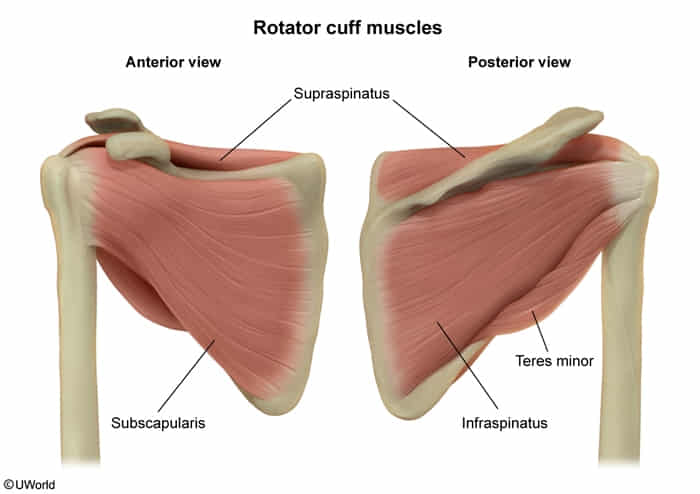
 (View in the front)
(View in the front)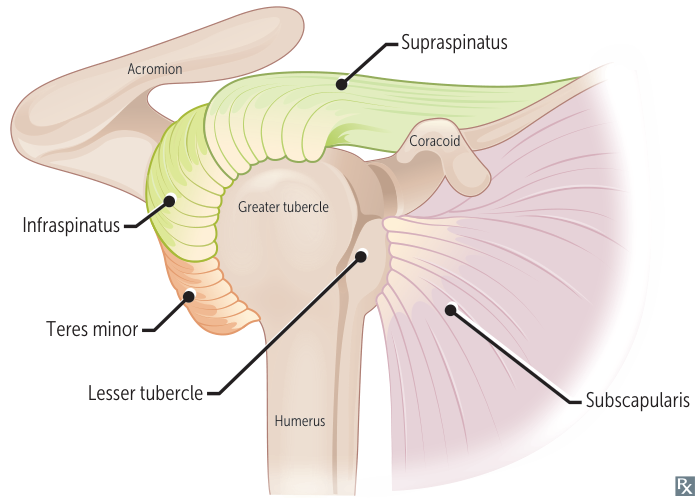 (like you put your hand on someone’s shoulder from the back)
(like you put your hand on someone’s shoulder from the back)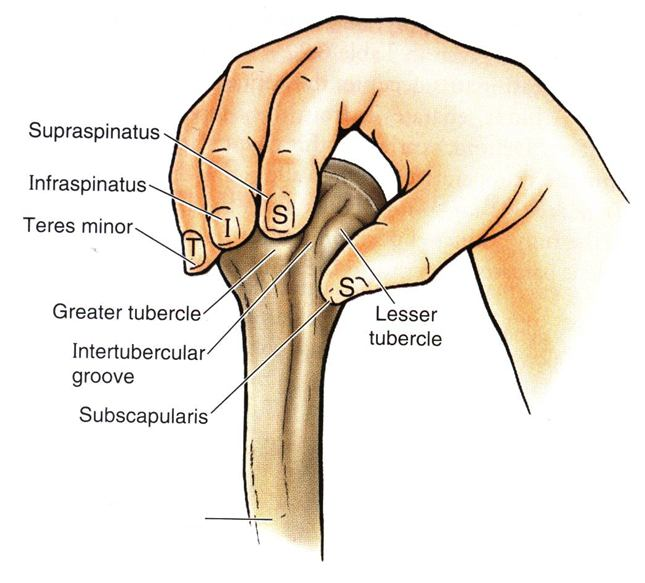
- Supraspinatus (suprascapular nerve)
- Abducts arm initially (before the action of the deltoid)
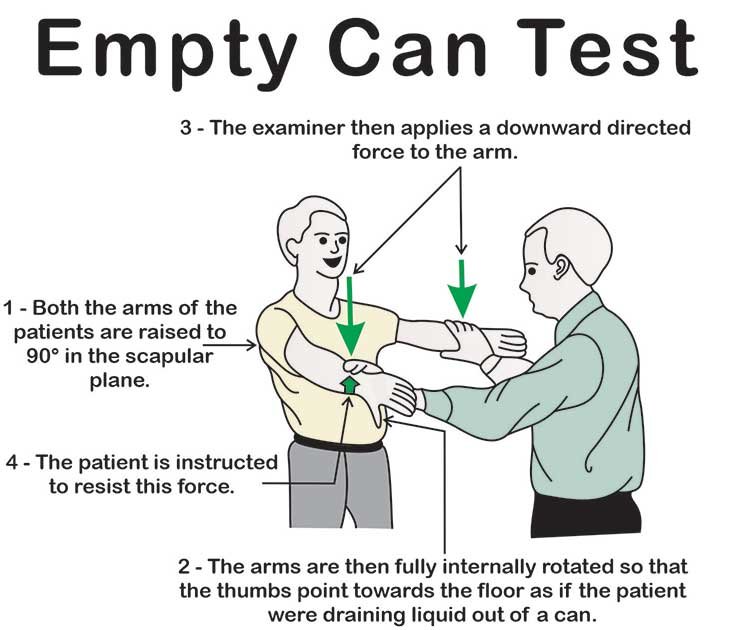
- Most common rotator cuff injury (trauma or degeneration and impingement leading to tendinopathy or tear)
- Assessed by the “empty/full can” test
- Infraspinatus (suprascapular nerve)
- Externally rotates arm
- The only one of these four muscles that does not participate in abduction.
- Common pitching injury
- Teres minor (axillary nerve)
- Adducts and externally rotates arm
- Subscapularis (upper and lower subscapular nerves)
- Internally rotates and adducts arm
Abduction of the upper limb
- (0°-15°) Abduction of the upper extremity is initiated by the supraspinatus muscle (suprascapular nerve).
- (15°-110°) Further abduction to the horizontal position is a function of the deltoid muscle (axillary nerve).
- (110°-180°) Raising the extremity above the horizontal position requires scapular rotation by action of the trapezius (accessory nerve CN XI) and serratus anterior (long thoracic nerve).
Mnemonic
“Start Dancing, Then Spin!”
- Start (Supraspinatus: 0°–15°)
- Dancing (Deltoid: 15°–110°)
- Then (Trapezius: 110°–180°)
- Spin! (Serratus anterior: 110°–180°)