Spasmolytics (Used for CNS-mediated spasticity or acute muscle spasm)
- Baclofen
- MOA: Agonist at GABA-B receptors in the spinal cord, leading to hyperpolarization and ↓ synaptic transmission.
- Use: Spasticity in multiple sclerosis (MS), spinal cord injuries.
- AE: Sedation, weakness. Abrupt withdrawal can cause seizures and hallucinations.
- Cyclobenzaprine
- MOA: Centrally acting; structurally related to tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs). Thought to act at the brainstem.
- Use: Short-term treatment of acute muscle spasms from musculoskeletal conditions.
- AE: Strong anticholinergic side effects (dry mouth, urinary retention, confusion), sedation.
- Tizanidine
- MOA: Centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonist. Reduces spasticity by ↑ presynaptic inhibition of motor neurons.
- Use: Spasticity from MS, stroke, or spinal cord injury.
- AE: Hypotension, sedation, dry mouth, hepatotoxicity.
- Dantrolene
- MOA: Acts directly on skeletal muscle. Prevents the release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum by binding to the ryanodine receptor (RyR1).
- Use: Malignant hyperthermia (first-line Tx), Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), spasticity from stroke, MS, spinal cord injury.
- AE: Hepatotoxicity (black box warning), muscle weakness.
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., Diazepam)
- MOA: Potentiate the effect of GABA at the GABA-A receptor, ↑ frequency of Cl- channel opening.
- Use: Muscle spasms, anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal.
- AE: Sedation, risk of tolerance/dependence.
Depolarizing NMJ blockers (depolarizing muscle relaxants)
Fast onset, short duration
Agents
- Succinylcholine (suxamethonium)
Indications
- Anesthesia induction (esp. rapid sequence induction)
Phases of Block:
- Phase I (Depolarizing): Initial muscle fasciculations followed by paralysis. Potentiated by cholinesterase inhibitors.
- Typical Duration: The clinically effective neuromuscular block from a single standard IV dose of succinylcholine is very brief, lasting 5 to 10 minutes.
- Pathophysiology: This short duration is due to its rapid hydrolysis by pseudocholinesterase (butyrylcholinesterase) in the plasma.
- Phase II (Desensitizing): Receptor becomes desensitized to ACh. Resembles non-depolarizing block; can be reversed by cholinesterase inhibitors.
- Typical Duration: The duration of a Phase II block is much more variable and prolonged. Spontaneous recovery is significantly longer, often taking 30 to 60 minutes or more to resolve after the drug is stopped.
- Pathophysiology: A Phase II block is an abnormal response that occurs when the postsynaptic receptors become desensitized. This is typically seen with:
- Large, repeated doses or a prolonged infusion of succinylcholine.
- It can also occur in patients with pseudocholinesterase deficiency, where a standard dose is not metabolized effectively, leading to a prolonged Phase I that eventually transitions into a Phase II block lasting for hours.
Monitoring
- Train-of-four stimulation shows an equal decrease in the amplitude of all 4 muscle twitches.
- The muscle fiber becomes unresponsive to any further stimulation
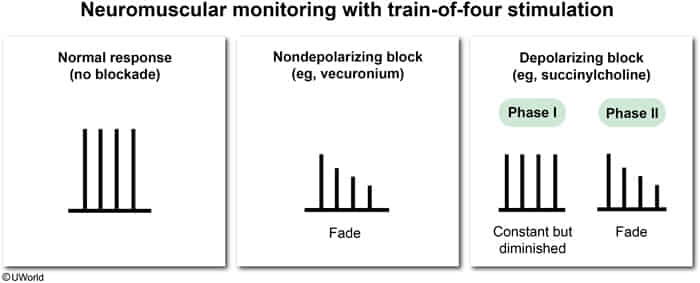
- The muscle fiber becomes unresponsive to any further stimulation
Adverse effects
- Hyperkalemia
- Mechanism: depolarization of large muscle groups → efflux of potassium ions into the extracellular space
- Succinylcholine is contraindicated in case of hyperkalemia or in conditions associated with a high-risk of hyperkalemia, including:
- Burn injuries
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Prolonged muscle paralysis, respiratory depression and/or apnea in patients with a congenital deficiency of plasma cholinesterase
- AChE (“True Cholinesterase”):
- Function: Rapidly hydrolyzes acetylcholine (ACh) in synaptic clefts & neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) to terminate neurotransmission. Essential for precise control of nerve impulses.
- Location: Primarily at postsynaptic NMJs, cholinergic synapses in CNS, red blood cells.
- PChE (Butyrylcholinesterase, “Plasma/Serum Cholinesterase”):
- Function: Hydrolyzes exogenous choline esters (e.g., succinylcholine, mivacurium) and some local anesthetics (e.g., procaine, cocaine). Physiological role not fully understood, but may be involved in nerve signal transmission.
- Location: Synthesized in the liver; found in plasma, liver, pancreas, heart, brain (white matter).
- Atypical pseudocholinesterase
- Pseudocholinesterase is responsible for the breakdown of succinylcholine through ester hydrolysis.
- Atypical pseudocholinesterase breaks down succinylcholine slowly and thus prolongs the duration of muscle relaxation during anesthesia from a few minutes to a few hours; this may cause respiratory depression.
- AChE (“True Cholinesterase”):
- Malignant hyperthermia
Nondepolarizing NMJ blockers (nondepolarizing muscle relaxants)
Slow onset, long duration
Mechanism of action
- Compete with ACh to bind with the (nicotinic) ACh receptors at the motor end plate (competitive antagonists) → prevention of motor end plate depolarization (nondepolarization block)
Agents
- Rocuronium t
- Vecuronium
- Atracurium
Indications
- Rapid-sequence induction of anesthesia when succinylcholine is contraindicated
Monitoring
- Train-of-four stimulation shows a fade-off in the amplitude of the muscle twitch
- NDMRs block nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) not only at the postsynaptic membrane but also at presynaptic nerve terminals
- These presynaptic receptors normally provide positive feedback for additional ACh release
- When blocked, there’s reduced mobilization of ACh vesicles for subsequent stimuli