
Angle-closure glaucoma
Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
The iris bows forward and physically obstructs the trabecular meshwork at the iridocorneal angle, preventing aqueous drainage. This can be acute or chronic.
- Primary: Due to a narrow anterior chamber angle anatomically. More common in people of Asian descent and those with farsightedness.
- Secondary: Caused by another condition, like hypoxia-induced neovascularization of the iris.
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Treatment
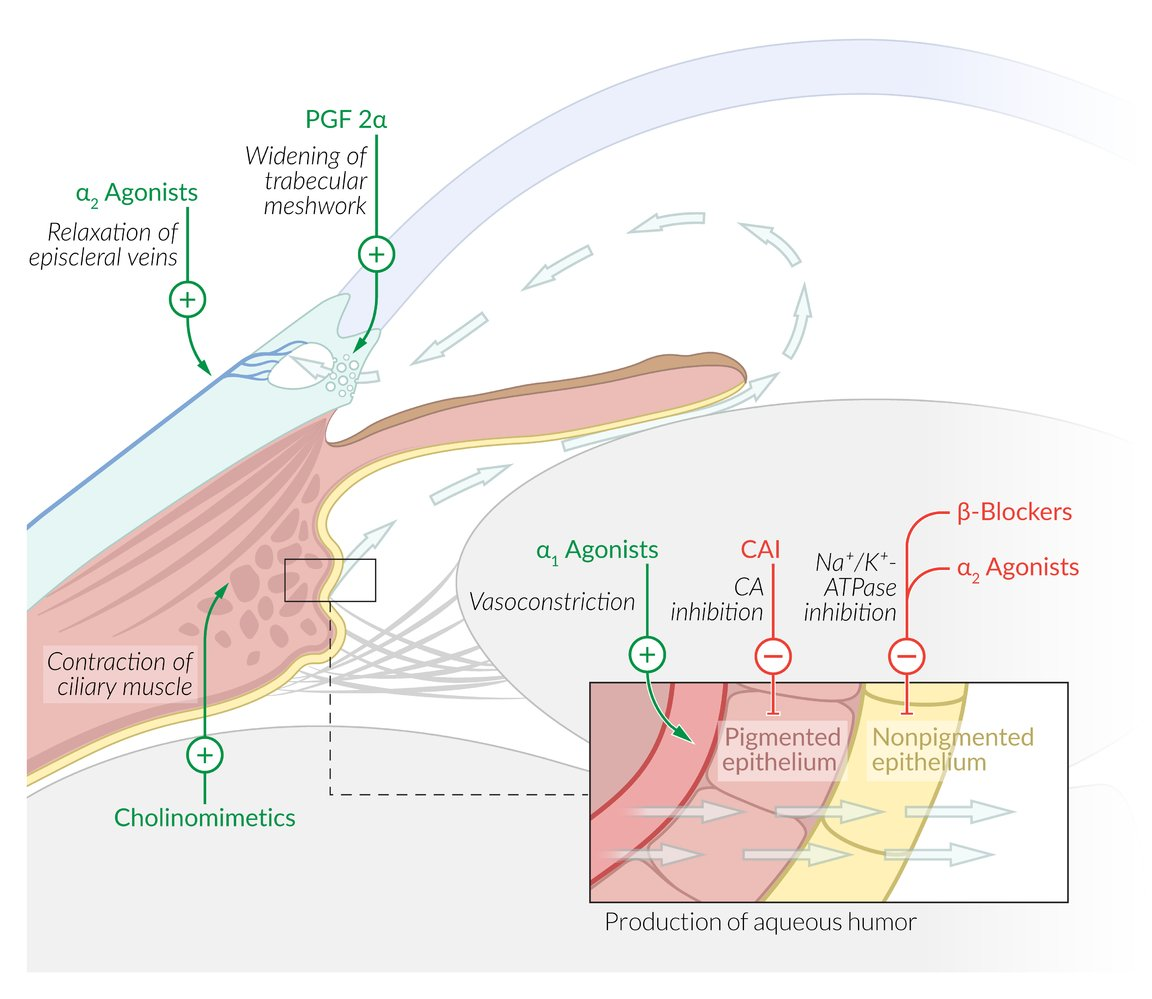
- Topical ophthalmic therapy. Administer the following eye drops in succession, one minute apart:
- Direct parasympathomimetic: pilocarpine
- Alpha-2 agonist: apraclonidine
- Beta blocker: timolol
- PLUS a systemic carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
- Acetazolamide
Cholinomimetic drugs include
- Cholinergic Receptor Agonists: Can directly stimulate cholinergic receptors.
- Anti-Cholinesterase Drugs: Inhibit the hydrolysis of acetylcholine (ACh), increasing the concentration of ACh in the synaptic cleft.
- Acetylcholine Release Promoters: Increase the release of ACh from nerve terminals.
Open-angle glaucoma
Diagnostics
- Slit-lamp examination of the anterior segment: normal appearing anterior chamber angle
- Tonometry
- To measure IOP (standard values range between 10–21 mm Hg)
- Gonioscopy: to rule out angle-closure glaucoma
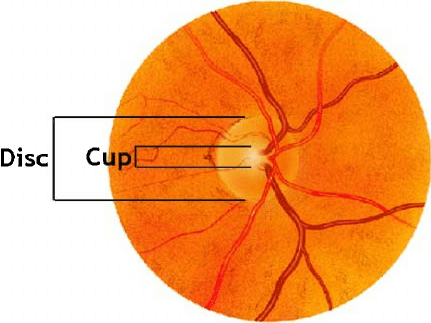
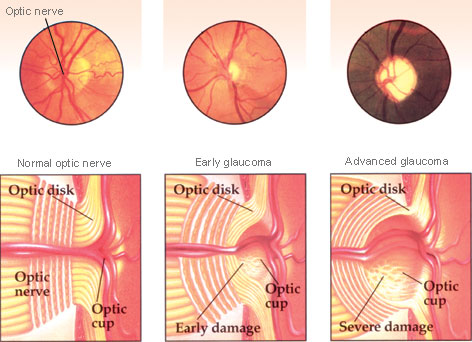
- Fundoscopy: cupping and pallor of optic disc, disc hemorrhage, diffuse or focal narrowing of the optic disc rim
- “Cupping” refers to the enlargement or deepening of this central optic cup relative to the overall size of the optic disc.
- Optic nerve fibers are outside of optic cup in the optic disk. So when nerve fibers are ischemic and lost, the optic cup increases in size.
Treatment of open-angle glaucoma
Topical prostaglandins are most effective and usually used initially; other drugs (with a different mechanism) may be added if topical prostaglandins are unsuccessful.
- Preferred first-line therapy: topical prostaglandin analogs
- Latanoprost