hCG physiology
- hCG is produced during pregnancy, primarily by the placental syncytiotrophoblast.
- The role of hCG is to:
- Stimulate progesterone secretion by the corpus luteum during the first 3–6 weeks of gestation to maintain pregnancy
- Prior to pregnancy, LH stimulates corpus luteal progesterone secretion.
- After the luteal placental shift, the placenta produces progesterone.
- Promote uterine angiogenesis
- Promote myometrial stability, preventing contractions prior to labor
- Support immune tolerance to the growing embryo
- Structure
- α-subunit: common to hCG, FSH, LH, and TSH
- β-subunit
- Specific to hCG
- Pregnancy tests generally detect hCG through antibodies to the β-subunit.
Types of pregnancy tests
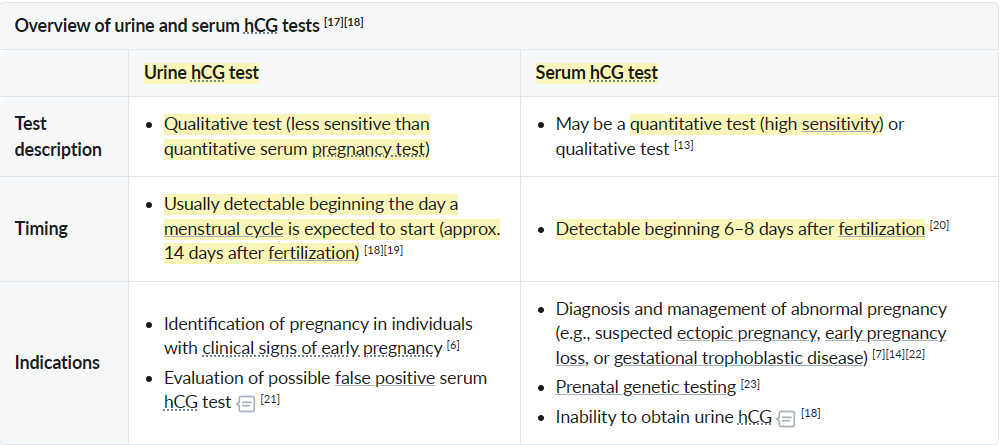
- hCG begins being produced by syncytiotrophoblast after invasion of endometrial connective tissue 6-7 days after fertilization
- Serum level at 8 days is <5 IU/L, once serum is 20 IU/L this can be detected in a urine pregnancy test (~14 days following fertilization)
