- Definition: inherited genetic disorder characterized by impaired pyruvate metabolism
- Inheritance: X-linked recessive or autosomal recessive
- Pathophysiology
- Why is it called pyruvate dehydrogenase? Because it takes the hydrogen from carbon and thus oxidizing it.
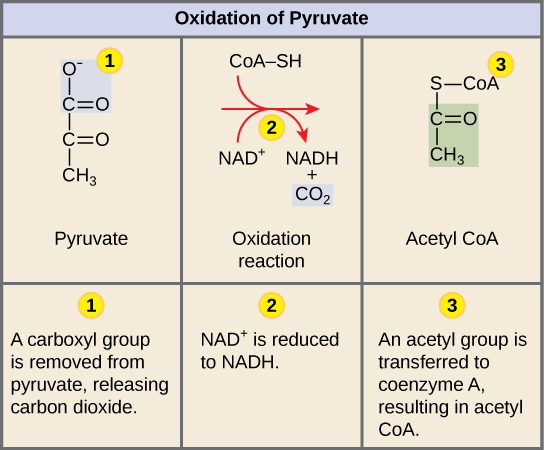
- Absent pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) → impaired conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA → reduced production of citrate → impaired citric acid cycle → energy deficit (especially in the CNS) → neurological dysfunction
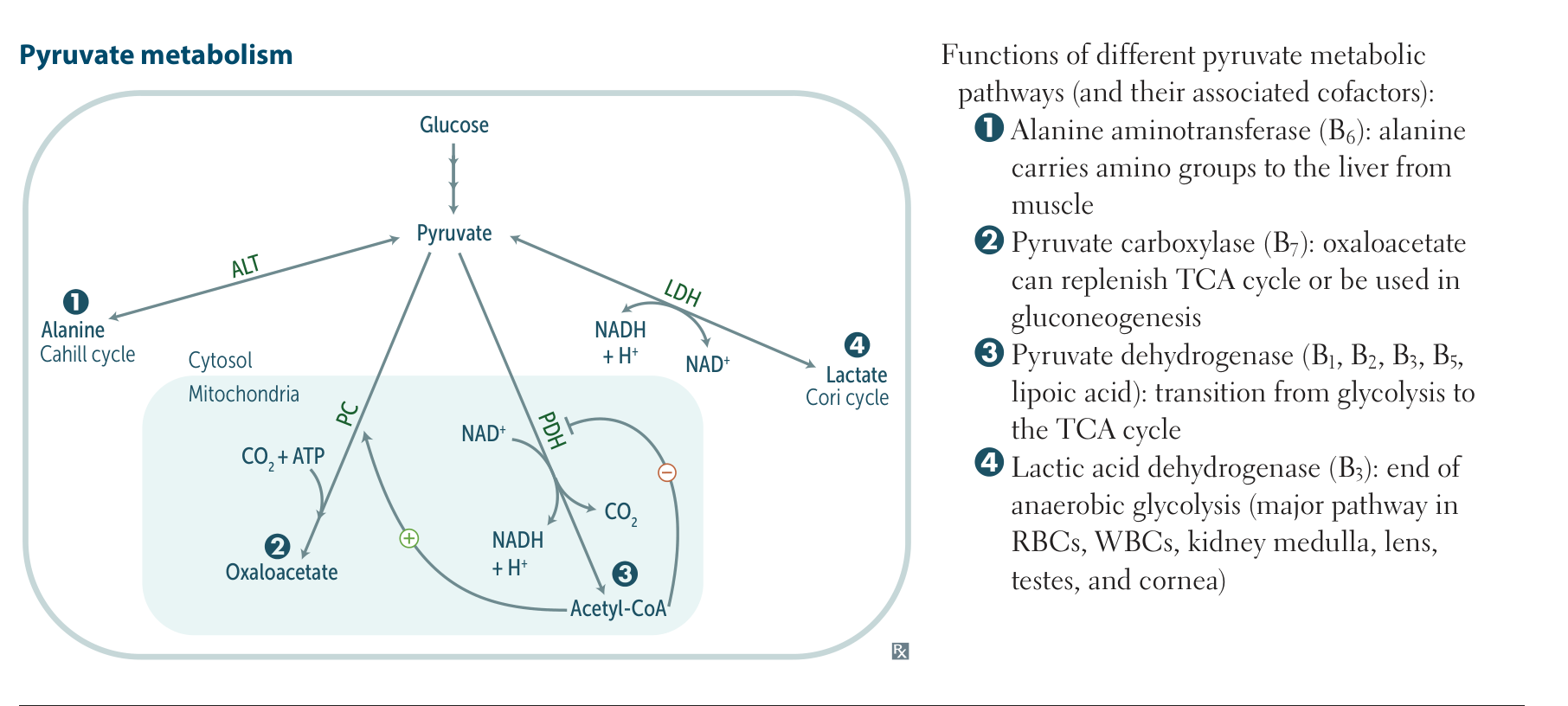
- Excess pyruvate is further metabolized in the Cahill cycle to the following
- Lactate via lactate dehydrogenase
- Alanine via alanine aminotransferase
- Clinical features
- Onset: early neonatal period
- Poor feeding, lethargy
- Tachypnea
- Developmental delay
- Progressive neurological symptoms (e.g., seizures)
- Diagnostics
- ↑ Lactate (lactic acidosis) and pyruvate in serum
- ↑ Alanine in serum and urine
- Treatment
- Acute: correction of acidosis
- Long-term: ketogenic diet

- High in fat, low in carbohydrates
- High in ketogenic amino acids (lysine and leucine) t
- Avoidance of glucogenic acids (e.g., valine)
- Avoid glucogenic amino acids: Methionine, histidine, valine.


