Etiology
- Risk Factors
- Age: Most significant risk factor.
- Obesity: Increases mechanical stress on weight-bearing joints (knees, hips).
- Female gender: More common in women, especially post-menopause.
- Joint Trauma/Overuse: Previous injuries or occupations with repetitive stress can predispose to OA.
- Genetics: A family history plays a role, particularly in OA of the hand and hip.
Differential diagnosis
- Traditionally, osteoarthritis (OA) has been classified as a non-inflammatory or “wear-and-tear” arthritis
- The inflammation is generally less pronounced
- It doesn’t typically feature systemic inflammation markers
- It doesn’t involve autoimmune mechanisms as its primary cause
- Morning stiffness is typically shorter in duration
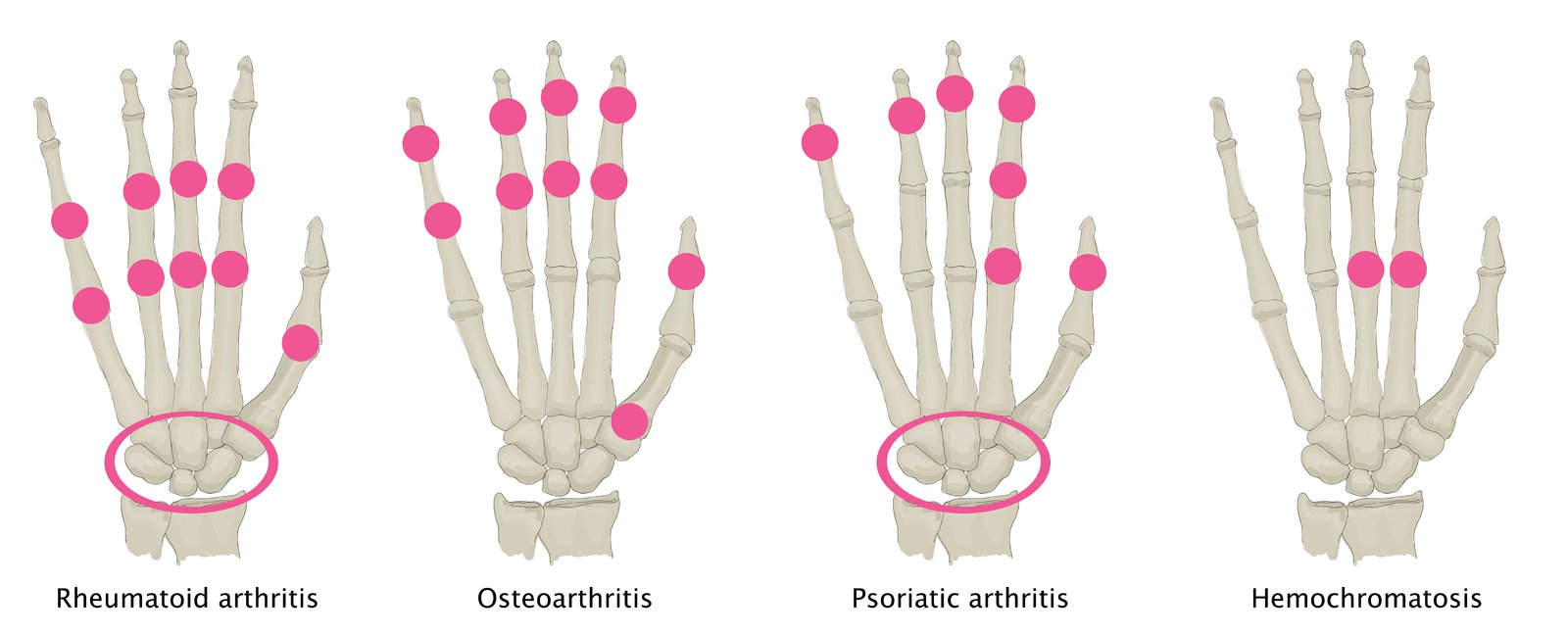
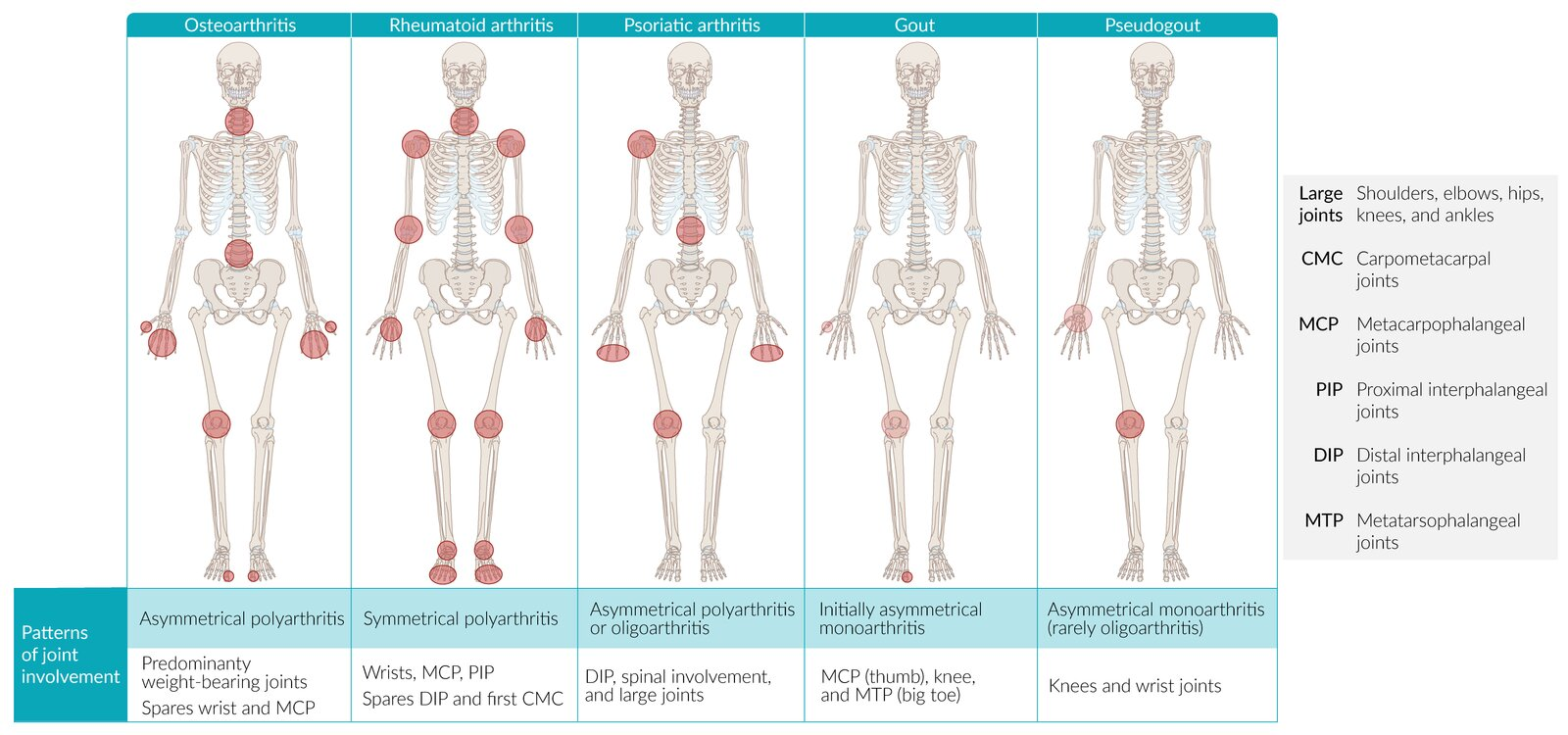
Osteoarthritis (OA) vs Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
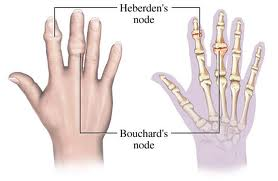
Feature Osteoarthritis (OA) Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Mechanism Mechanical “Wear & Tear” Autoimmune (Pannus) Stiffness < 30 min (Worse w/ use) > 1 hr (Better w/ use) Symmetry Asymmetric Symmetric Key Joints DIP (Heberden), PIP, Knees MCP, PIP, Wrist (Spares DIP) Labs Normal +Anti-CCP (Specific), +RF, ↑ ESR X-ray Osteophytes, Sclerosis Marginal Erosions, Osteopenia Treatment NSAIDs, Acetaminophen DMARDs (Methotrexate) 1. Stiffness
- OA (<30m): “Gelling.” Synovial fluid gets thick at rest. Movement quickly warms and lubricates it.
- RA (>1h): Edema. Inflammatory fluid pools during sleep. Takes time to mechanically pump/drain the boggy joint.
2. Pain
- OA (Worse w/ use): Mechanical. Bone-on-bone friction compresses exposed nerve endings.
- RA (Better w/ use): Washout. Movement flushes out stagnant inflammatory cytokines and fluid, relieving pressure.
3. Pathology
Link to original
- OA (Osteophytes): Construction. Bone grows spurs to widen surface area and stabilize the failing joint.
- RA (Erosions): Destruction. Pannus (granulation tissue) releases enzymes/RANKL that eat into the bone.
Treatment
Approach
Follow a stepwise approach to treatment: Start with nonpharmacological management, followed by pharmacological and/or surgical treatment if needed.
- Nonpharmacological management: e.g., exercise and weight loss
- Pharmacotherapy
- First line: e.g., topical or oral NSAIDs
- Second line: e.g., acetaminophen or intraarticular glucocorticoid injections
- Surgical management: e.g., complete or partial joint replacement (arthroplasty) using an endoprosthesis
Tip
Pharmacotherapy should only be used as a short-term treatment in symptomatic patients; long-term therapy is associated with many adverse effects.