Epidemiology
- Peak incidence: older male individuals (70-80 y)
- Zenker diverticulum is the most common type.
Etiology
Pathophysiology
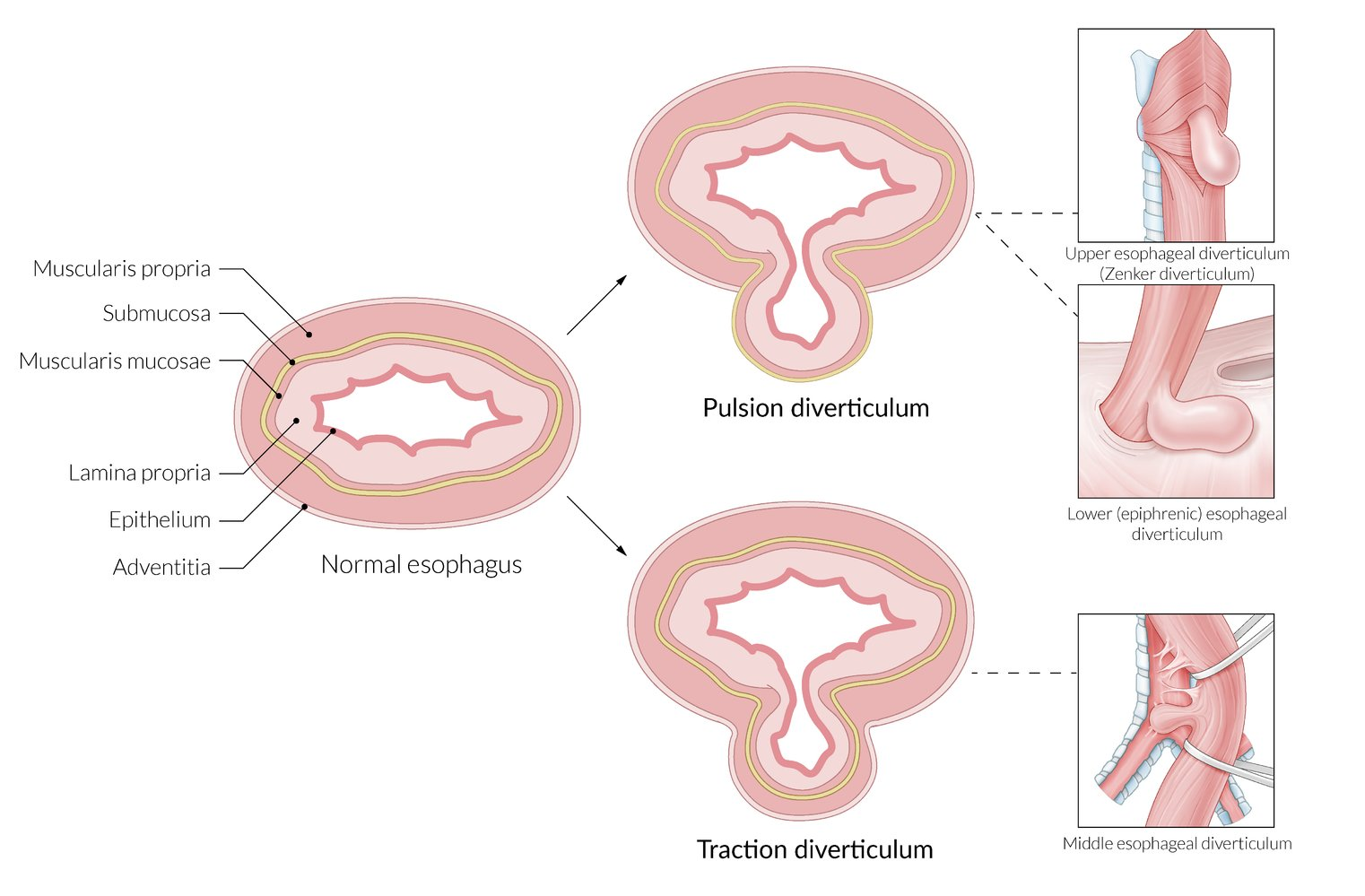
- Classified by location and mechanism (pulsion vs. traction)
- Zenker Diverticulum (Pharyngoesophageal)
- Most common type
- Pulsion diverticulum (↑ intraluminal pressure)
- Location: Killian triangle (between thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus muscles) - posterior hypopharynx
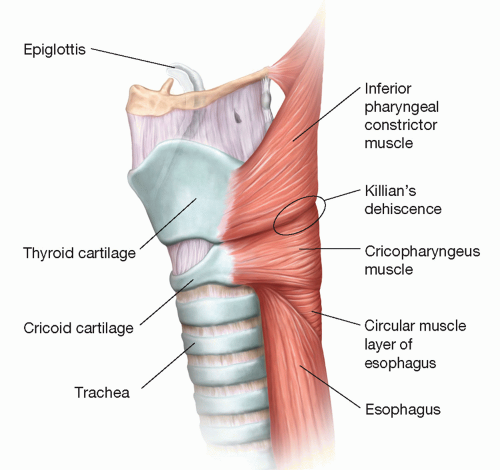
- Pathophysiology: Failure of cricopharyngeus muscle relaxation → ↑ pressure → herniation through weak point
- False diverticulum (mucosa/submucosa only, no muscle layer)
- Traction Diverticulum (Mid-esophageal)
- Less common
- Caused by external pulling forces (e.g., mediastinal inflammation, granulomatous disease like TB or histoplasmosis)
- Location: Mid-esophagus near carina
- True diverticulum (all layers of esophageal wall)
- Usually asymptomatic
- Epiphrenic Diverticulum (Distal esophageal)
Clinical features
- Zenker: Dysphagia, halitosis, regurgitation of undigested food, gurgling sounds, neck mass, aspiration risk
- Traction: Often asymptomatic
- Epiphrenic: Dysphagia, chest pain, regurgitation
Diagnostics
- Barium swallow with videofluoroscopy (best initial test)
Treatment

