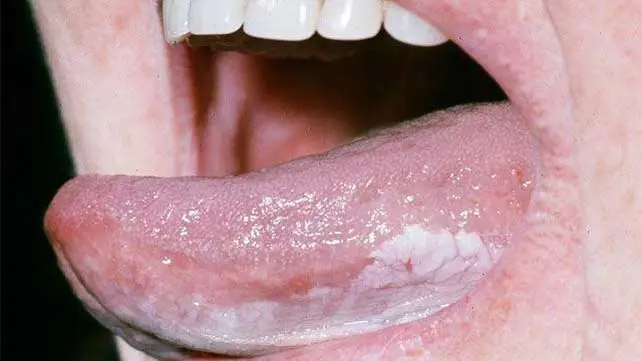
Leukoplakia
- Definition: hyperkeratosis of the epithelium and mucous membranes
- Persistent white plaques that cannot be scraped off
- Associated with alcohol and tobacco use
- Leukoplakia is considered a precancerous lesion since it carries an increased risk of malignant transformation. Needs to biopsy and remove.
Oral cavity cancer
- Halitosis
- Pain (e.g., earache)
- Pain in oral cavity cancer is usually due to infiltration/compression of nerves
- Dysphagia
- Nonhealing ulcer
- Unusual bleeding in the mouth
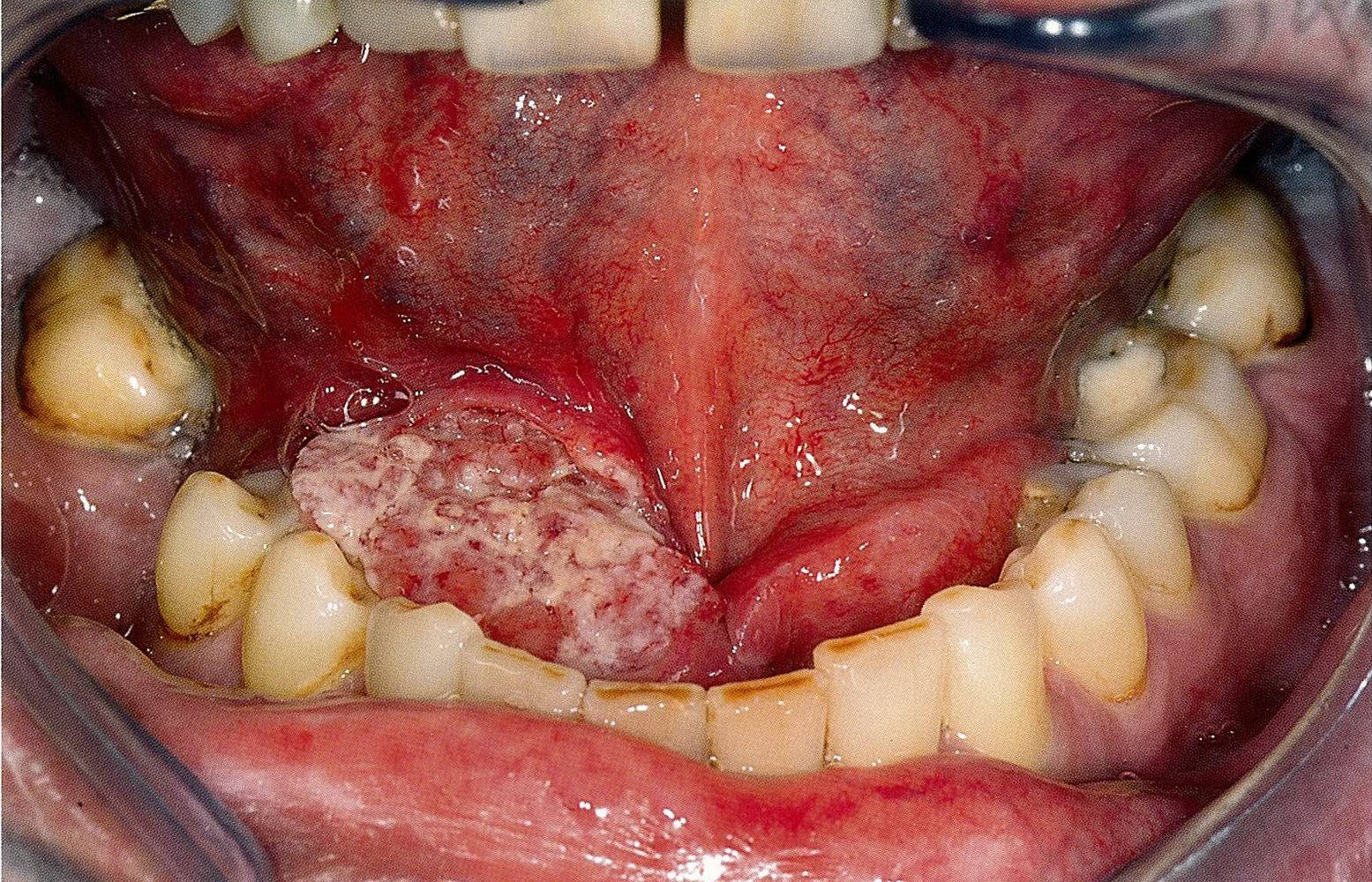
- Lymphadenopathy
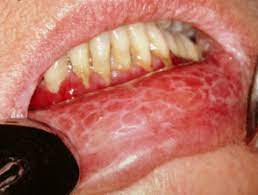
- Thin, gray-white lines that form a reticular pattern (Wickham striae)
- Painful, atrophic, and erosive lesions may be present.
- Associated with dental materials, drugs (e.g., NSAIDs, ACE inhibitors), infection, autoimmunity (e.g., PBC), and IBD
Oral hairy leukoplakia
- Benign, painless, irregularly shaped white plaques with feathery or hairy appearance
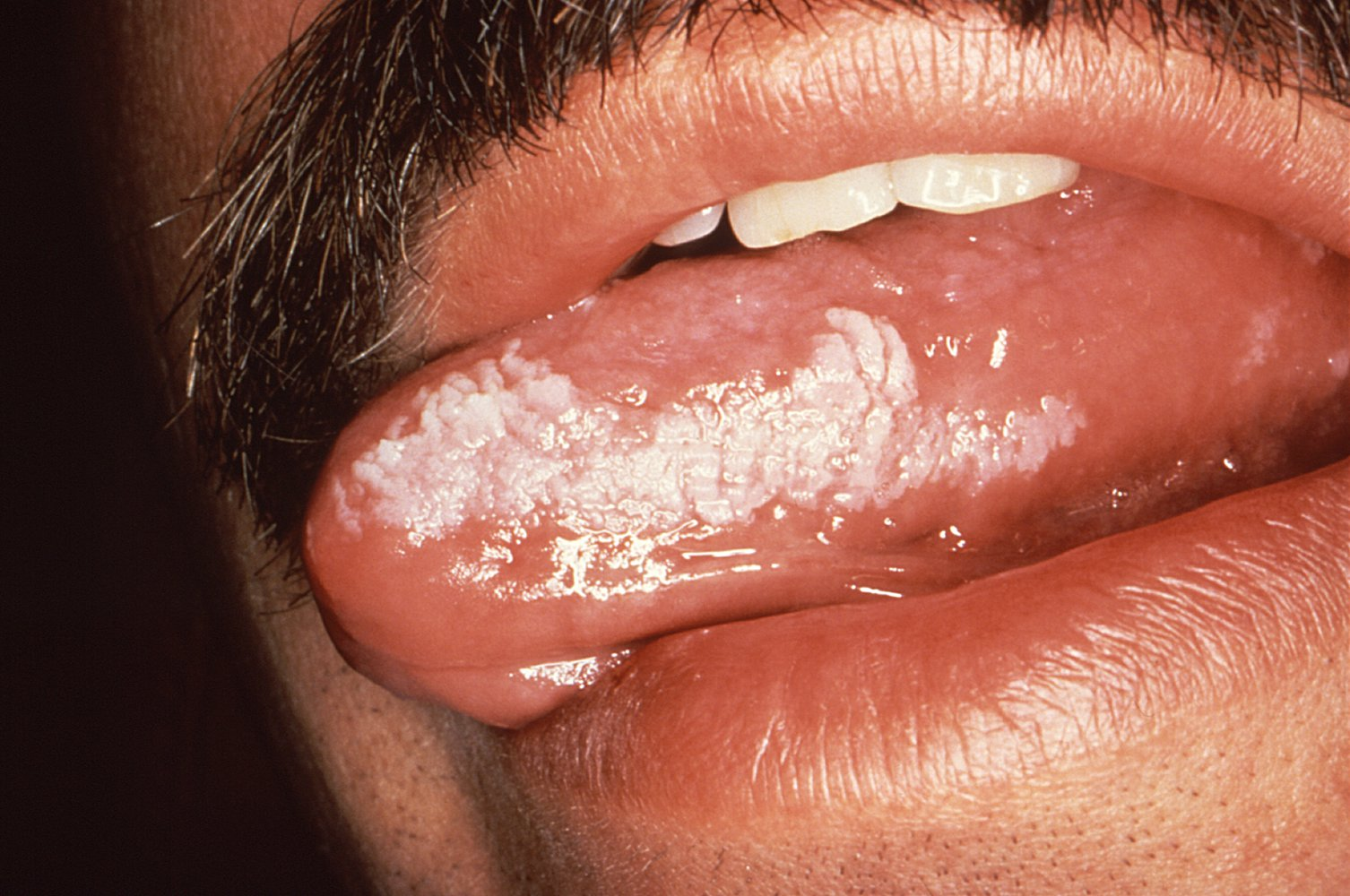
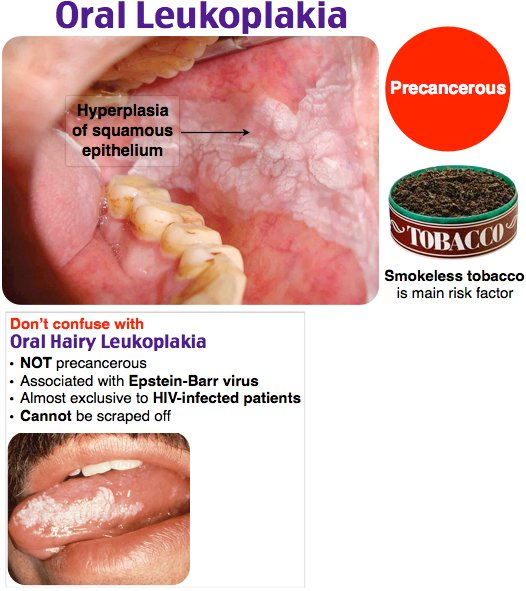
- Most commonly located on the lateral tongue, but can also occur on the floor of the mouth, palate, or buccal mucosa
- Patches cannot be scraped off (in contrast to oral thrush)
- Etiology
- EBV
- Immunosuppression (e.g., patients with a history of organ transplantation)
- Immunocompromise (e.g., HIV-positive individuals)




