Epidemiology
Typically seen in infants
Etiology
Diaper-related
| Feature | Irritant Dermatitis | Candidal Dermatitis | Bacterial Dermatitis | Allergic Dermatitis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Urine/feces, friction | C. albicans (fungus) | S. aureus, GAS | Type IV HSR |
| Presentation | Erythema, scaling | Beefy-red plaques | Pustules, bullae | Papules, vesicles; Intense pruritus |
| Distribution | Affects convex surfaces | Involves skin folds | At sites of broken skin | Matches allergen contact |
| Hallmark | SPARES folds | SATELLITE lesions | HONEY-COLORED crusts | Sharply demarcated pattern |
| Tx | Barrier cream (ZnO), air | Topical antifungal (nystatin) | Topical Abx (mupirocin) | Avoid allergen; topical steroids |
Irritant contact dermatitis (most common cause)
- Pathophysiology
- Caused by prolonged contact with urine and feces, leading to skin maceration and irritation from friction and chemical breakdown (↑ pH from urease, activation of fecal enzymes). Diarrhea is a major risk factor.
- Clinical features
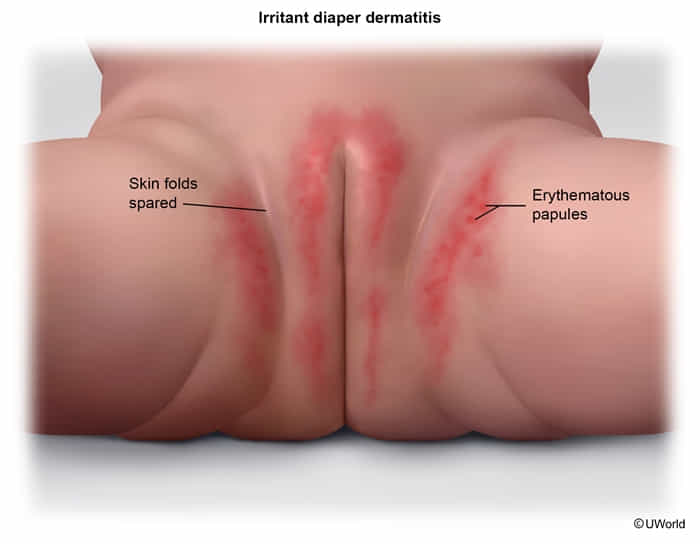
- Acute: pruritic and/or painful erythema, edema, and vesicular rash
- Chronic: pruritic and/or painful xerosis, scaling, lichenification, hyperkeratosis, and fissuring
- Well-defined borders
- Does not have skinfold involvement or satellite lesions
- Treatment
- Thick barrier ointment (eg, petrolatum) or paste (eg, zinc oxide), which provides the skin an adherent layer of protection from contact with the stool and urine
Allergic contact dermatitis
- Patho/Etiology: Type IV hypersensitivity reaction to allergens in diapers (dyes, elastics), wipes (fragrances, preservatives), or creams.
- Personal care products (e.g., perfumes, soaps, cosmetics)
- Intensely pruritic erythematous papules, vesicles with serous oozing
- Ill-defined borders
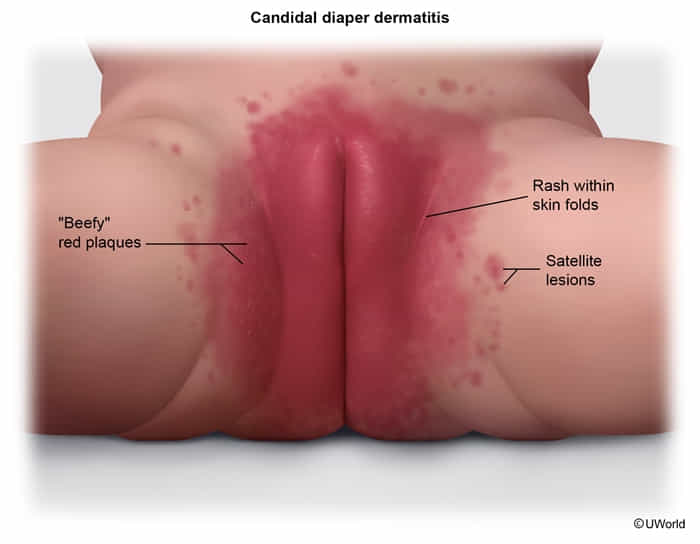
Candidiasis
- Clinical Presentation: Beefy-red plaques that involve the skin folds. Characteristic satellite lesions (papules and pustules) are a key finding. May be associated with oral thrush.