Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Cryptococcal meningoencephalitis or brain abscess
- Hematogenous spread of fungi to meninges
- Headache, fever, signs of increased intracranial pressure, confusion, absent meningeal signs
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis
- Most commonly seen in immunocompromised patients
- Clinical presentation is variable and nonspecific (e.g., cough, fever, shortness of breath).
Diagnostics
- Latex agglutination test: positive for cryptococcal polysaccharide capsular antigen
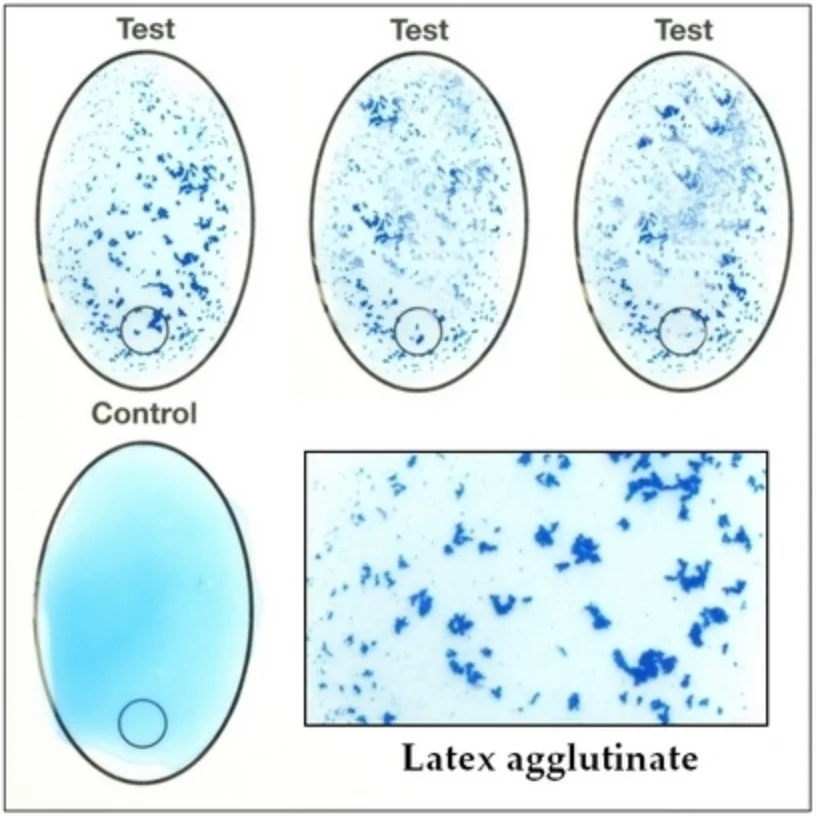
- High specificity and sensitivity
- Specimen: Blood or CSF
- CSF analysis
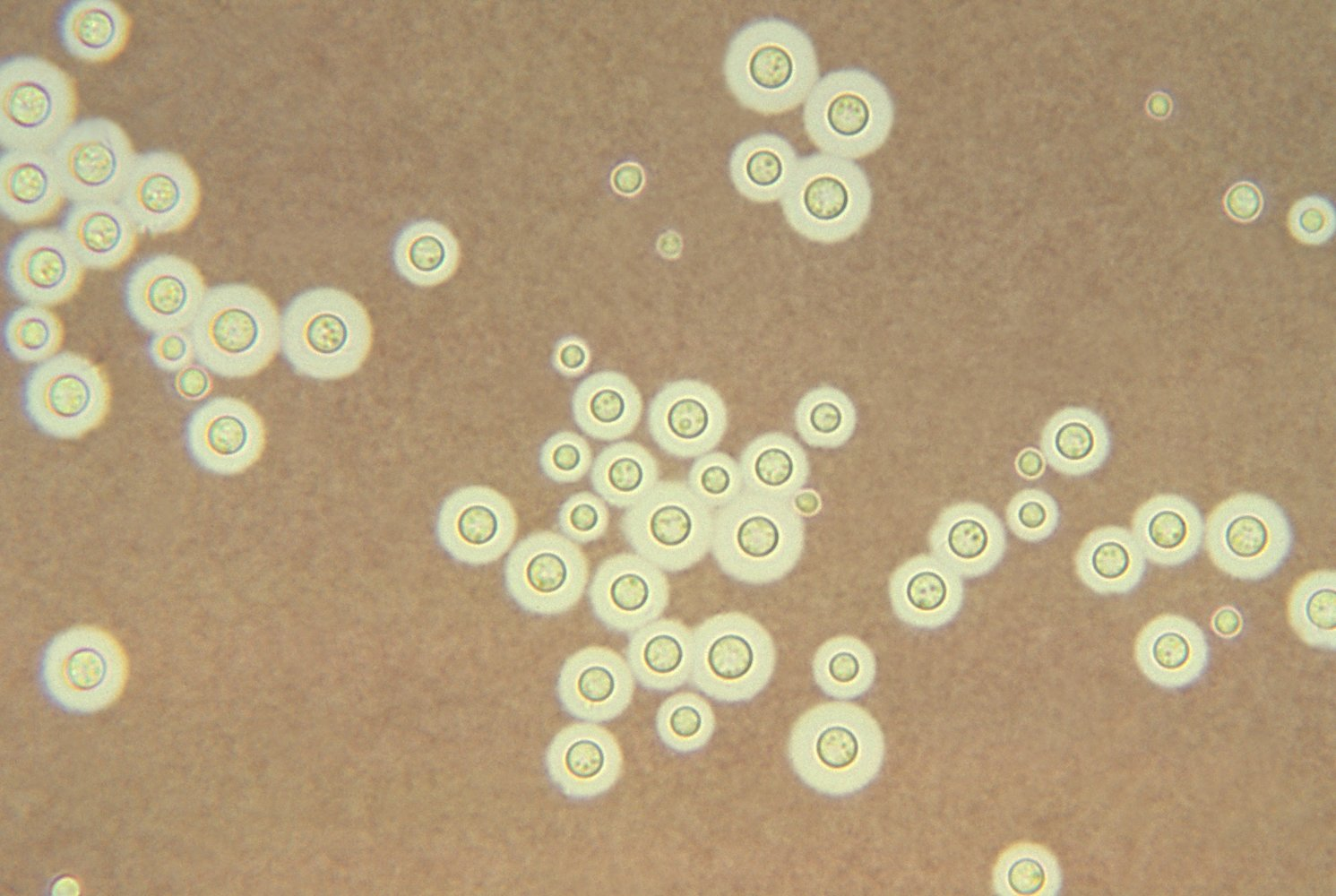
- India ink stain: clear halo; Round or oval budding yeast
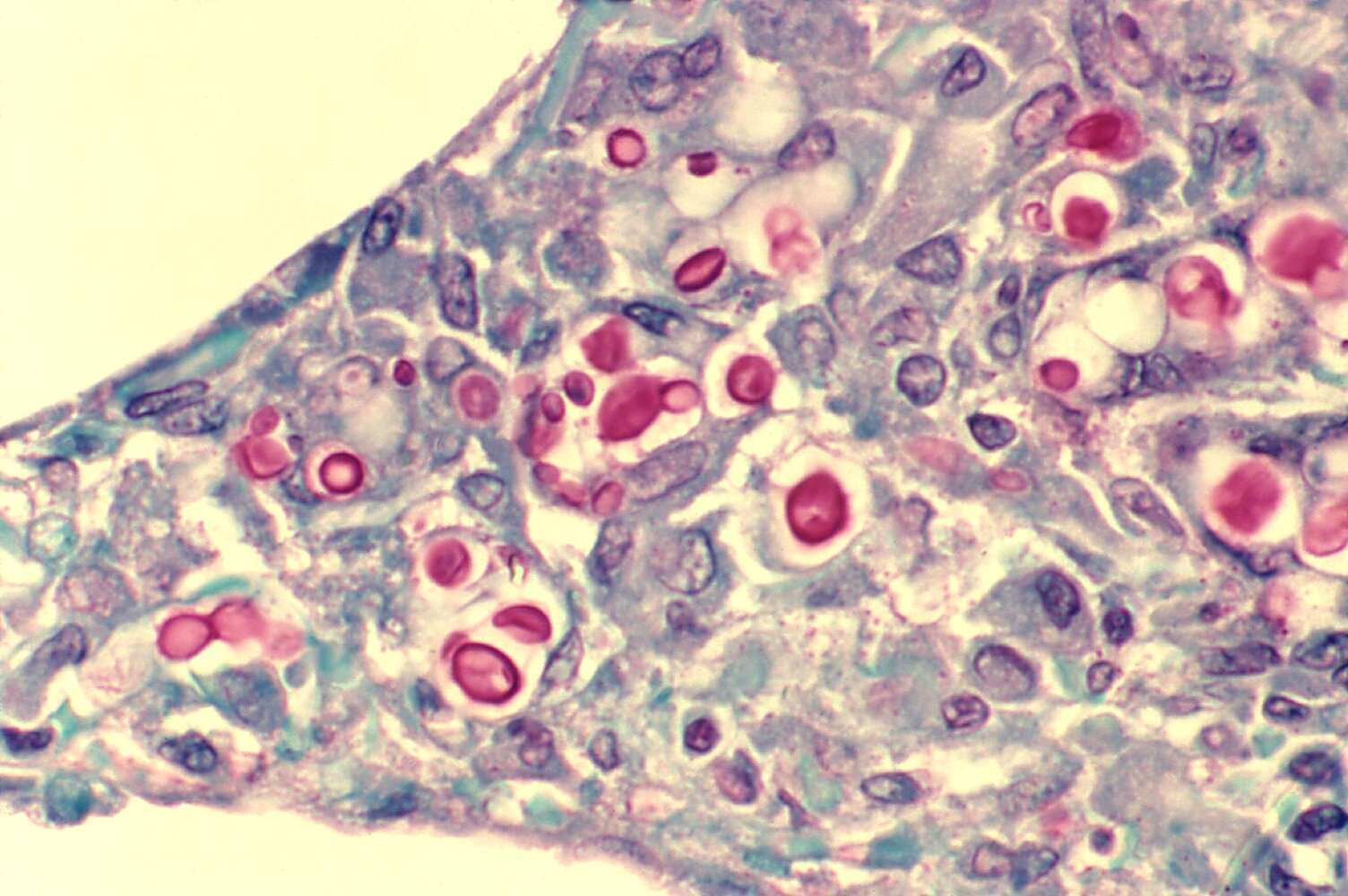
- Mucicarmine: stains the thick inner polysaccharide capsule bright red
- Fungal culture (Sabouraud agar) showing:
- 5–10 μm yeast
- Thick polysaccharide capsule
- Narrow, unequal budding
- MRI: “Soap bubble” lesions in cryptococcal encephalitis
Treatment


