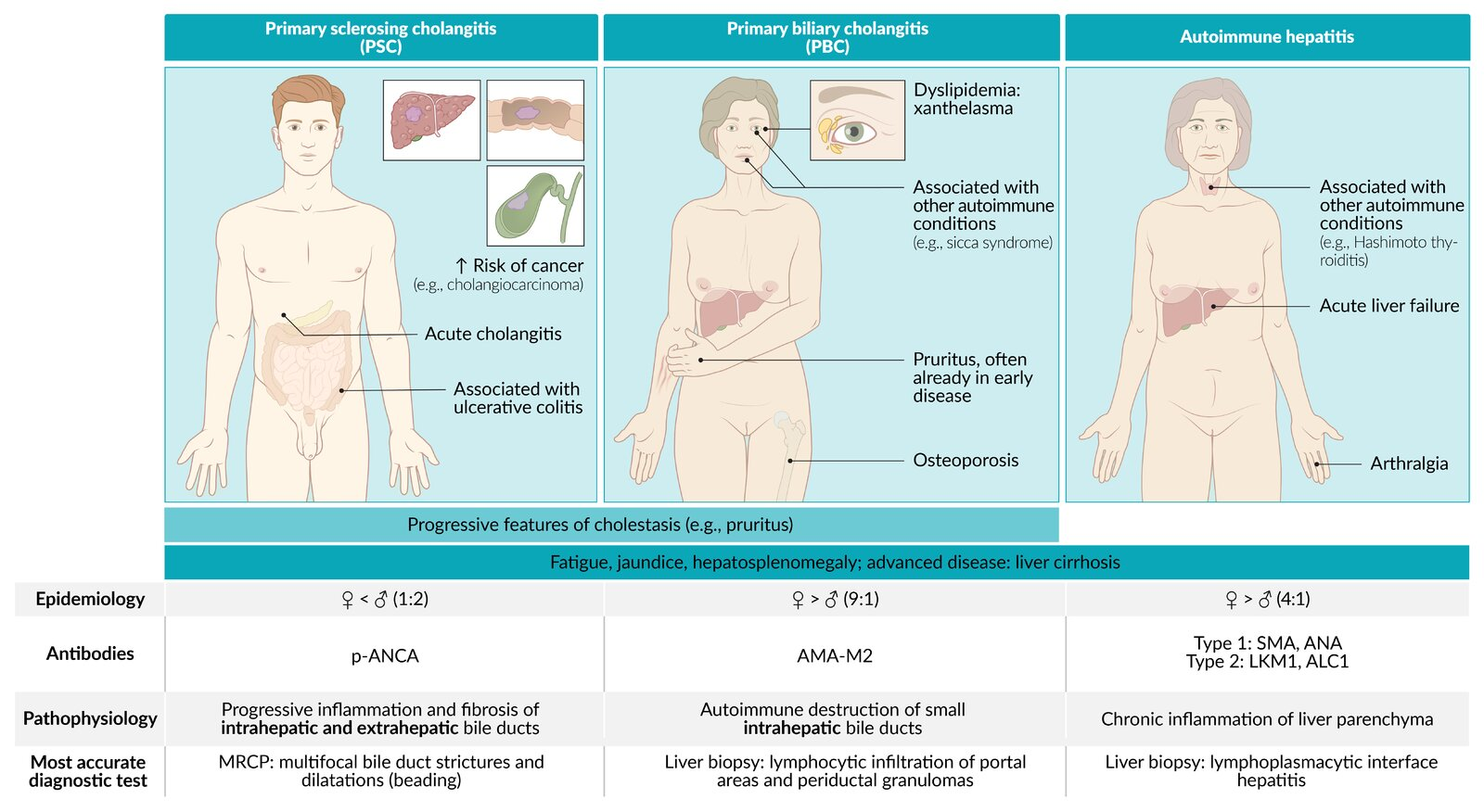
Epidemiology
- Sex: ♂ > ♀ (2:1)
- Age: The median age at diagnosis is ∼ 40.
Tip
Compared with Primary biliary cholangitis, which are common among middle-aged women.
Etiology
- The exact cause is unknown.
- Associations
- Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD)
- ∼ 90% of patients with PSC have IBD (approx. 87% of these patients have ulcerative colitis)
- Presence of HLA-B8 and HLA-DR3
- Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD)
The majority of patients with PSC also have
Pathophysiology
Progressive chronic inflammation of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts
Clinical features
- Signs of cholestasis
- Jaundice/scleral icterus
- Pruritus
- Pale stool, dark urine
- Fatigue
- Can lead to acute cholangitis (fever, chills, right upper quadrant pain)
- Later stages: signs of cirrhosis
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Portal hypertension
- Liver failure
- Symptoms of chronic inflammatory bowel disease, which is frequently associated with PSC, or other associated comorbidities
Diagnostics
- Cholestatic enzymes
- ↑ ALP
- ↑ GGT
- Normal or ↑ conjugated bilirubin
- Transaminases: normal or moderately elevated (approx. 2–3× ULN) AST and ALT
- Lipid profile: ↑ total cholesterol
Mnemonic
Suspect PSC in patients with a history of inflammatory bowel disease and elevated cholestatic enzymes (ALP, GGT, and conjugated bilirubin).
- Typical perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (pANCA): present in up to 80% of patients with PSC.
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
- Method of choice (if there is no biliary obstruction)
- Supportive findings: multifocal intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct strictures alternating with dilatation and beading of bile ducts
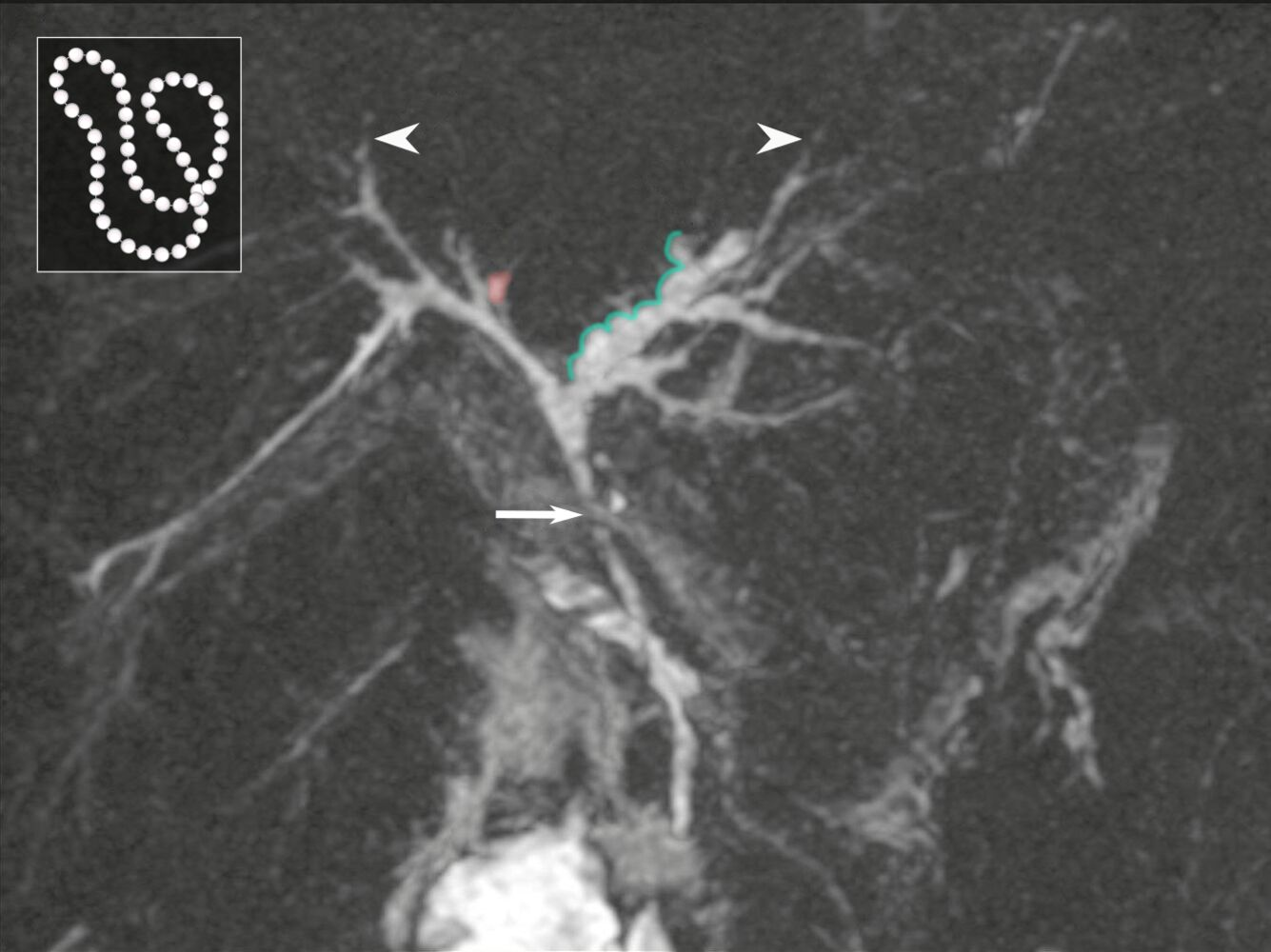 There is irregular dilatation (green overlay) of intrahepatic bile ducts proximal to a common duct stenosis (arrow). Alternation of strictured and dilated segments creates a beaded appearance. Peripheral ducts appear pruned as a result of obliteration (examples indicated by arrowheads), and scattered biliary diverticula are seen (example indicated by red overlay).
There is irregular dilatation (green overlay) of intrahepatic bile ducts proximal to a common duct stenosis (arrow). Alternation of strictured and dilated segments creates a beaded appearance. Peripheral ducts appear pruned as a result of obliteration (examples indicated by arrowheads), and scattered biliary diverticula are seen (example indicated by red overlay).
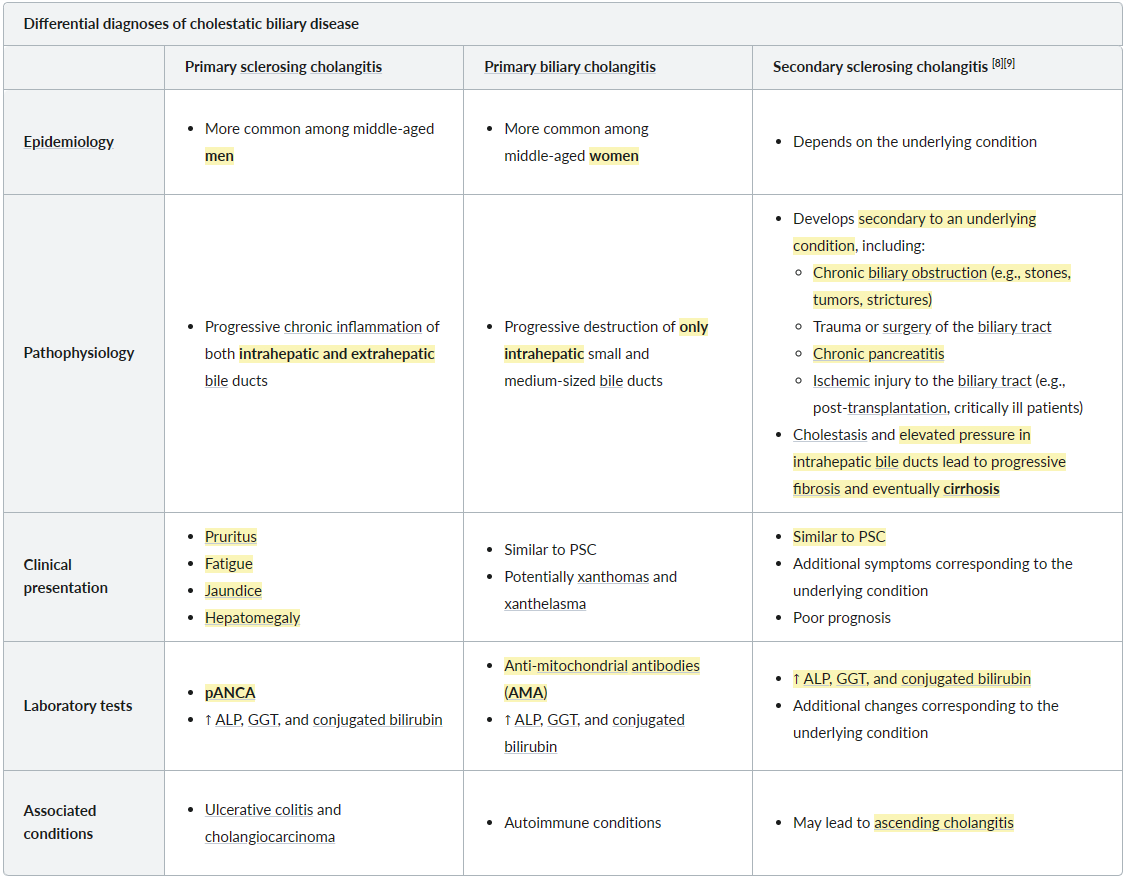
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
Complications
- Cholangiocarcinoma (∼ 10–15% of cases)