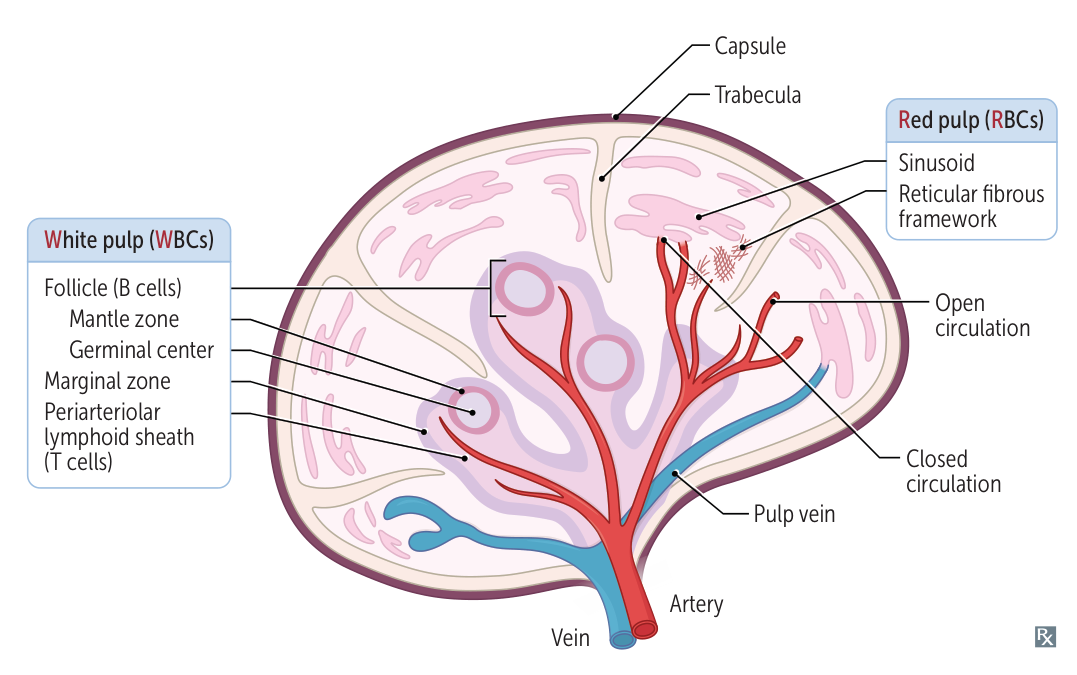
Microscopic anatomy
Red pulp
Red pulp is composed of splenic cords and sinuses (sinusoids).
- Splenic cords: a reticular meshwork filled with blood (open circulation system) that filters the blood from damaged erythrocytes
- Spleen sinusoids: long vessels with a fenestrated ring-like (“barrel hoop”) basement membrane that prevent old or malformed RBCs/platelets from reentering venous circulation
- Open circulation: Blood empties from sheathed capillaries into the splenic cords and then enters the sinusoids through slits in the vessel wall.
- Closed circulation: Blood empties from sheathed capillaries of the red pulp directly into the sinusoids.
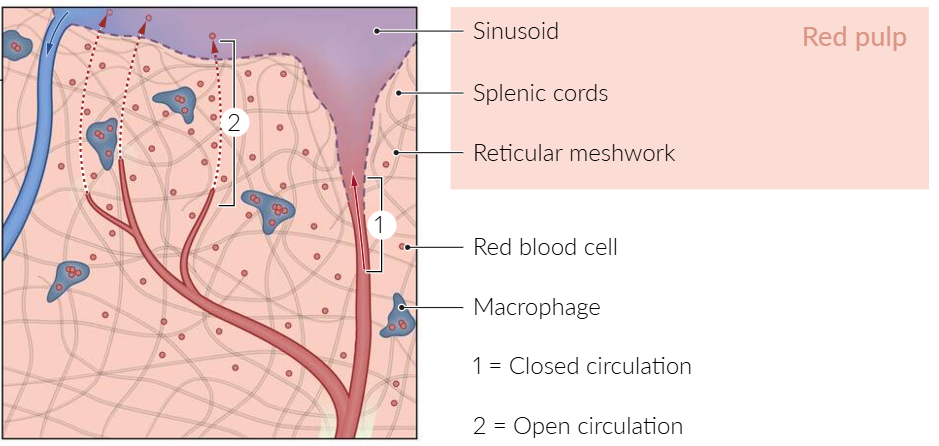
- Macrophages: found in the cords and around the sinusoids
- Phagocytosis of damaged RBCs/platelets that do not reenter circulation
- Capture of viruses and opsonized pathogens that enter the red pulp
- Blood flow: splenic artery → arterioles → red pulp (cords → sinusoids) → venules → splenic vein → portal circulation
White pulp
- Periarteriolar lymphatic sheath
- Surrounds the arterioles
- Dense lymphoid tissue containing T lymphocytes
- Splenic follicles
- Main component of white pulp
- Close to periarteriolar lymphatic sheath
- Contain B lymphocytes
- Splenic marginal zone
- Located between the red pulp and white pulp
- Contains antigen-presenting cells (APCs): macrophages and specialized B cells (marginal zone B cells)