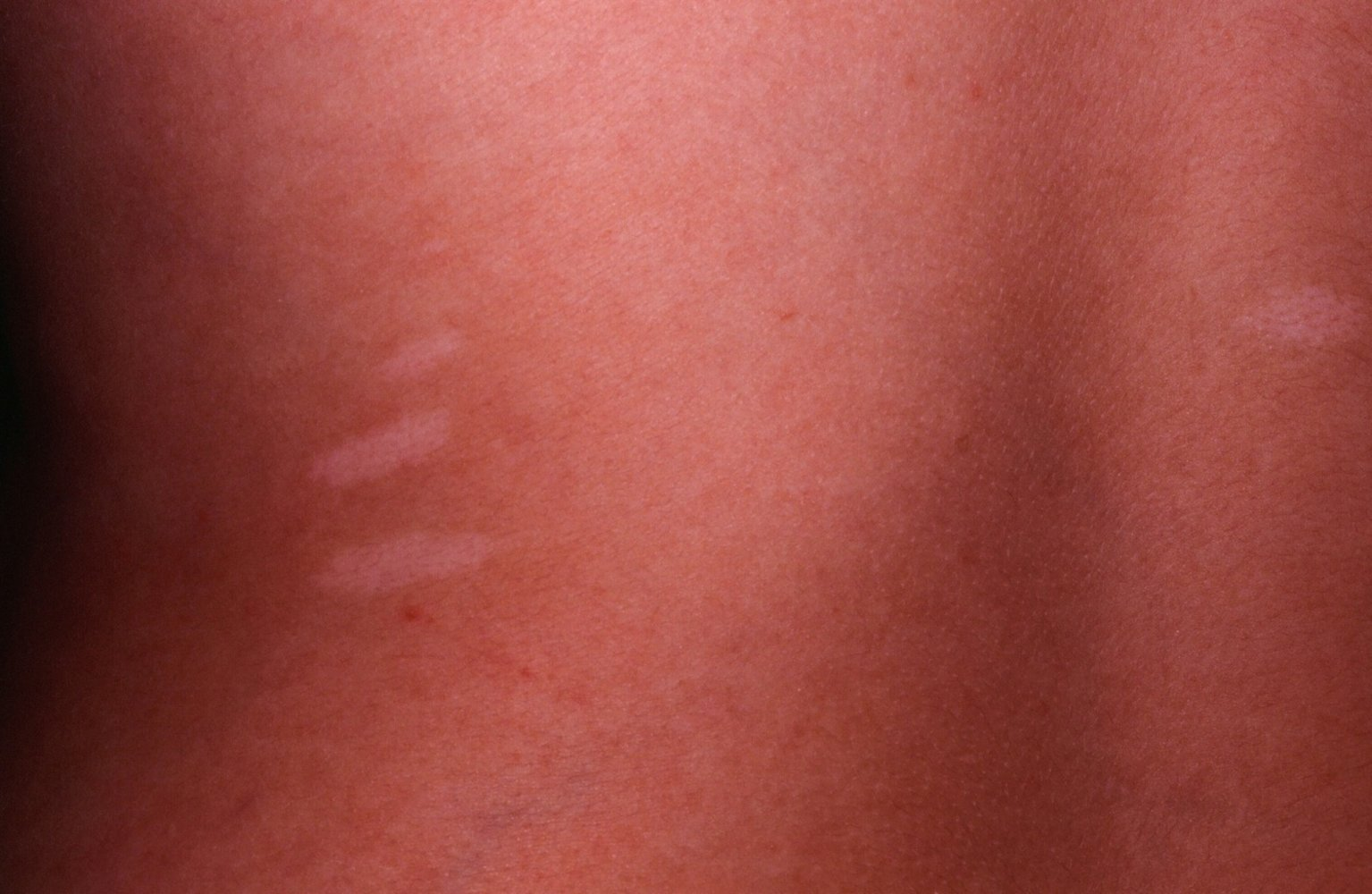
- Ash-leaf spots: hypopigmented (white) macules on the trunk and extremities
- Shagreen patch: flesh-colored papule in the lumbosacral region with an orange-peel appearance
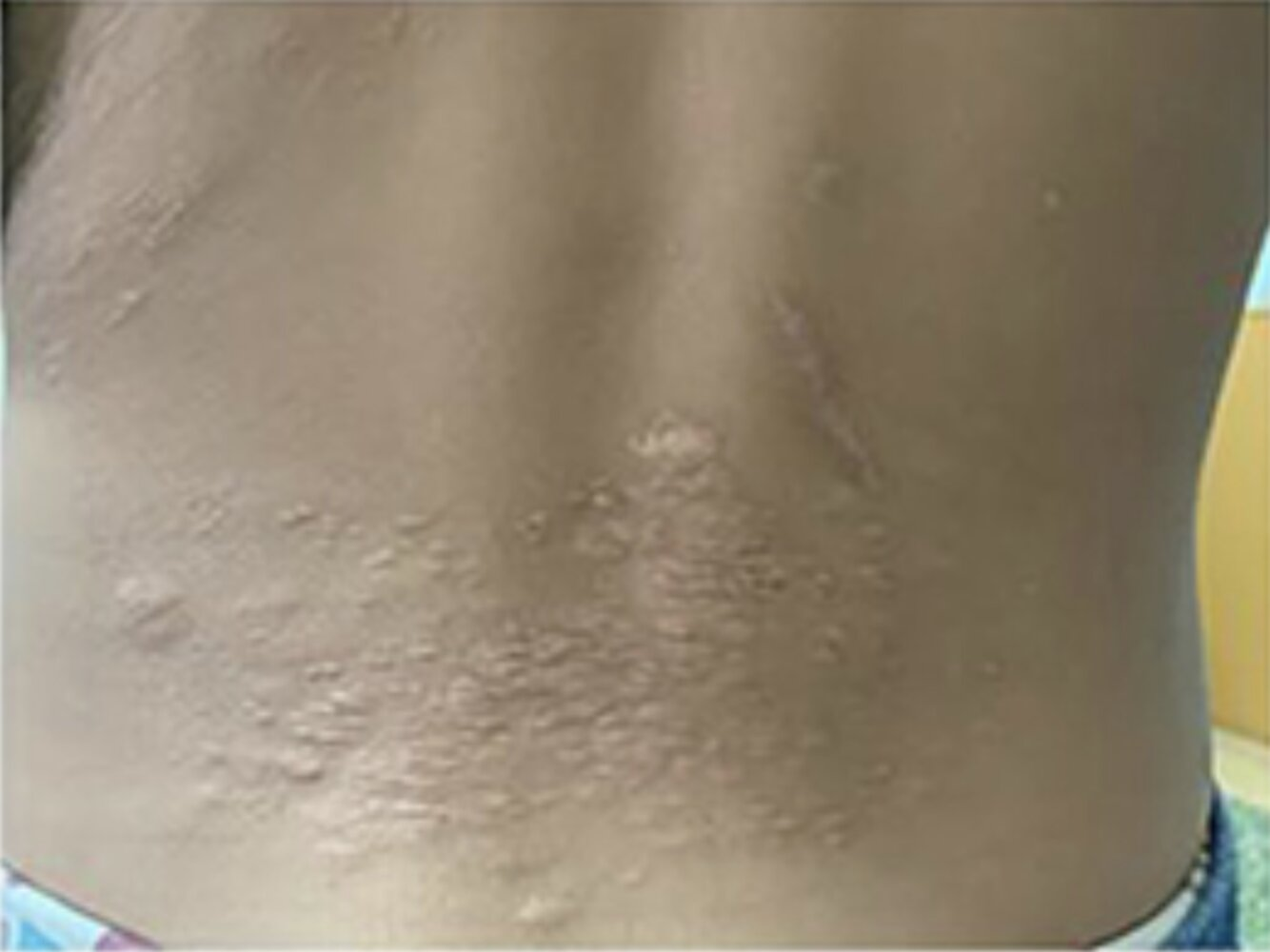
- Adenoma sebaceum (facial angiofibroma): benign tumor composed of blood vessels and fibrous connective tissue

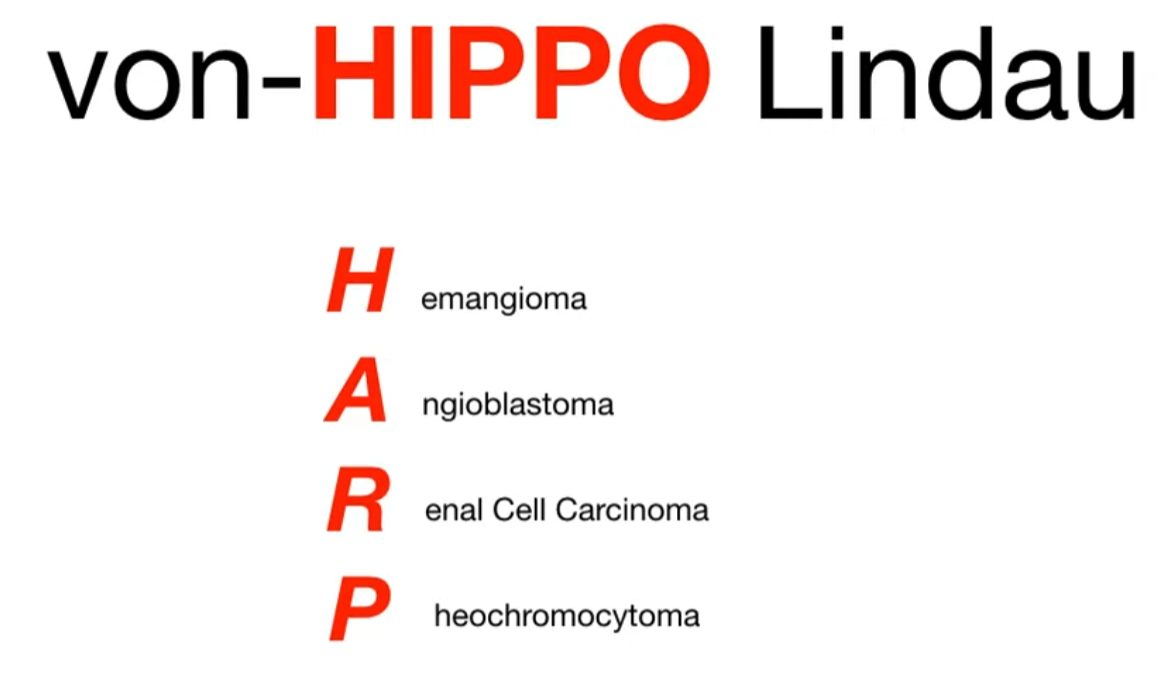
von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
- See Hereditary cancer syndromes
- VHL gene: tumor suppressor gene on the short arm of chromosome 3
- Deletion of VHL gene → impaired ubiquitination and elimination of hypoxia-inducible factor 1a → loss of function → tumor and cyst development

Neurofibromatosis
- Etiology
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 and type 2: autosomal dominant inheritance or spontaneous mutation
Neurofibromatosis type I
- Café-au-lait spots
Mnemonic
If you drink too much coffee, you are gonna go number one.
- Cutaneous neurofibromas
- Cutaneous neurofibromas are benign nerve sheath tumors composed of diverse cells and are often found within the dermis. The dermis is composed of collagen, elastic fibers, and ground substance and contains extracellular components including nerves, vasculature, hair follicles, and glands. Neurofibromas are composed of a mixture of cells normally found in peripheral nerves, including neoplastic Schwann cells, as well as non-neoplastic fibroblasts, perineural cells, and mast cells.
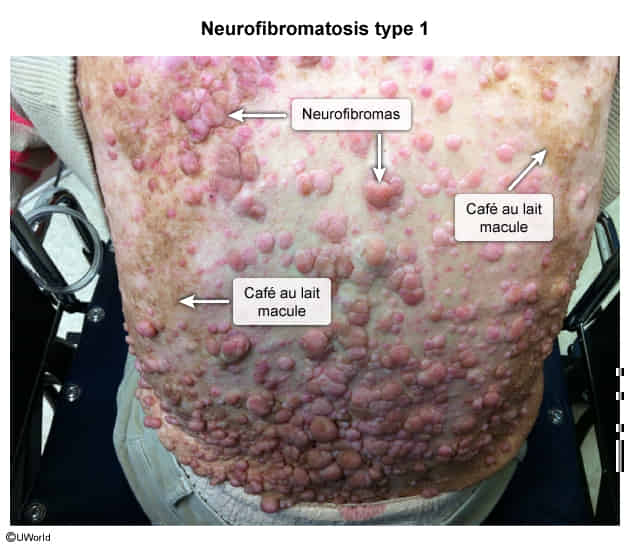
- Cutaneous neurofibromas are benign nerve sheath tumors composed of diverse cells and are often found within the dermis. The dermis is composed of collagen, elastic fibers, and ground substance and contains extracellular components including nerves, vasculature, hair follicles, and glands. Neurofibromas are composed of a mixture of cells normally found in peripheral nerves, including neoplastic Schwann cells, as well as non-neoplastic fibroblasts, perineural cells, and mast cells.
- Optic gliomas
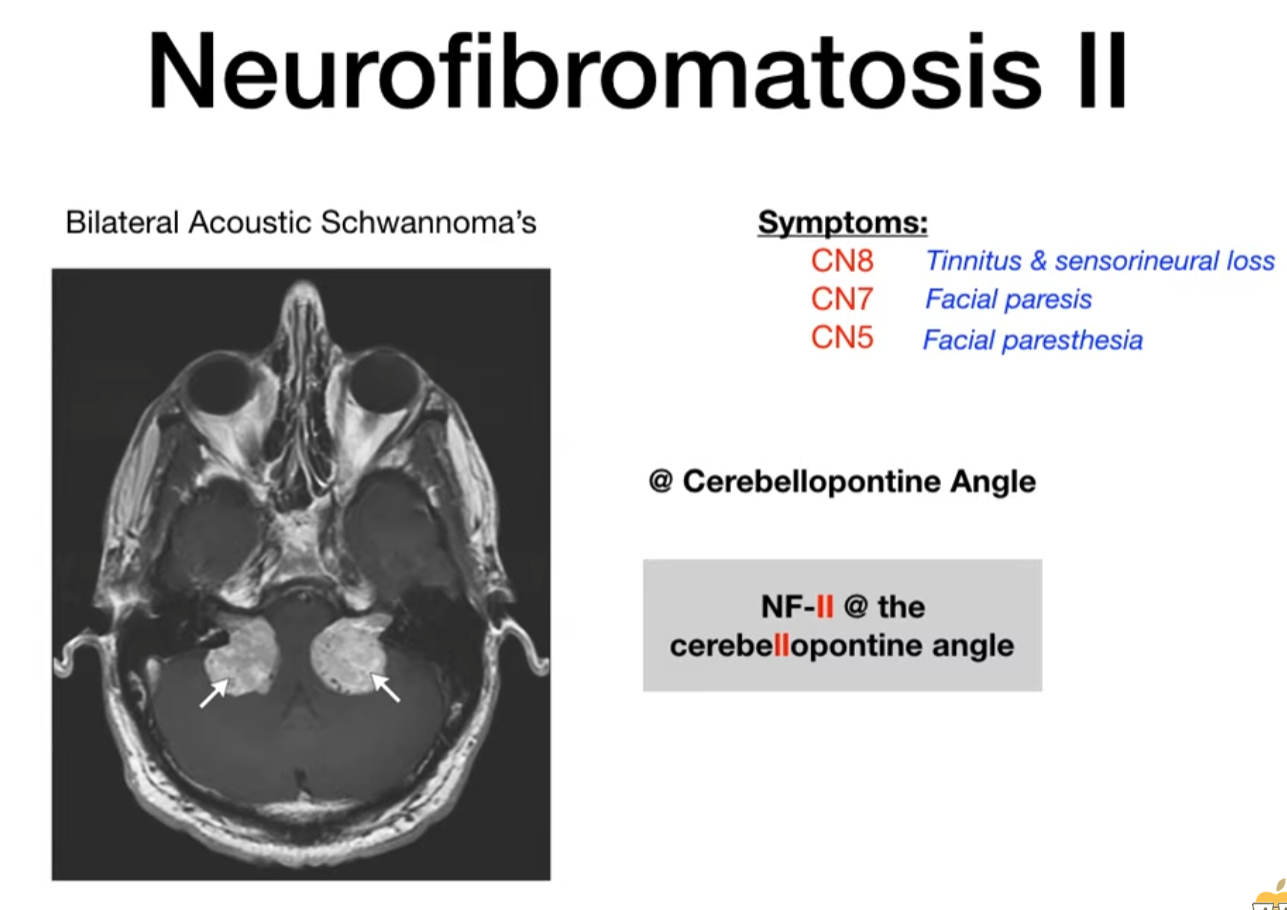
Neurofibromatosis type II