Epidemiology
Etiology
- Pathogen: Mumps virus from the Paramyxoviridae family
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Incubation period: 16–18 days
- Prodrome
- Duration: 3–4 days
- Symptoms: low-grade fever , malaise, headache
- Classic course: inflammation of the salivary glands, particularly parotitis
- May initially present with local tenderness, pain, and earache
- Unilateral swelling of the salivary gland (lateral cheek and jaw area); During the course of disease, both salivary glands are usually swollen.
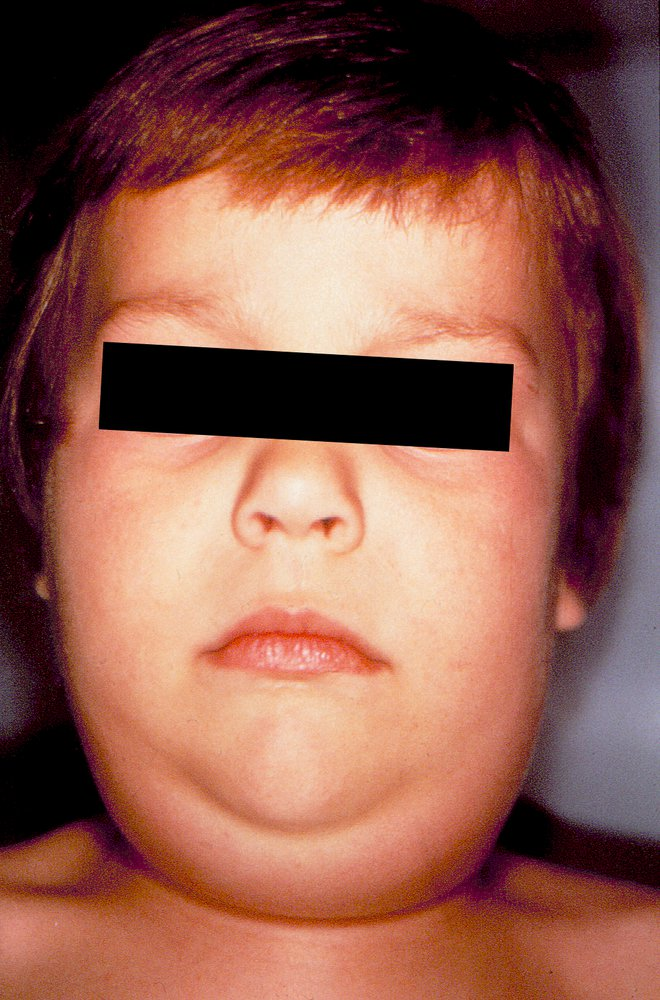
- Redness in the area of the parotid duct
- Possible protruding ears
Complications
Orchitis
- Definition: inflammation of the testis
- Epidemiology: most common complication of mumps in postpubertal male individuals (20–30% in unvaccinated postpubertal and 6–7% in vaccinated males)
- Clinical features
- Sudden onset of fever, nausea, vomiting
- Swollen and tender affected testicle(s); primarily unilateral, although bilateral in ∼ 15% of cases
- Complications: may lead to atrophy and, in rare cases, hypofertility
Other complications
- Aseptic meningitis (1–10% of cases): predominantly mild course and usually no permanent sequelae
- Acute pancreatitis (< 1% of cases)
- ↑ Lipase in addition to ↑ amylase
- Hearing loss (extremely rare)
Diagnostics
Treatment
