Epidemiology
- Most common malignant skin tumor
Etiology
- Intermittent UV exposure is the most significant risk factor
- As opposed to cumulative UV exposure, which is a recognized risk factor for cSCC.
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Nonhealing well-circumscribed pearly papule, nodule, or plaque with rolled borders, telangiectasia, and/or central umbilication
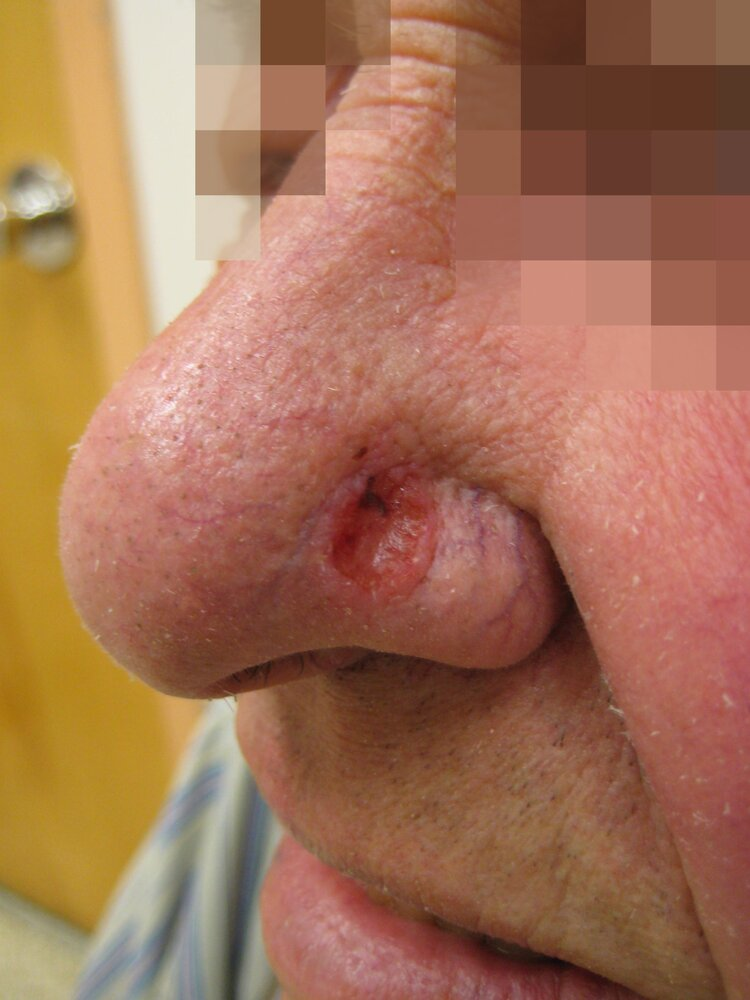
- Typically located in areas with sun exposure; most commonly on the face and neck
- Often painless
- Lesions gradually increase in size (indolent growth)
- Metastasizes rarely (< 1%); if lack of treatment, can spread to lymph nodes, soft tissue, lungs, and bone
Subtypes
Nodular basal cell carcinoma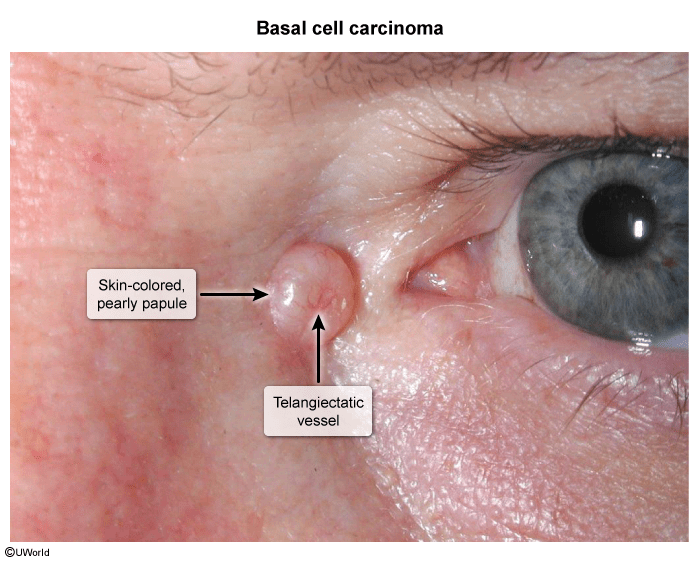
- Papule or nodule with the following:
- Pink or skin-colored papule, shiny with a pearl-like appearance
- Rolled borders
- Central depression, erosion, or ulceration (rodent ulcer)
- Superficial telangiectasias with arborizing pattern (tree-like branching)
- Most commonly located on the face, especially the nose
Superficial basal cell carcinoma
- Thin and scaly
- Raised border with a pearl-like appearance
- Most commonly located on the trunk and legs
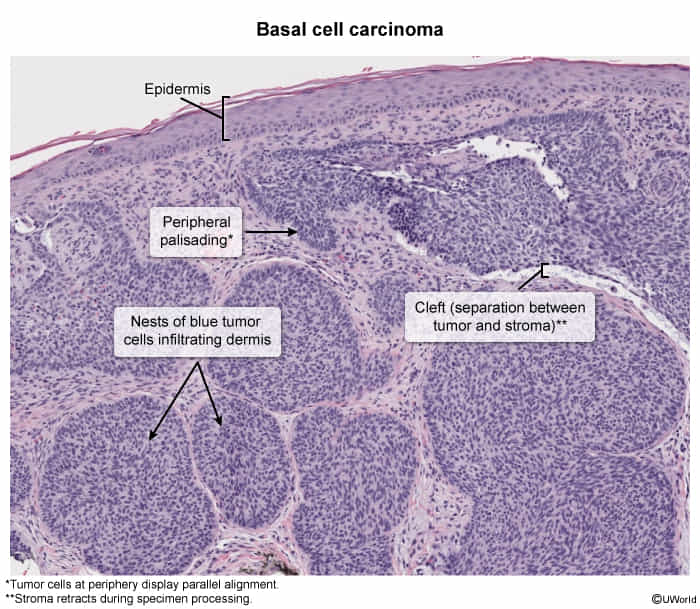
Diagnostics
- Pathology
- Palisading nuclei: Nuclei appear aligned.
Treatment


