Epidemiology
Etiology
- Senile: Age >60 (Most common cause); oxidative damage.
- Diabetes: ↑ Glucose → Sorbitol accumulation (osmotic damage).
- Galactosemia: ↑ Galactitol → “Oil droplet” cataract (infants).
- Wilson Disease: Copper deposition → “Sunflower” cataract.
- Congenital: Rubella (Triad: Cataract, PDA, Deafness), Trisomies (13, 18, 21).
- Drugs: Prolonged Corticosteroids → Posterior subcapsular cataract.
- Environmental: Trauma, Radiation, UV-B light.
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Painless, progressive, bilateral vision loss
- Difficulty with nighttime driving
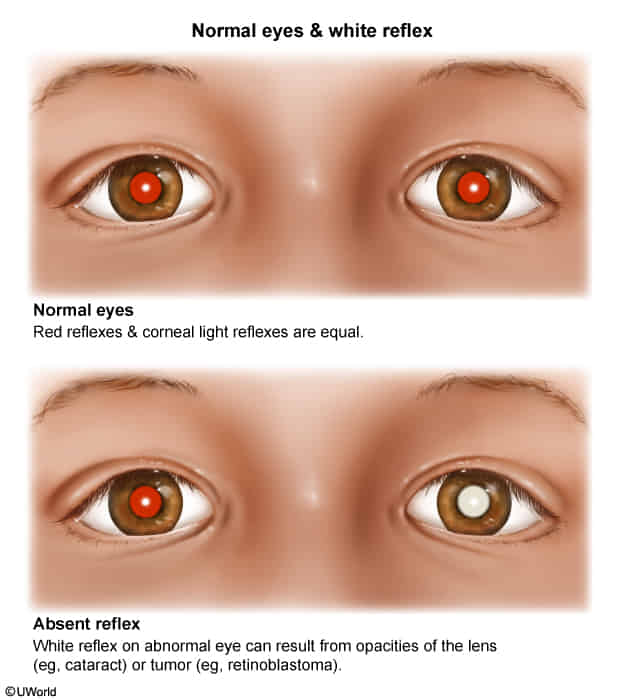
- Loss of red reflex
- Opacified lens
Diagnostics
- Fundoscopy
- Changes to the red reflex (the reflection of light in the ocular fundus, which is normally red in color), including:
- Opacities (including leukocoria)
- Darkening
- Absent or decreased red reflex
- Slit-lamp examination
- Common: grey, white, yellow, or brownish clouding of the lens (see also “Types of cataracts”)
Treatment
