Urinary casts
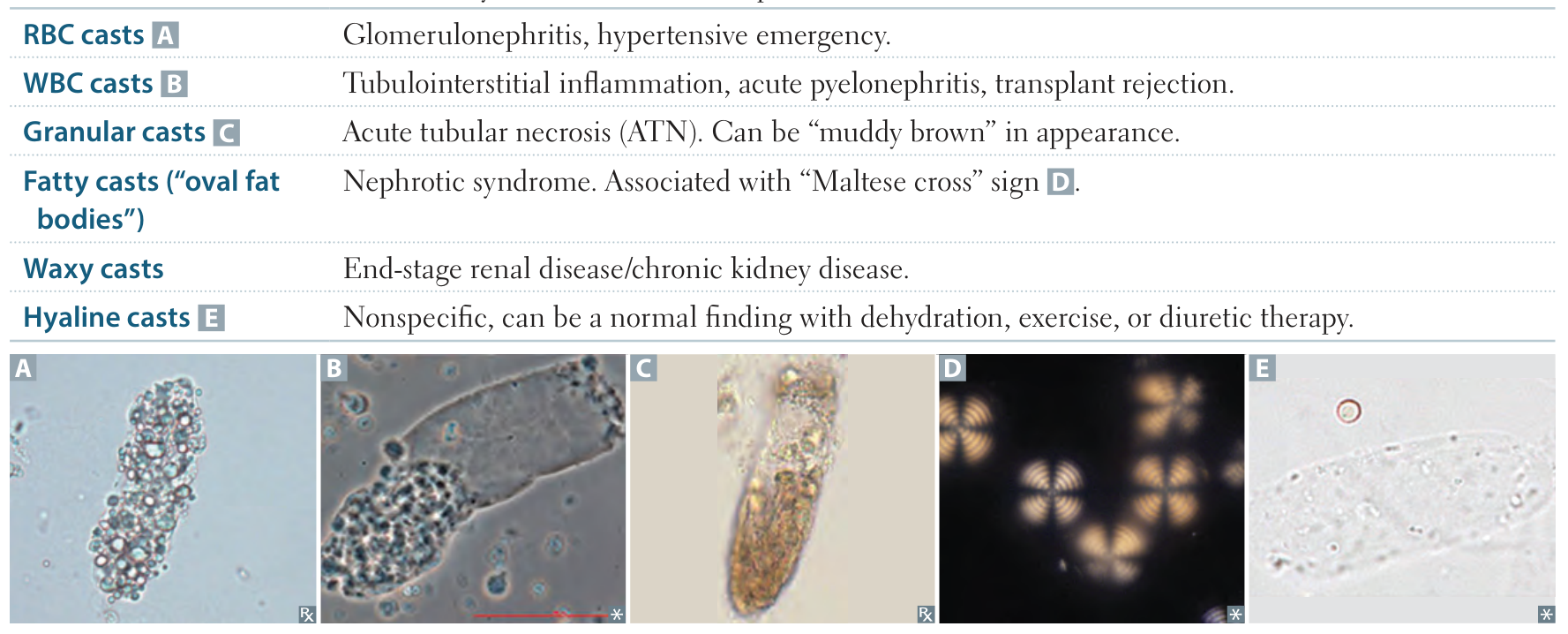
| Urinary Casts | Composition | Associated Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Hyaline | Tamm-Horsfall protein | Nonspecific, concentrated urine |
| Fatty | Lipid droplets | Nephrotic syndrome |
| Waxy | Degenerated hyaline cast | Chronic kidney disease |
| Granular | (muddy brown) Sloughed tubular epithelial cells with pigmented granules | Acute tubular necrosis |
| WBC | White blood cells | Pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis |
| RBC | Red blood cells | Glomerulonephritis |
Urinary casts are formed only in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) or the collecting duct (distal nephron). The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and loop of Henle are not locations for cast formation.
 Granular casts (acute) → waxy casts (chronic)
Granular casts (acute) → waxy casts (chronic)
Hyaline casts
The factors which favor protein cast formation are low flow rate, high salt concentration, and low pH, all of which favor protein denaturation and precipitation, particularly that of the Tamm-Horsfall protein. Protein casts with long, thin tails formed at the junction of Henle’s loop and the distal convoluted tubule are called cylindroids. Hyaline casts can be seen even in healthy patients.

Red blood cells may stick together and form red blood cell casts. Such casts are indicative of glomerulonephritis, with leakage of RBC’s from glomeruli, or severe tubular damage.
White blood cell casts are most typical for acute pyelonephritis, but they may also be present with glomerulonephritis. Their presence indicates inflammation of the kidney, because such casts will not form except in the kidney.

When cellular casts remain in the nephron for some time before they are flushed into the bladder urine, the cells may degenerate to become a coarsely granular cast, later a finely granular cast, and ultimately, a waxy cast. Granular and waxy casts are be believed to derive from renal tubular cell casts. Broad casts are believed to emanate from damaged and dilated tubules and are therefore seen in end-stage chronic renal disease.


The so-called telescoped urinary sediment is one in which red cells, white cells, oval fat bodies, and all types of casts are found in more or less equal profusion. The conditions which may lead to a telescoped sediment are: 1) lupus nephritis 2) hypertensive emergency 3) diabetic glomerulosclerosis, and 4) rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
In end-stage kidney disease of any cause, the urinary sediment often becomes very scant because few remaining nephrons produce dilute urine.