Neuroblastoma is a malignant, embryonal neuroendocrine neoplasm of the sympathetic nervous system that originates from neural crest cells, potentially secretes catecholamines, and is usually found in the adrenal glands or sympathetic ganglia.
Epidemiology
- Most common malignancy of the adrenal medulla in infants
- Mean age at diagnosis: 1–2 years
Etiology
- Amplification and overexpression of oncogene MYCN (N-myc)
Pathophysiology
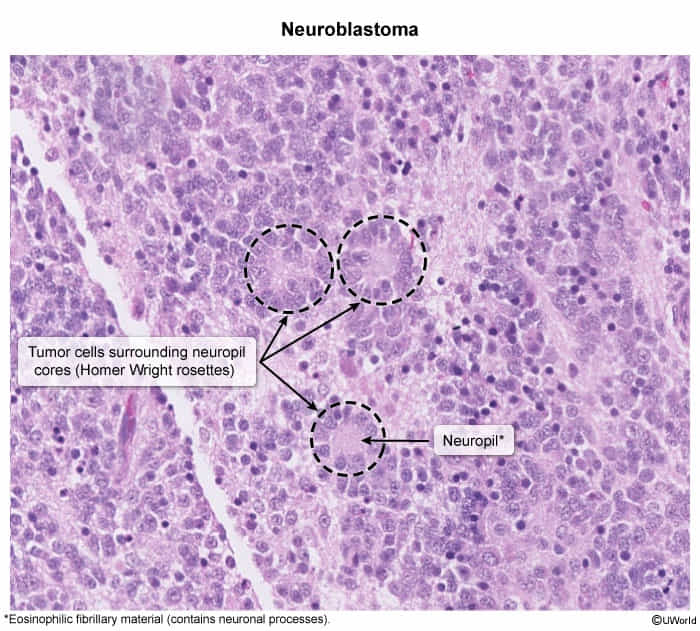
- Homer Wright rosettes: Halo-like clusters of neuroblast cells surrounding a central pale area containing neuropil (associated with tumors of neuronal origin such as neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma, primitive neuroectodermal tumors, and pineoblastoma)
- Bombesin and NSE positive
-
A tumor marker for neuroblastoma, small cell carcinoma of the lung, pancreatic cancer, and gastric cancer.
-
Clinical features
General symptoms
- Failure to thrive or weight loss
- Fever
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite
Localized symptoms
Primary Tumor Locations and Symptoms
- Abdomen (in > 60% of cases)
- In adults, pheochromocytoma is the most common tumor of the adrenal medulla, while in children it is neuroblastoma.
- Palpable, firm, irregular abdominal mass that may cross the midline (in contrast to nephroblastoma, which is smooth and usually does not cross the midline)
- Chest (in ∼ 20% of cases): particularly paravertebral ganglia
- Spinal cord compression → back pain, weakness, numbness, ataxia, loss of bowel or bladder control
- Scoliosis
- Dyspnea, cough
- Inspiratory stridor
- Neck
- Horner syndrome
Metastases Locations and Symptoms
-
Orbit of the eye
- Periorbital ecchymoses (“raccoon eyes”)

- Proptosis
- Periorbital ecchymoses (“raccoon eyes”)
-
Bones
- Bone pain
- Anemia (bone marrow suppression)
-
Skin
- Subcutaneous nodules
Paraneoplastic syndromes
- Chronic diarrhea → electrolyte imbalances
- Opsoclonus-myoclonus-ataxia: a paraneoplastic syndrome of unclear etiology characterized by rapid and multi-directional eye movements, rhythmic jerks of the limbs, and ataxia (dancing eyes dancing feet syndrome)
- Possibly hypertension, tachycardia, palpitations, sweating, flushing (hypertension is more commonly seen in pheochromocytoma)
Diagnostics
Laboratory tests
- Urine
- ↑ Catecholamine metabolites homovanillic acid (HVA) and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) in 24-hour urine
- Blood
- ↑ Catecholamine metabolites (HVA/VMA)
- ↑ Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), ferritin, neuron-specific enolase (NSE)