Neonatal soft tissue injuries
Soft tissue injuries of the scalp in infants are mostly caused by shearing forces during vacuum or forceps delivery.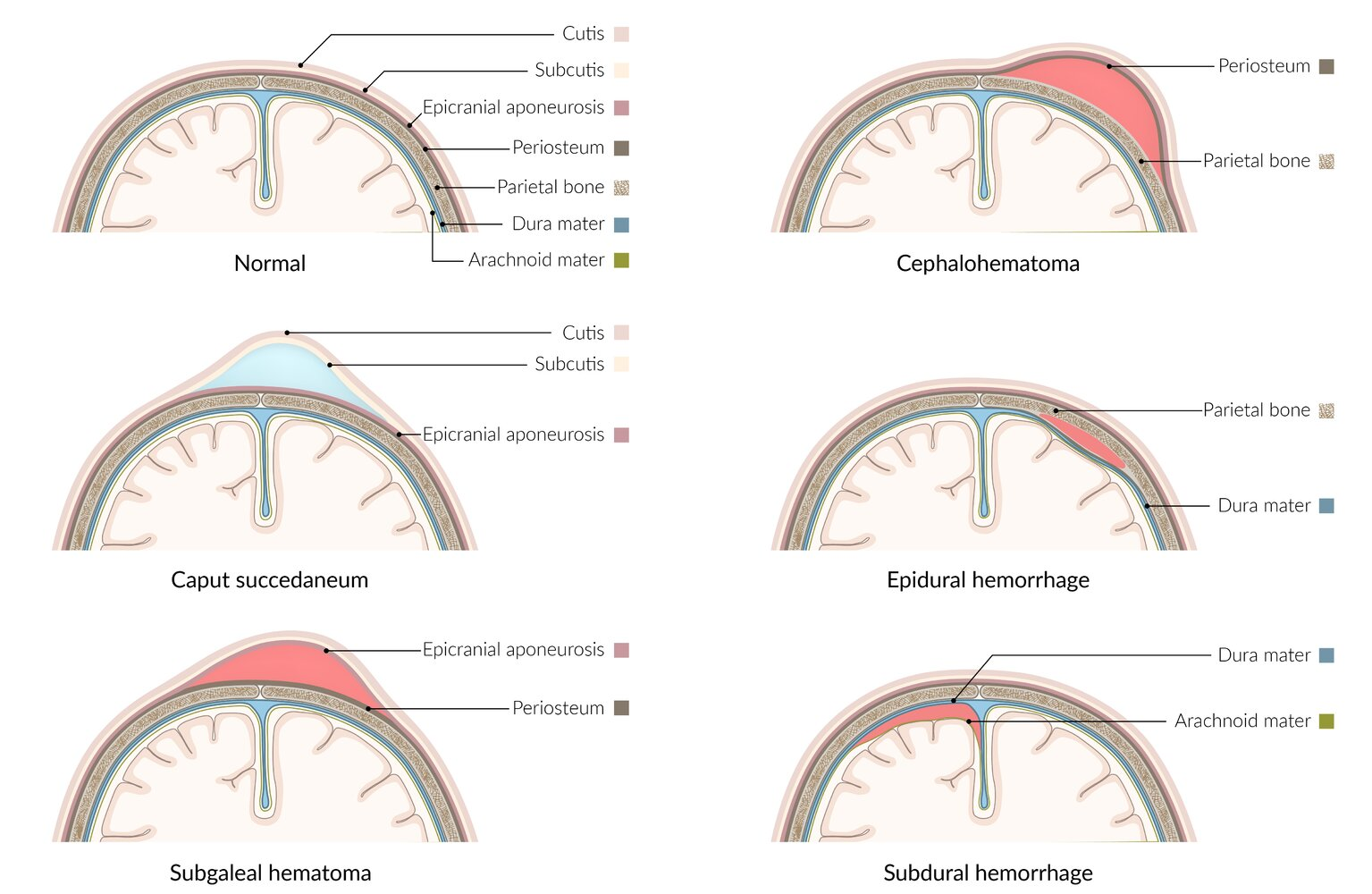
- Head molding
- Transient deformation of the head into an elongated shape due to external compression of the fetal head as it passes through the birth canal during labor
- Typically resolves within a few days after the birth
- Caput succedaneum: benign edema of the scalp tissue that extends across the cranial suture lines
- Cephalohematoma: subperiosteal hematoma that is limited to cranial suture lines
- Complications: calcification of the hematoma, secondary infection
- No treatment required; resolves within several weeks or months
- Subgaleal hemorrhage
- Rupture of the emissary veins and bleeding between the periosteum of the skull and the aponeurosis that may extend across the suture lines
- Associated with a high risk of significant hemorrhage and hemorrhagic shock