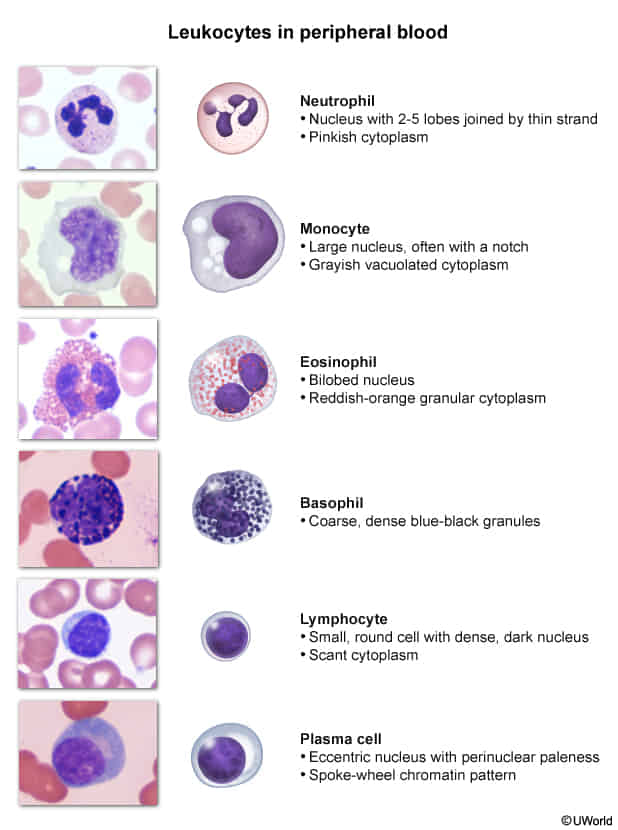
Lymphocytosis
Lymphocytosis: > 33%
Etiology
- Acute viral infections (e.g., rubella, infectious mononucleosis, mumps)
- Chronic bacterial infections
- Bordetella pertussis (Whooping cough)
- Often causes marked lymphocytosis, particularly in children
- Can elevate lymphocyte counts to 20,000-30,000/μL or higher
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Chronic TB infection can produce lymphocytic responses
- More common in the later stages of infection
- Brucella species (Brucellosis)
- Often presents with relative lymphocytosis
- Treponema pallidum (Syphilis)
- Secondary and tertiary syphilis can produce lymphocytosis
- Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease)
- Can cause lymphocytosis, especially in later stages
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Often associated with atypical lymphocytes
- Bordetella pertussis (Whooping cough)
- Neoplasia (e.g., Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, CLL)
Tip
The lymphocyte count may be increased or decreased in lymphoma.
T cell
T cell activation
Mnemonic
- T cell activation: B7 (CD80/86) on the APC binds CD28 on the T-Cell.
- Mnemonic: 28 ÷ 7 = 4
- 28 (on the T cell) divided by 7 (B7 on the APC) equals 4 (reminds you this activates CD4+ T Cells).
- B cell activation: CD40L on the T-Cell binds CD40 on the B-Cell.
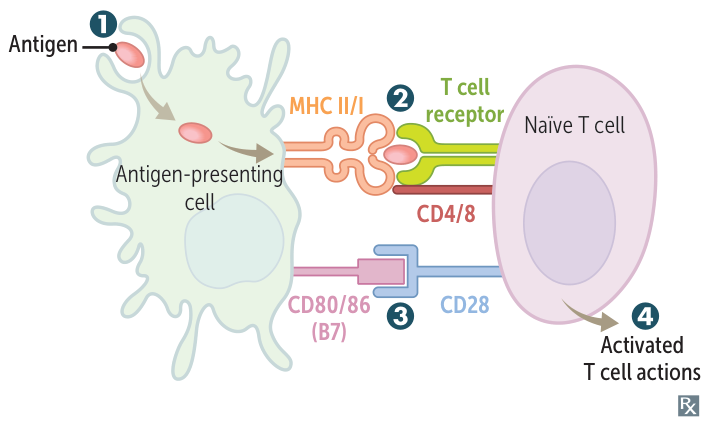
- APC ingests and processes antigen, then migrates to the draining lymph node.
- T-cell activation (signal 1): exogenous antigen is presented on MHC II and recognized by TCR on Th (CD4+) cell. Endogenous or cross-presented antigen is presented on MHC I to Tc (CD8+) cell.
- Proliferation and survival (signal 2): costimulatory signal via interaction of B7 protein (CD80/86) on dendritic cell and CD28 on naïve T cell.
- Antigen presentation without this co-stimulatory signal will lead to T-cell anergy:
- Important self-tolerance mechanism
- The cell will not be activated even though it is exposed to its antigen
- Superantigens (e.g., toxic shock syndrome toxin 1, enterotoxin B) link MHC II antigen-presenting cells and T-cell receptors on T cells and lead to activation of T cells without a costimulatory signal.
- Antigen presentation without this co-stimulatory signal will lead to T-cell anergy:
- Activated Th cell produces cytokines. Tc cell able to recognize and kill virus-infected cell.
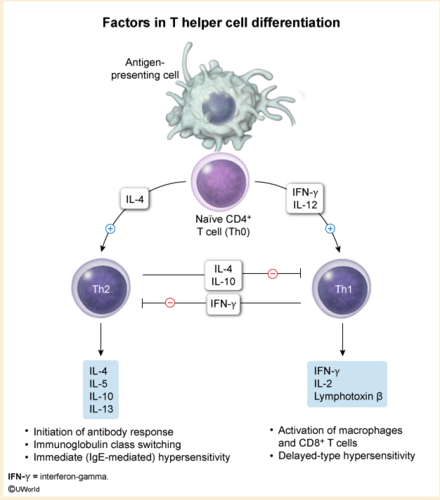
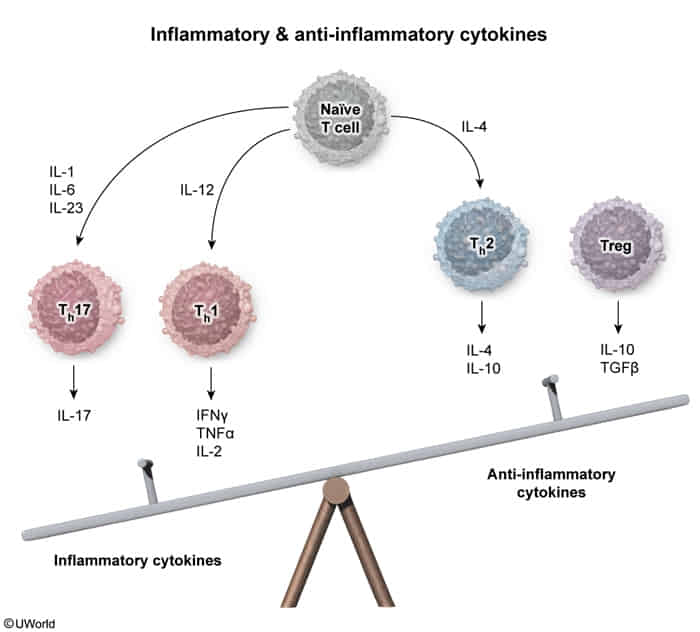
T cell differentiation
| Cell | Induced by | Inhibited by | Secretes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Th1 | IFN-γ, IL-12 | IL-4, IL-10 | IFN-γ, IL-2 |
| Th2 | IL-2, -4 | IFN-γ | IL-4, -5, -6, -10, -13 |
| Th17 | IL-1, -6, TGF-β | IFN-γ, IL-4 | IL-17, -21, and -22 |
| Treg | TGF-β, IL-2 | IL-6 | TGF-β, IL-10, -35 |
Mnemonic
- Th1:你(1)干(γ)吗(α)啊(2)
- Th2:你是(4)我(5)的,我是(10)你的谁(13)

T-cell development
- Positive Selection (MHC Restriction)
- Location: Thymic Cortex. t
- Interaction: Double-positive thymocytes interact with cortical thymic epithelial cells expressing MHC Class I and II.
- The Test: “Can you recognize self-MHC?”
- Outcomes:
- No/Weak/too strong binding: T-cell undergoes apoptosis (Death by neglect).
- Moderate binding: T-cell receives survival signal.
- Lineage Commitment:
- Binds MHC Class I → Retains CD8, downregulates CD4 (CD8+ Cytotoxic T-cell).
- Binds MHC Class II → Retains CD4, downregulates CD8 (CD4+ Helper T-cell).
- Result: T-cells are MHC Restricted (capable of interacting with host MHC).
- Negative Selection (Central Tolerance)
- Location: Thymic Medulla. t
- Interaction: Single-positive (CD4+ or CD8+) thymocytes interact with medullary thymic epithelial cells and dendritic cells presenting self-antigens.
- The Test: “Do you bind self-antigen too strongly?”
- Key Mechanism: The AIRE gene (Autoimmune Regulator) allows medullary epithelial cells to express peripheral tissue antigens (e.g., insulin, thyroglobulin) to test T-cells for autoreactivity.
- Outcomes:
- High affinity binding: T-cell undergoes apoptosis.
- Low affinity binding: T-cell survives and matures into a naive T-cell.
- Result: Central Tolerance (elimination of autoreactive T-cells).
T-cell subtypes
Cytotoxic T cells (killer T cells)
- Surface markers: CD8
- Function: Important component of cell-mediated immunity; recognize and kill cells infected with intracellular pathogens (especially viruses) and neoplastic cells; interact with foreign antigens presented via MHC I; induce apoptosis or cell lysis of presenting cells
- Stimulated by: Macrophages
- Clinical significance: HIV, Hepatitis B, Adult T cell lymphoma
T-helper cells (Th cells)
Th1 cells
- Surface markers: CD4, CD40L
- Function: Promote cellular immune response; fight intracellular pathogens
- Stimulate: Macrophages, Cytotoxic T cells, NK cells, B cells (leading to IgG production)
- Clinical significance: Infections with intracellular pathogens (e.g., Mycobacteria, Salmonella), IL-12 receptor deficiency, Type I diabetes, Rheumatoid arthritis, Multiple sclerosis
Th2 cells
- Function: Initiate humoral immune response in cooperation with B lymphocytes; fight extracellular pathogens (especially parasites)
- Stimulate: Eosinophils, Mast cells, Basophils, B cells (leading to IgE production)
- Clinical significance: Helminth infections, Type 1 hypersensitivity (asthma, allergic rhinitis)
Th17 cells
- Function: Regulate tissue inflammation (both proinflammatory and antiinflammatory effects); fight extracellular pathogens
- Stimulate: Neutrophils
- Clinical significance: Hyper IgE syndrome
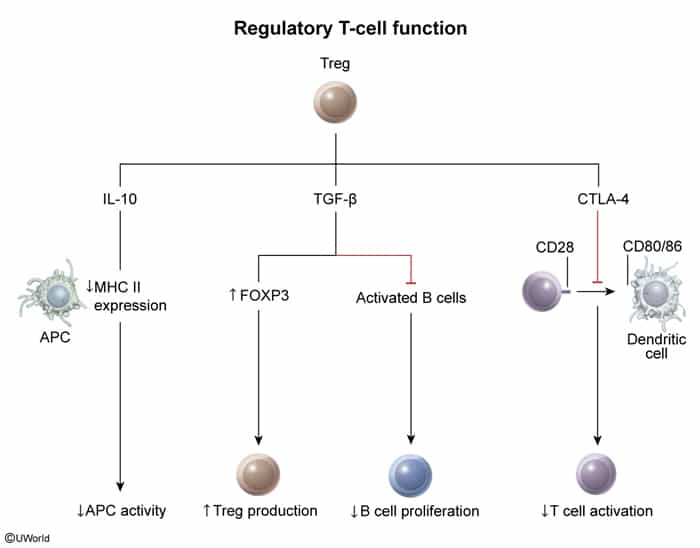
Regulatory T cells (Treg, suppressor T cells)
- Surface markers: CD4, CD25
- Function: Limit and protect against excessive immune response; promote immune self-tolerance; prevent formation of autoantibodies
- Stimulate/suppress: CD4+ and CD8+ T effector cells
- Clinical significance: sIPEX syndrome
B cell
B cell activation and class switching
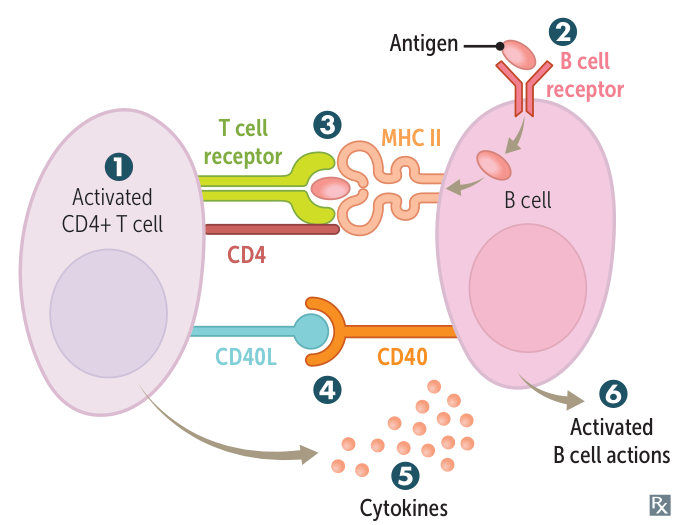
- Th-cell activation as above.
- B-cell receptor–mediated endocytosis.
- B lymphocytes recognize antigens via their B-cell receptors (membrane‑bound immunoglobulins, IgD or IgM) → B cell receptor-mediated endocytosis of the BCR/antigen complex → breakdown of antigen into small fragments by lysosomal proteases → presentation of antigen fragment via MHC class II receptors on B cell surface to Th cells plus costimulation of B cell CD40 receptor by Th cell CD40L → T cell‑dependent activation of B cells (plasma cells) → immunoglobulin production
- B cell and T cell need to be activated by the same antigen
- Exogenous antigen is presented on MHC II and recognized by TCR on Th cell.
- CD40 receptor on B cell binds CD40 ligand (CD40L) on Th cell.
- Th cells secrete cytokines that determine Ig class switching of B cells.
- Th1 (IFN-γ), Th2 (IL-4), Tfh (IL-21), Th17 (IL-21): stimulates class switching to IgG.
- Th2 (IL-4, IL-13): stimulate class switching to IgE.
- Th2 (IL-5) + Treg (TGF-β): stimulate class switching to IgA.
- B cells are activated and produce IgM. They undergo class switching and affinity maturation.
Lymphatic system
Lymph nodes
Function
- Nonspecific lymph filtration: macrophages within lymph node
- Storage and circulation of B cells and T cells
- Immune system activation: Antigen presentation induces differentiation and proliferation of B lymphocytes and activation of T lymphocytes.
Structure
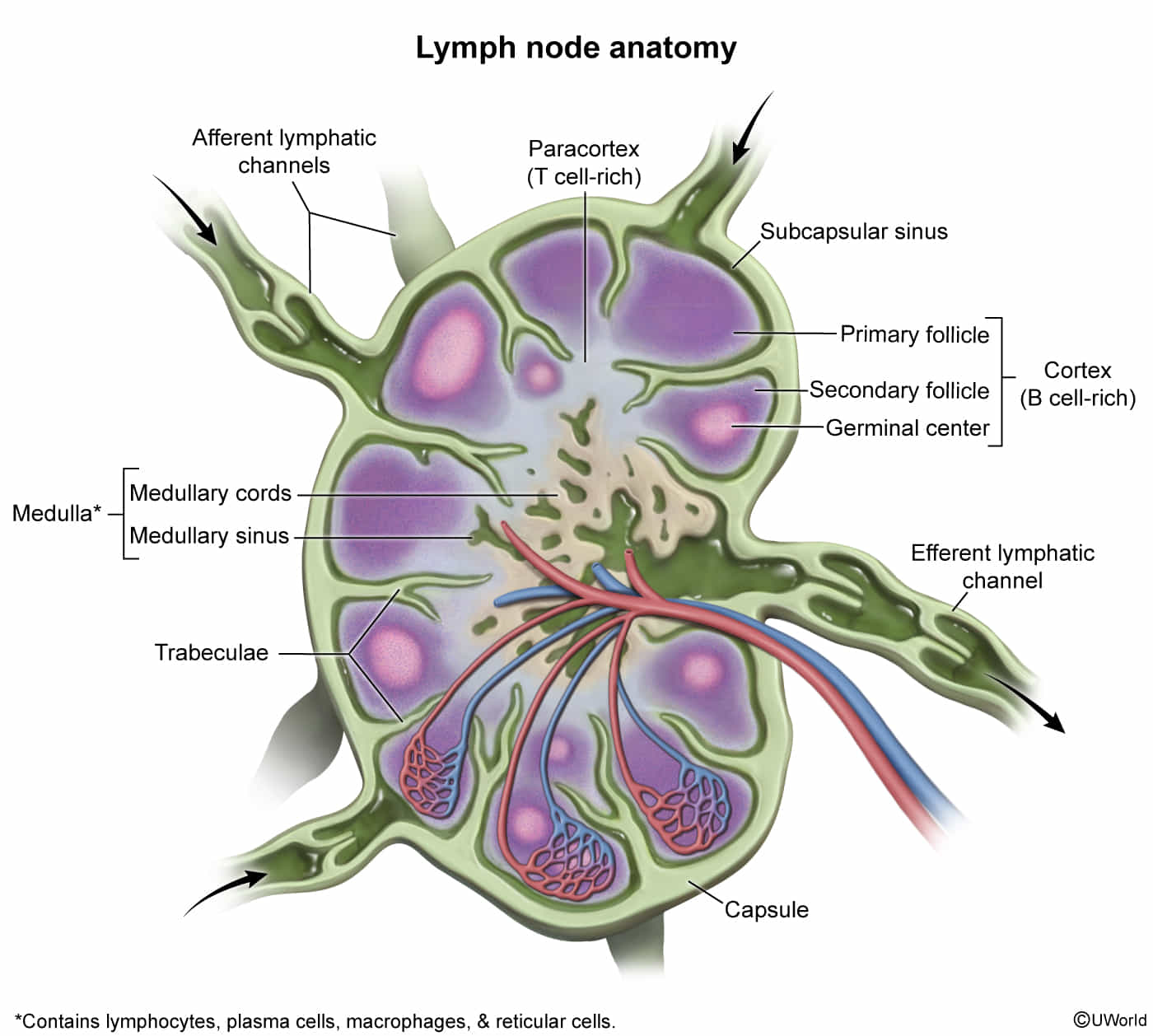
Histology
- Cortex (B-cell zone): contains lymphoid follicles, which is the site of B lymphocyte storage, differentiation, and proliferation
- Secondary lymphoid follicle (active): dense mantle zone surrounding a pale germinal center
- Primary lymphoid follicle (inactive): dense aggregates of naive B lymphocytes
- Paracortex (T-cell zone)
- Region between the cortex and medulla
- Contains T lymphocytes and high endothelial venules, which allows circulating B and T lymphocytes to enter or leave the bloodstream
- Site of T-cell activation
- Medulla
- Medullary cords: tightly packed with plasma cells and lymphocytes
- Medullary sinus of the lymph node
- Composed of macrophages, reticular cells
- Connected to the efferent lymphatic structures
Clinical significance
- Inflammatory or immune reactions (e.g., due to EBV infection) → reactive paracortical hyperplasia → clinically apparent lymphadenopathy
- Depletion of paracortical lymphocytes: DiGeorge syndrome
NK cells
- Surface markers
- Fc receptor (CD16): a membrane receptor protein that recognizes and binds to antibodies that have attached to pathogens
- Mediates a phagocytic and/or cytotoxic response
- Found on many immune cells, e.g., NK cells, neutrophils, and macrophages
- CD56: a neural cell adhesion molecule specific to NK cells
- Fc receptor (CD16): a membrane receptor protein that recognizes and binds to antibodies that have attached to pathogens
Mnemonic
CD16 for NK cells because when 16 year olds get their driver’s licenses they become killers, naturally.
- Mechanism of Recognition:
- Activated by the absence of MHC Class I on target cell surfaces (“missing-self” hypothesis). This is a key mechanism for cells evading cytotoxic T-cells.
- Can also be activated via Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) by binding to IgG-coated cells.