Epidemiology
Etiology
- Typically a sexually transmitted infection
- Gonococcal urethritis (GU): Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Chlamydia trachomatis (most common)
- Coinfection is also common
Tip
- Urethritis is often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs), e.g. N gonorrhoeae.
- UTIs are generally caused by bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract, e.g. E coli.
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Diagnostics
- Thayer-Martin agar
- Used to detect Neisseria
- Gram stain
- Findings: polymorphonuclear leukocytes and intracellular gram-negative diplococci
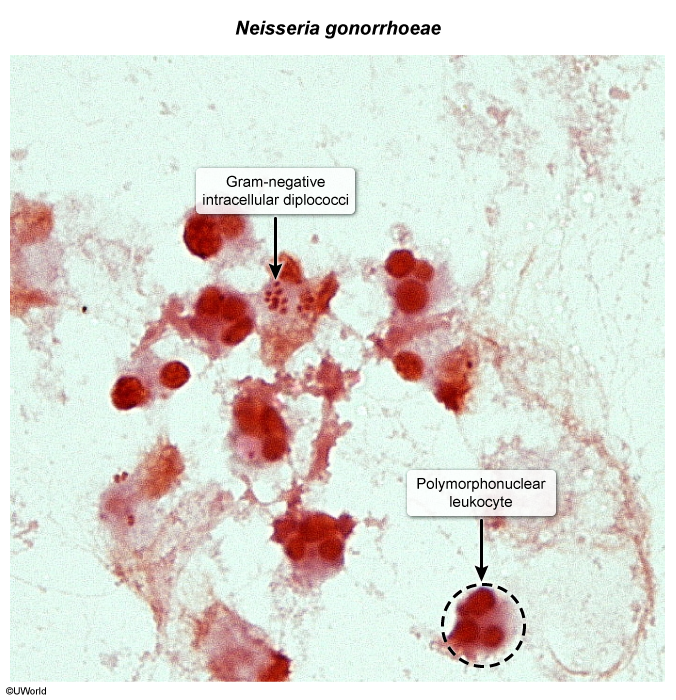
- Findings: polymorphonuclear leukocytes and intracellular gram-negative diplococci
Mnemonic
Selectively favors growth of Neisseria by inhibiting growth of gram ⊕ organisms with vancomycin, gram ⊝ organisms except Neisseria with trimethoprim and colistin, and fungi with nystatin.
Very typically cultures Neisseria
Treatment
Divided into either a GU (gonococcal urethritis) or NGU regimen.
- GU alone: ceftriaxone
- GU + Chlamydia (whether certain or uncertain): ceftriaxone + doxycycline
- Chlamydia/Mycoplasma: azithromycin
- Trichomonas: metronidazole