Epidemiology
Etiology
- Bacterial: C. difficile (pseudomembranous colitis), Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter infections
- Inflammatory colitis: Ulcerative colitis, Crohn disease
Pathophysiology
- Colonic accumulation of inflammatory mediators and bacteria → nitric oxide synthesis → colonic dilation
- Edema and inflammation of the colonic smooth muscle → colonic dysmotility → colonic dilation
Clinical features
- (Bloody) diarrhea and vomiting
- Abdominal distention and pain
- Signs of sepsis (fever, tachycardia, hypotension) and dehydration
Diagnostics
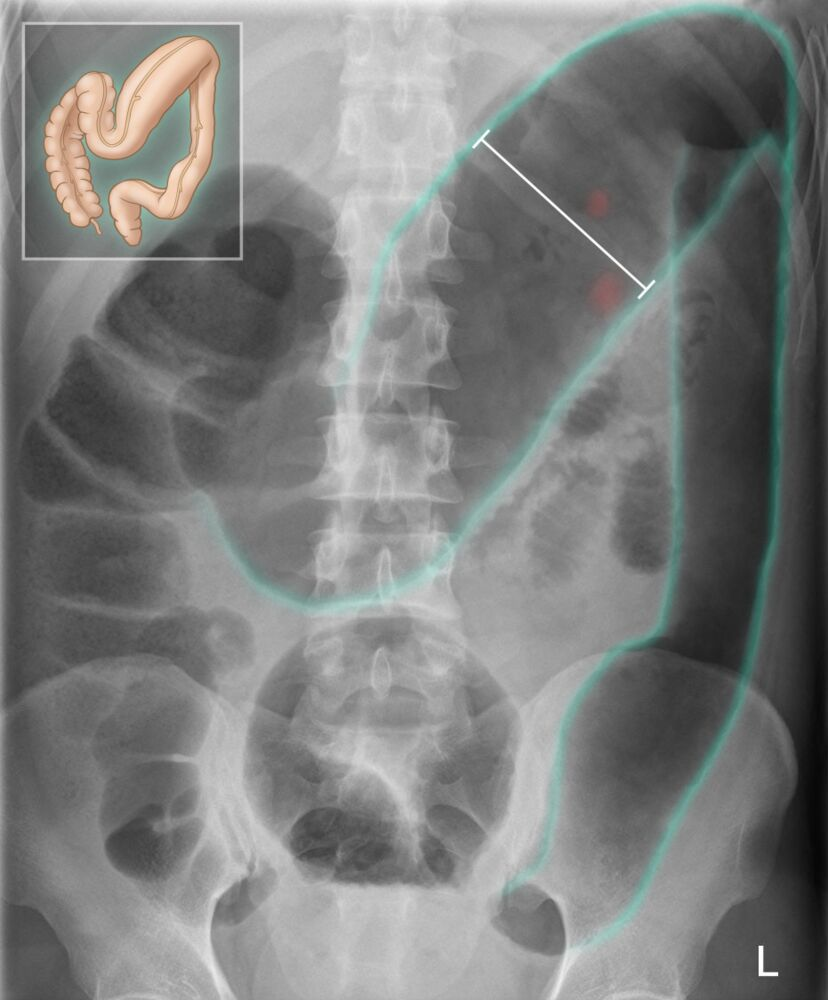
- Abdominal x-ray findings
- Dilation of the colon (transverse colon diameter > 6 cm)
- Loss of haustration
- Multiple air-fluid levels
Warning
Colonoscopy should be avoided in patients with suspected toxic megacolon since it increases the risk of colonic perforation.
Treatment
<% tp.file.cursor() %>