- Definition: progressive hereditary dystrophy of the retina or of the photoreceptors and the retinal pigment epithelium
- Epidemiology: early onset (5–30 years)
- Etiology
- Hereditary or spontaneous mutations (> 45 genes are known as triggers; e.g., mutations in the rhodopsin gene)
- Clinical features
- Loss of rods:
- Night blindness
- Peripheral visual field loss
- Loss of cones:
- Decreased central visual acuity (late finding)
- Diagnostics
- Fundoscopy
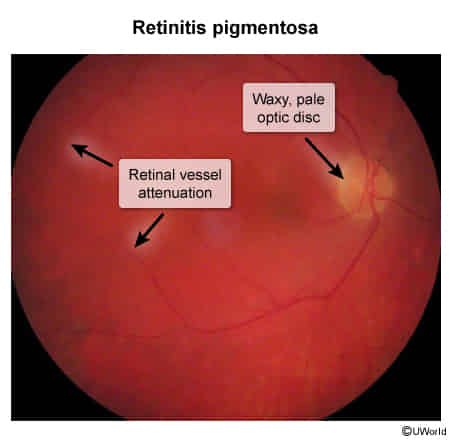
- Retinal vessel attenuation (likely due to altered metabolic demand)
- Optic disc pallor (optic nerve atrophy and gliosis)
- Pigment accumulation (characteristic bone-spicule pattern around vessels)
