Epidemiology
Etiology
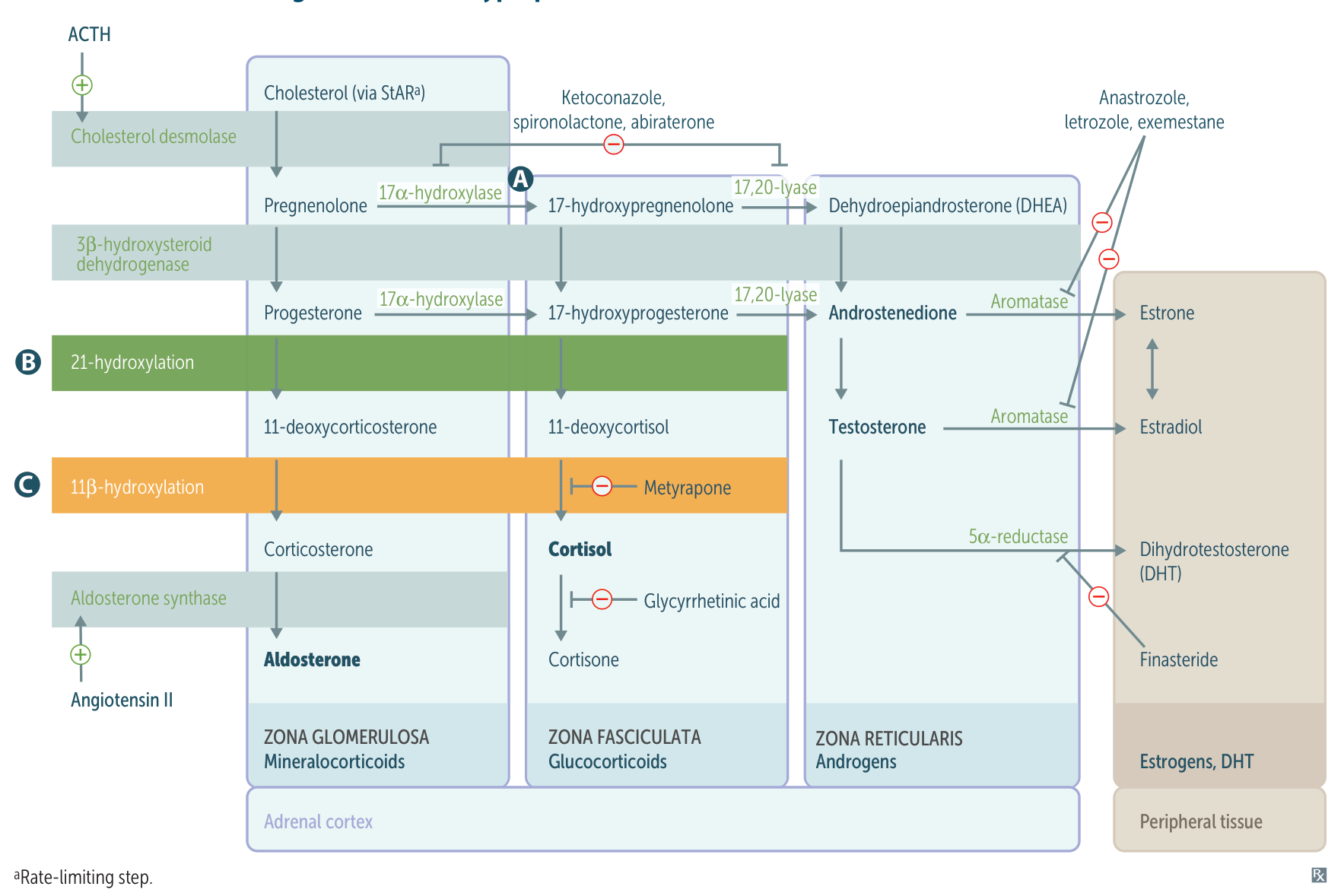
Pathophysiology
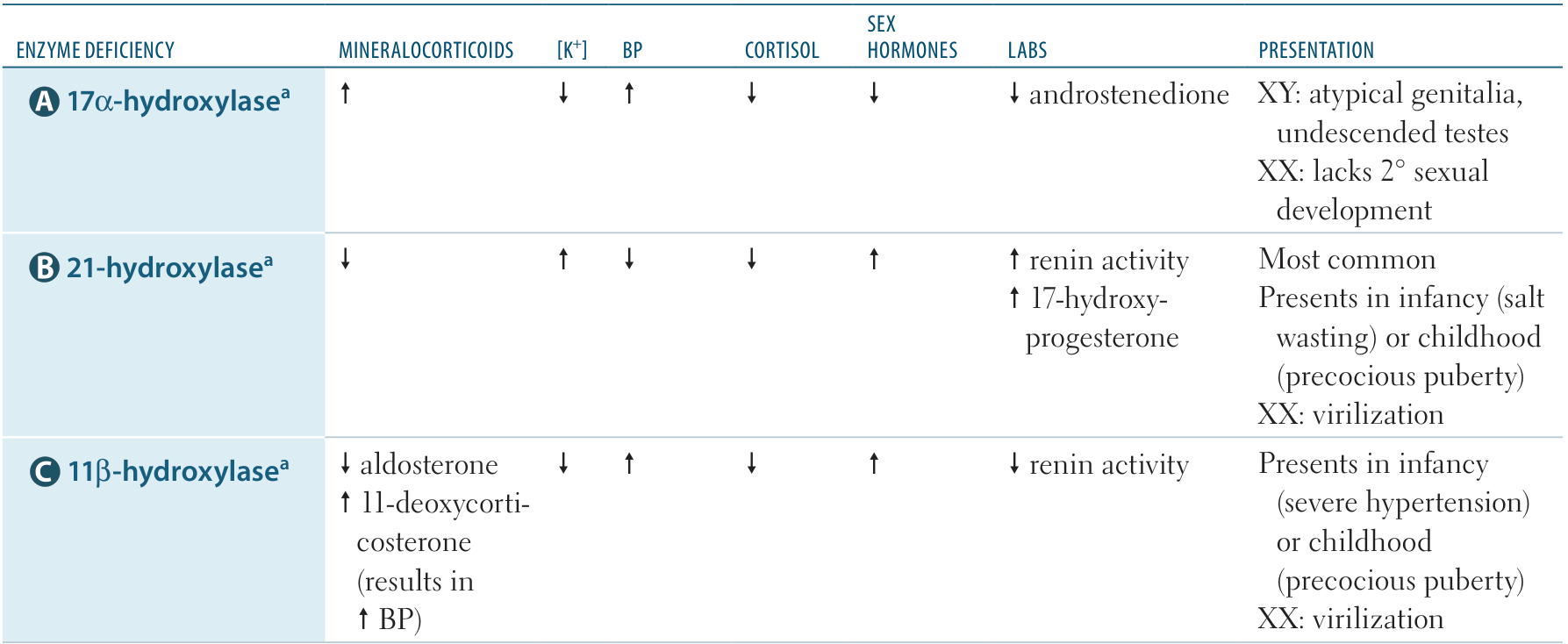
- CAH is caused by autosomal recessive defects in enzymes that are responsible for the production of cortisol.
- There are three subtypes of CAH:
- 21β-hydroxylase (∼ 95% of CAH)
- 11β-hydroxylase (∼ 5% of CAH)
- 17α-hydroxylase (rare)
- Low levels of cortisol → lack of negative feedback to the pituitary → increased ACTH → adrenal hyperplasia and increased synthesis of adrenal precursor steroids
Tip
DOC (11-Deoxycorticosterone) has aldosterone-like activity, and in high levels, it causes hypertension and kaluresis and inhibits the production of renin and consequently aldosterone.
Mnemonic
- “1 DOC:” If the deficient enzyme starts with 1 (11β-, 17‑), there is increased DOC.
- “AND 1:” If the deficient enzyme ends with 1 (21-, 11β‑), androgens are increased.