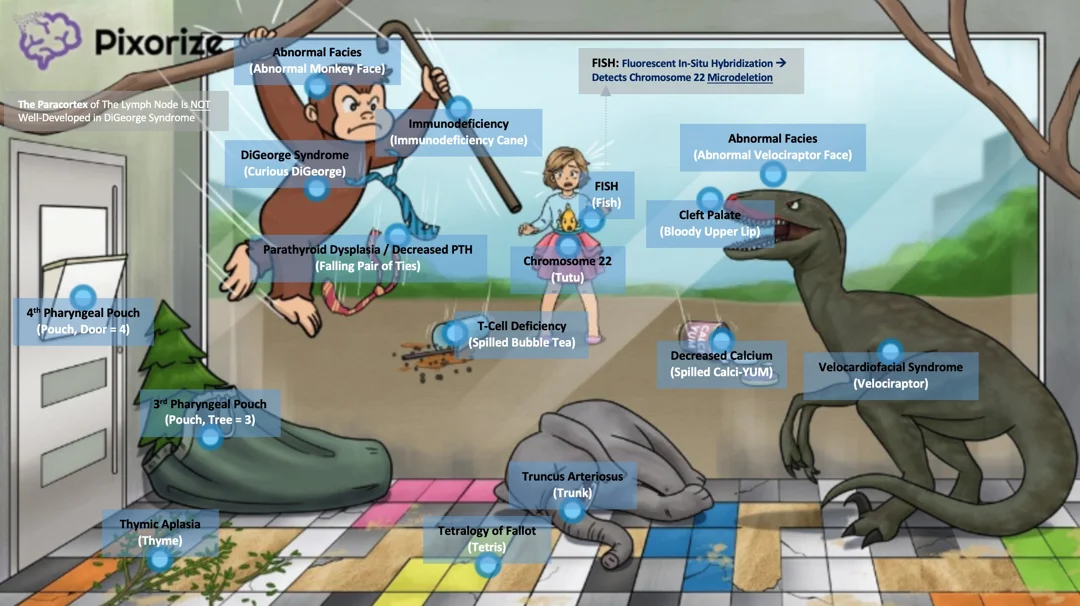
- Definition: syndrome characterized by defective development of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches leading to hypoplastic thymus and parathyroids
- Etiology: autosomal dominant; microdeletion at chromosome 22 (22q11.2)
- Clinical features
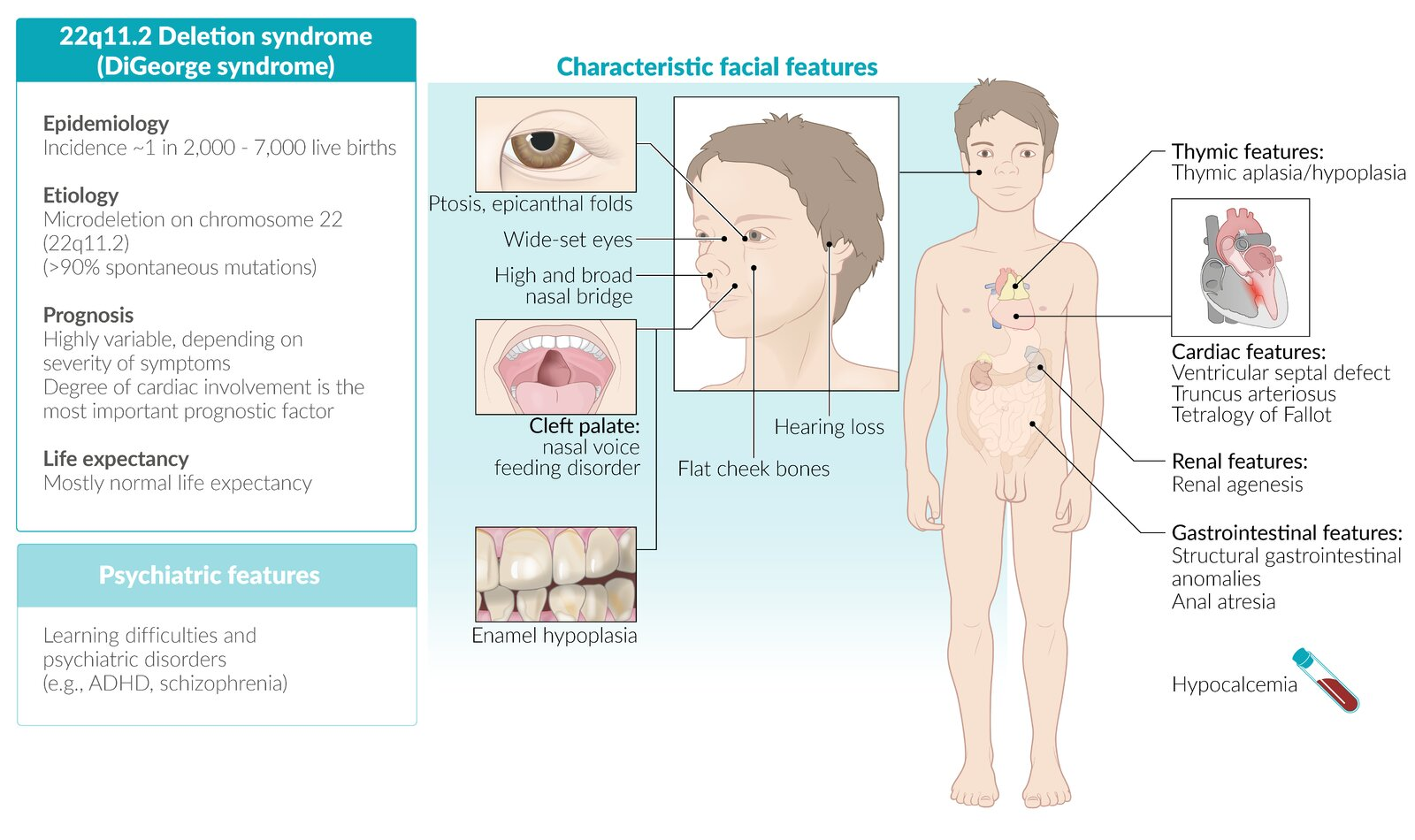
- Cardiac anomalies
- Conotruncal abnormalities (e.g., tetralogy of Fallot or persistent truncus arteriosus)
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- Anomalous face
- Prominent nasal bridge
- Hypoplastic wing of the nose
- Dysplastic ears
- Micrognathia (small lower jaw) and/or retrognathia
- Thymus aplasia/hypoplasia: recurrent infections (viral/fungal/PCP pneumonia) due to T-cell deficiency
- Cleft palate
- Hypoparathyroidism: hypocalcemia with tetany
- Cardiac anomalies
- Diagnosis
- Detection of 22q11.2 deletion via fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
- ↓ PTH and Ca2+
- ↓ Absolute T-lymphocyte count
- Delayed hypersensitivity skin testing
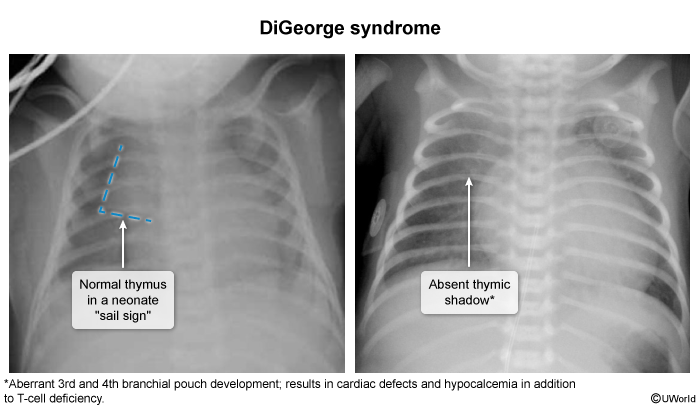
- CXR: absence of thymic shadow
Mnemonic
CATCH-22 is the acronym for typical features of DiGeorge syndrome: Cardiac anomalies; Anomalous face; Thymic aplasia/hypoplasia; Cleft palate; Hypocalcemia; Chromosome 22.