Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Treatment
<% tp.file.cursor() %>
Complications
- Gallstones ileus: mechanical bowel obstruction due to obstructive Gallstones
- Pathophysiology: gallbladder perforation or Mirizzi syndrome → biliary-enteric fistula formation (most commonly cholecystoenteric fistula) between the inflamed gallbladder and bowel → Gallstones passing down into bowel lumen
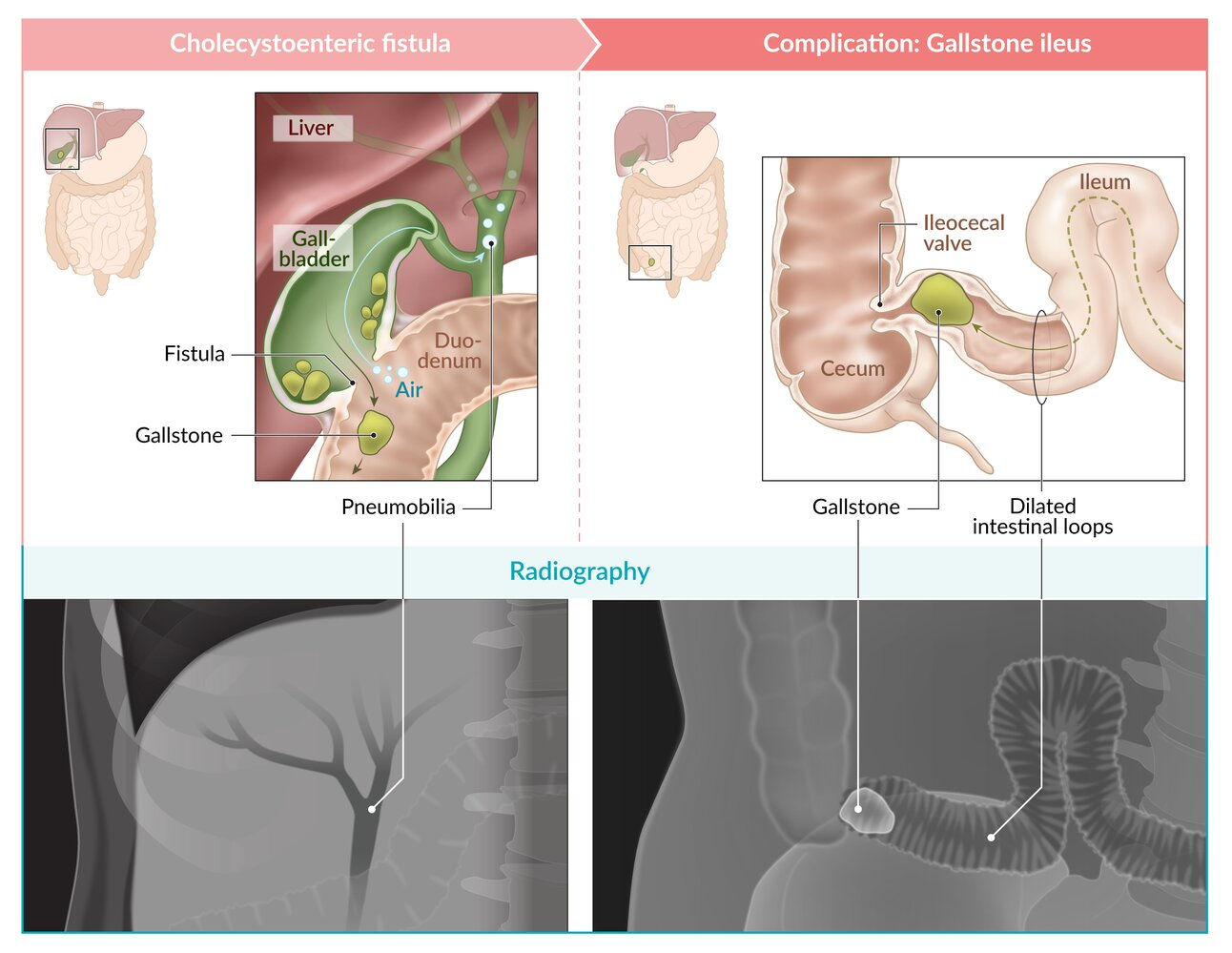
- Sites of obstruction: terminal ileum, at ileocecal valve (most common)
- Symptoms: distal bowel obstruction: features of mechanical bowel obstruction (abdominal pain and distention, nausea, vomiting)
- Diagnosis is based on the Rigler triad: imaging findings of small bowel obstruction, Gallstones (most commonly in iliac fossa), and pneumobilia.
- Air can move up toward the biliary ducts through a cholecystoenteric fistula.
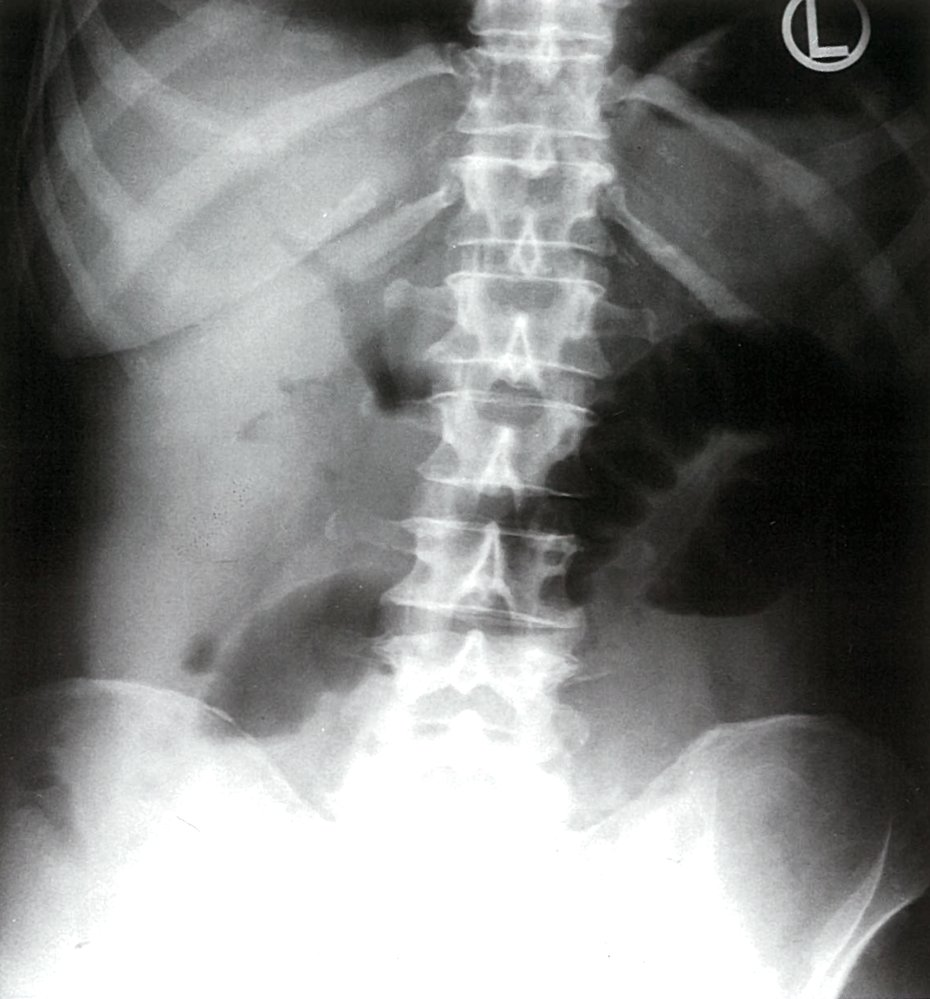
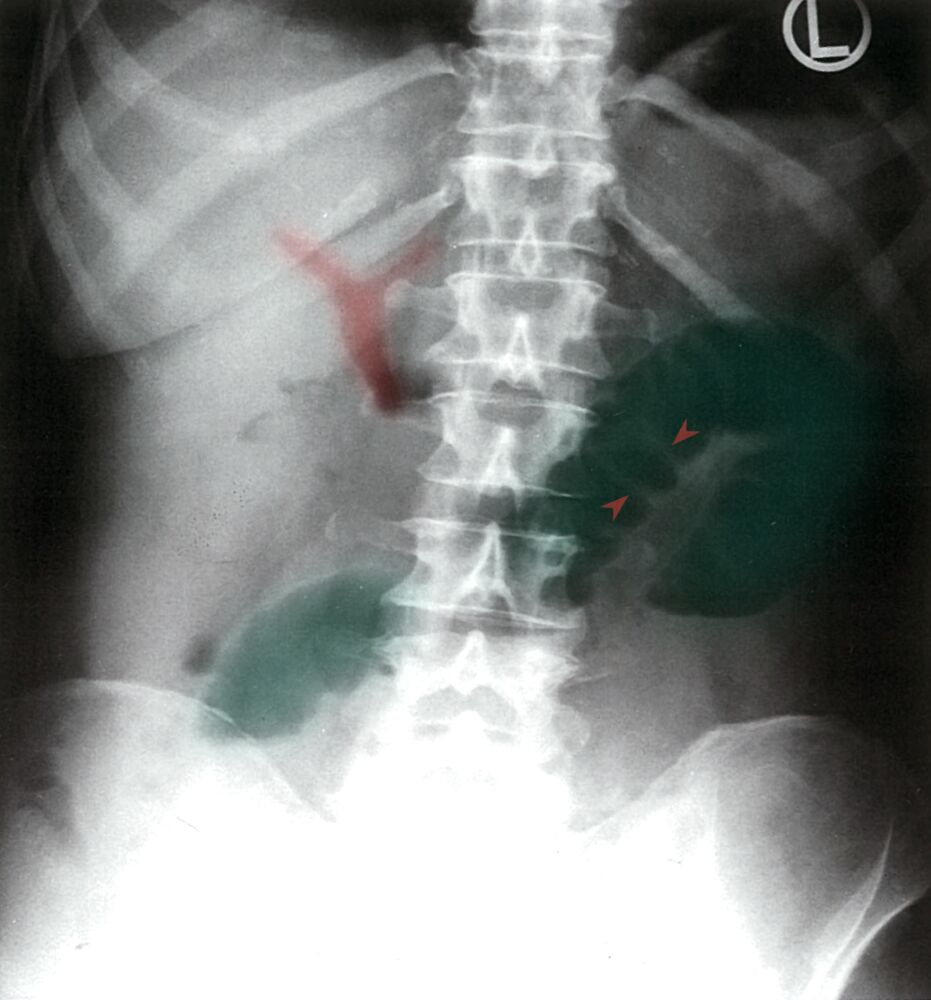
- Air can move up toward the biliary ducts through a cholecystoenteric fistula.
- Pathophysiology: gallbladder perforation or Mirizzi syndrome → biliary-enteric fistula formation (most commonly cholecystoenteric fistula) between the inflamed gallbladder and bowel → Gallstones passing down into bowel lumen