Epidemiology
Etiology
- Pathogen: a DNA poxvirus (molluscum contagiosum virus)
- Transmission:
- Direct skin contact (contact sports, sexually transmitted)
- Autoinoculation (scratching or touching lesion, e.g., while shaving)
- Fomites (e.g., on bath sponges/towels)
- Risk factors: immunosuppression
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Nontender, skin-colored, pearly, dome-shaped papules with central umbilication (individual lesions may also be painful or pruritic)
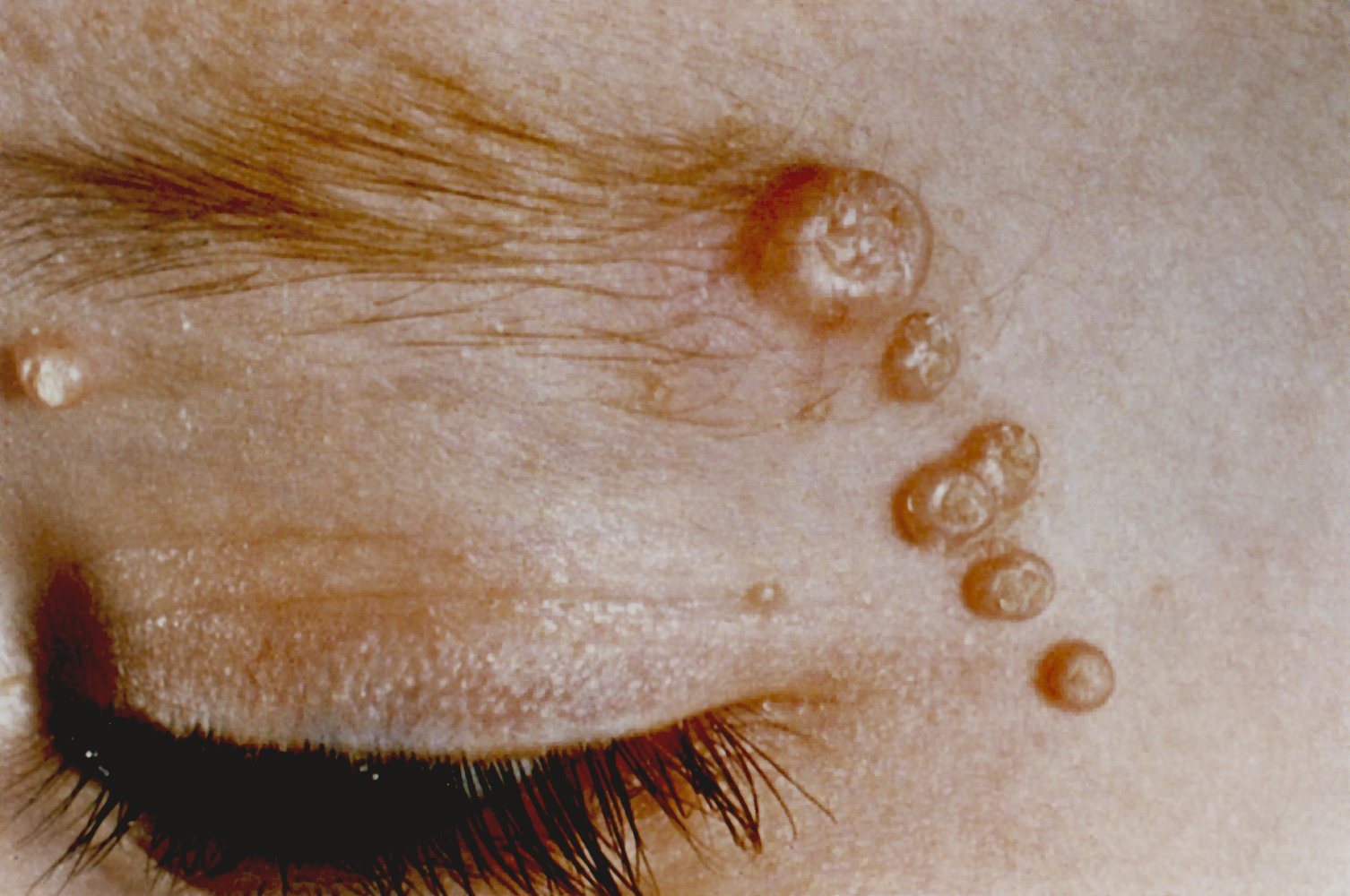
- Predilection sites:
- In children: face, trunk, and extremities (e.g., axilla, antecubital and popliteal fossa)
- In adults: lower abdomen, groin, genitalia, and proximal thighs
Diagnostics
Treatment
