Epidemiology
- Adenocarcinoma: most common type of esophageal cancer in the US (67%)
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): most common type of esophageal cancer worldwide (90%)
Etiology
Adenocarcinoma
- Exogenous risk factors
- Smoking (twofold risk)
- Obesity
- Increases intragastric pressure, frequency of lower esophageal sphincter relaxation, and rates of hiatal hernia, which promote GERD
- Endogenous risk factors
- Male sex
- Older age (50–60 years)
- Gastroesophageal reflux
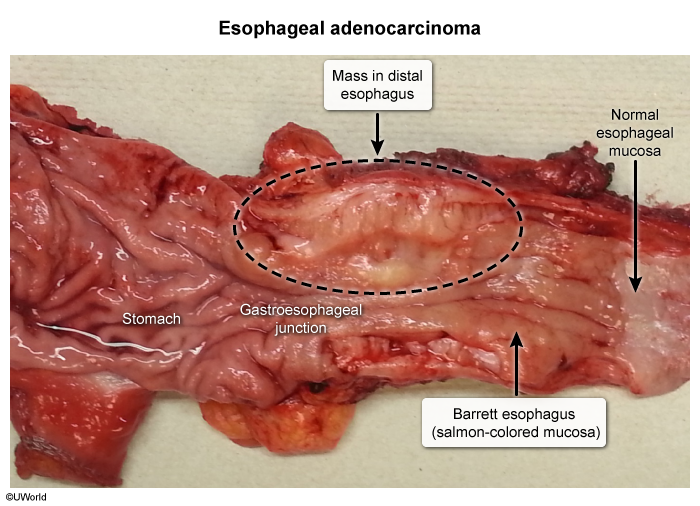
- Barrett esophagus
- Localization: mostly in the lower third of the esophagus
Tip
The most important risk factors for esophageal adenocarcinoma are gastroesophageal reflux and associated Barrett esophagus.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- Exogenous risk factors
- Alcohol consumption
- Smoking (ninefold risk)
- Diet low in fruits and vegetables
- Hot beverages
- Nitrosamines exposure (e.g., cured meat, fish, bacon)
- Endogenous risk factors
- Localization: mostly in the upper two-thirds of the esophagus
Tip
The primary risk factors for squamous cell esophageal cancer are alcohol consumption, smoking, and dietary factors (e.g., diet low in fruits and vegetables).
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Pathology
- Squamous cell carcinoma
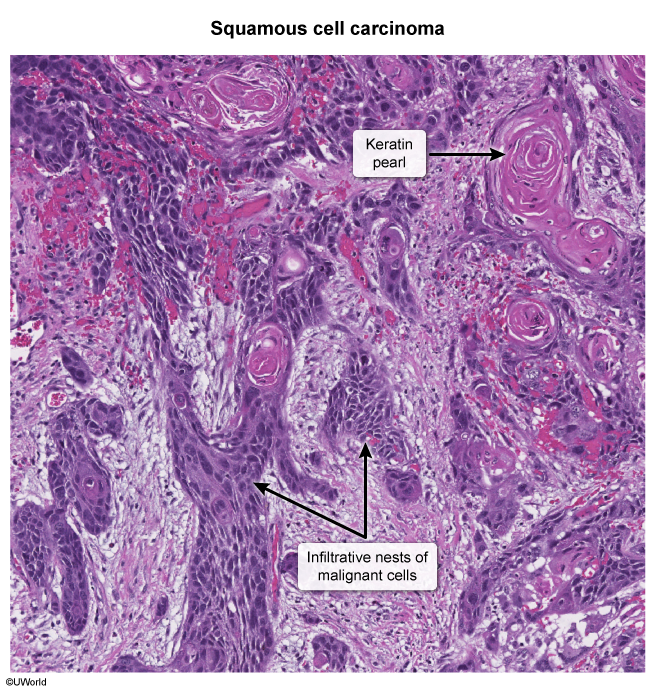
- Breakdown of uniform tissue structure
- Squamous cell carcinoma clusters with circular keratinization
- Lymphocytic infiltration between the carcinoma clusters