Definition: deficiency of superoxide production by polymorphonuclear neutrophils and macrophages
Etiology
X-linked recessive or autosomal recessive inheritance (2:1)
Pathophysiology
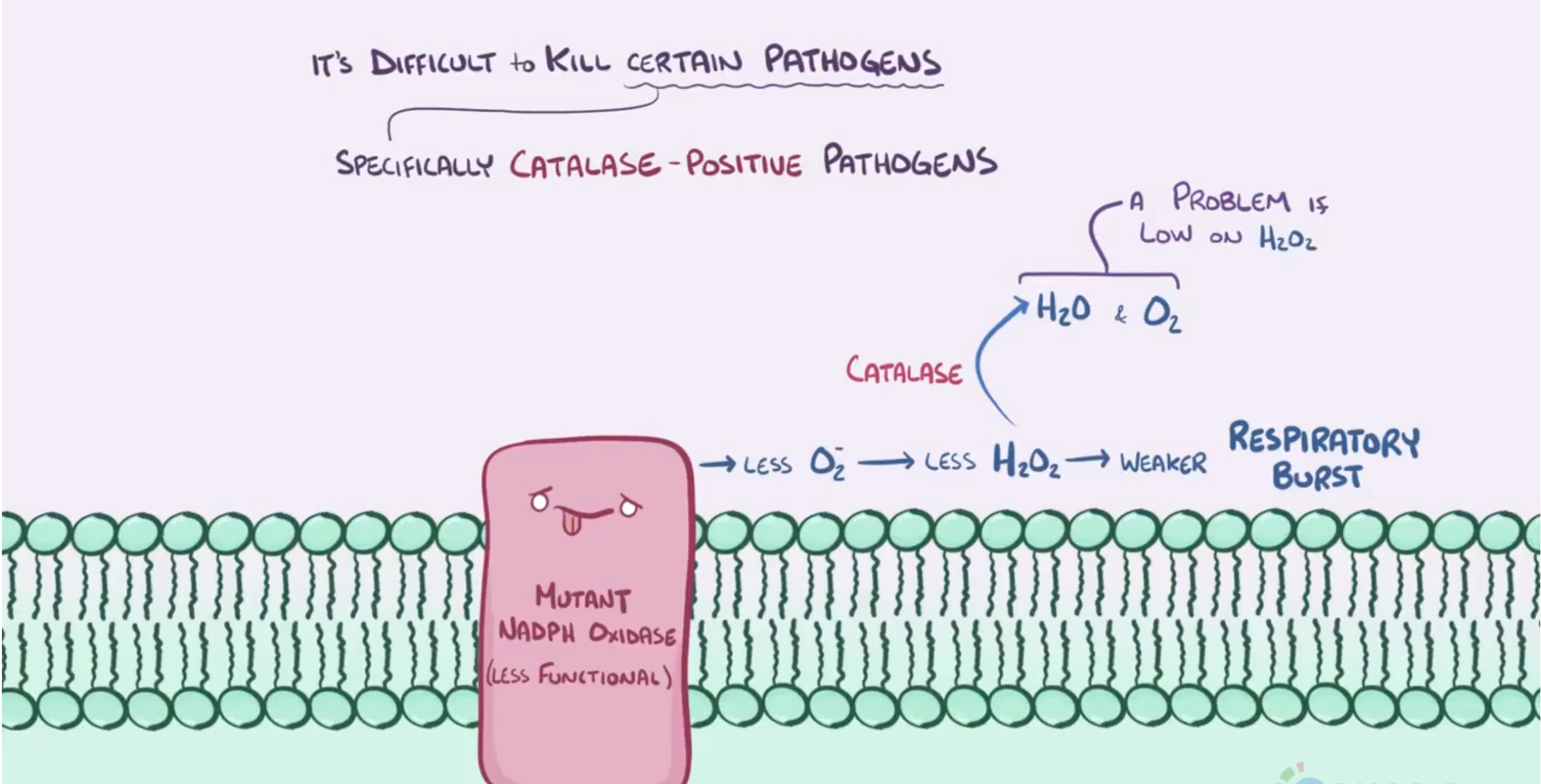 Defective phagocytic nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase that results in:
Defective phagocytic nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase that results in:
- Impaired respiratory burst & ↓ reactive oxygen species → inhibition of phagocytic intracellular killing
Clinical features
- Recurrent, severe infections (chronic skin, lymph node, bone, respiratory, GI, and urinary tract infections) with catalase-positive organisms
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Burkholderia cepacia
- Serratia marcescens
- Nocardia
- Aspergillus
- Lymphadenopathy
- Granulomas of the skin and GI/GU tract
Diagnostics
- Neutrophil assay
- Dihydrorhodamine test (DHR): flow cytometry test showing abnormal NADPH oxidase activity (inability to metabolize dihydrorhodamine to fluorescent product, rhodamine → decreased green fluorescence)
- The DHR assay detects the conversion of DHR (a colorless substance) to rhodamine (fluoresces green) by free radicals produced when the NADPH oxidase pathway is stimulated (eg, by a protein kinase C agonist such as phorbol myristate acetate). In unaffected patients, stimulated cells show increased intensity of fluorescence (ie, rightward shift along the x-axis), indicating appropriate NADPH activity, whereas unstimulated cells remain colorless. In patients with CGD, the stimulated cells show no increased fluorescence (ie, no oxidation of DHR).
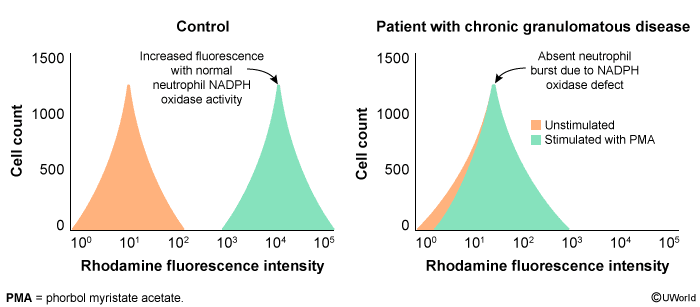
- The DHR assay detects the conversion of DHR (a colorless substance) to rhodamine (fluoresces green) by free radicals produced when the NADPH oxidase pathway is stimulated (eg, by a protein kinase C agonist such as phorbol myristate acetate). In unaffected patients, stimulated cells show increased intensity of fluorescence (ie, rightward shift along the x-axis), indicating appropriate NADPH activity, whereas unstimulated cells remain colorless. In patients with CGD, the stimulated cells show no increased fluorescence (ie, no oxidation of DHR).
- Dihydrorhodamine test (DHR): flow cytometry test showing abnormal NADPH oxidase activity (inability to metabolize dihydrorhodamine to fluorescent product, rhodamine → decreased green fluorescence)
- Nitroblue tetrazolium dye reduction test: negative
Treatment
- Life-long prophylactic antibiotics, e.g., TMP-SMX (for catalase-positive infections)
- IFN-γ therapy
- Bone marrow transplant