- Definition: gastritis featuring massive enlargement of the mucosal folds
- Pathophysiology
- Foveolar hyperplasia leads to:
- Increased mucus production → loss of protein → peripheral edema
- Atrophy of parietal cells → decreased gastric acid production
- Hyperplasia of gastric rugae
- Clinical features
- Dyspeptic symptoms (i.e., abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss)
- Protein-loss gastropathy → hypoalbuminemia and peripheral edema
- Diagnostics: based on endoscopic and histopathological findings
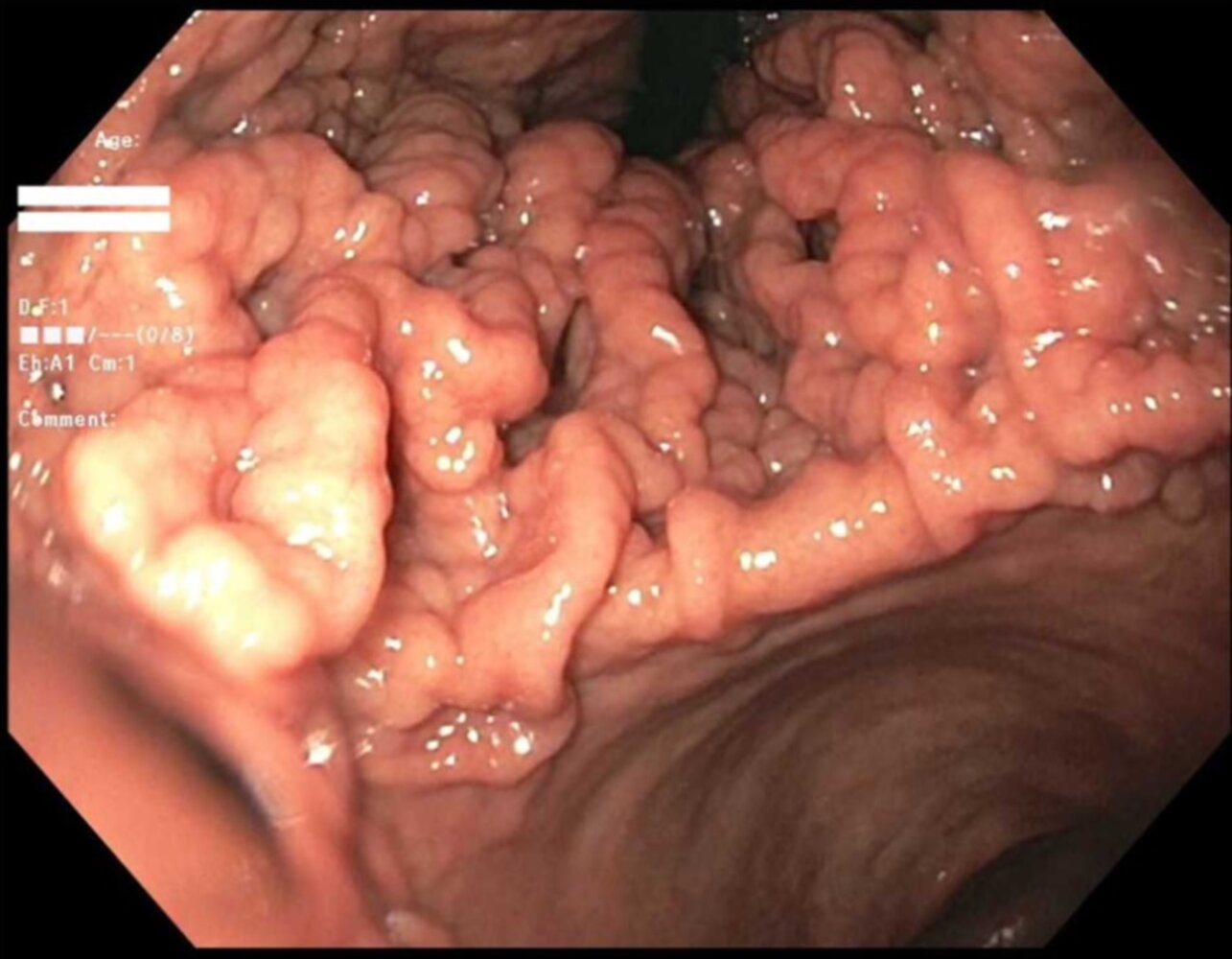
- Endoscopic findings: prominent rugae in the gastric fundus
- Histopathological findings: foveolar hyperplasia and parietal cell atrophy
