| Types | Conductive hearing loss | Sensorineural hearing loss |
|---|---|---|
| Pathophysiology | External or middle ear pathology that disrupts conduction of sound into the inner ear | Inner ear, cochlear, or auditory nerve pathology that impairs neuronal transmission to the brain |
| Clinical features | Hearing improves in noisy environments Volume of voice remains normal because inner ear and auditory nerve are intact Sound normally is not distorted Features of external auditory canal pathology (e.g., cerumen impaction) are present. | Hearing worsens in noisy environments Volume of voice may be loud because nerve transmissions are impaired Tend to lose higher frequencies preferentially, such that sounds may be distorted Often associated with tinnitus Features of external auditory canal pathology are absent. |
| Speech audiometry | No discrimination loss. | Discrimination loss is common. |
| Audiogram | Difference between air and bone conduction | Hearing loss for higher frequency sounds. |
| Impedance audiometry | Elevated acoustic reflex threshold | Normal acoustic reflex threshold |
Etiology
- Conductive Hearing Loss (CHL): Affects Outer/Middle Ear
- Cerumen Impaction: External canal; Common, easily fixed.
- Otitis Media: Middle ear; Fluid/infection, common in kids.
- Otosclerosis: Middle ear (stapes); Bony overgrowth, familial, progressive.
- Tympanic Membrane Perforation: Middle ear (TM); Trauma/infection.
- Cholesteatoma: Middle ear/mastoid; Destructive skin growth, chronic OM.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Middle ear; Leads to negative pressure/effusion.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL): Affects Inner Ear/Nerve
- Presbycusis: Inner ear (cochlea); Age-related, high-frequency loss.
- Noise-Induced: Inner ear (cochlea); Loud noise exposure, 4kHz notch.
- Meniere’s Disease: Inner ear (endolymph); Vertigo, tinnitus, fluctuating low-frequency SNHL.
- Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannoma): CN VIII; Unilateral SNHL, tinnitus. (Bilateral in NF2).
- Ototoxicity: Inner ear (hair cells); Drug-induced (e.g., aminoglycosides, diuretics, cisplatin).
- Viral Infections (e.g., Measles, Mumps): Inner ear; Can cause sudden SNHL.
Subtypes and variants
Presbycusis
- Definition: age-related, sensorineural hearing loss
- Pathophysiology: progressive and irreversible damage of the hair cells of the organ of Corti (especially near the basal turn of the cochlea) that impairs high-frequency hearing
- Epidemiology
- Most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss
- Age 75: > 50%
- Age 90: nearly 100%
- Clinical features
- Progressive bilateral hearing loss, particularly of higher frequencies (using a low-pitched and clear voice to speak with older patients can improve communication)
- Difficulty hearing in noisy, crowded environments.
- Can cause depression and/or isolation
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL)
- Definition: hearing loss due to continuous exposure to sounds > 85 dB (e.g., during construction work, mining, welding) or a single exposure to sounds > 120 dB (e.g., gunshots, jet engines, fireworks)
- Pathophysiology
- Repeated or constant exposure to noise > 85 dB → cumulative microtrauma and irreversible damage to the stereocilia of hair cells of the organ of Corti → sensorineural hearing loss
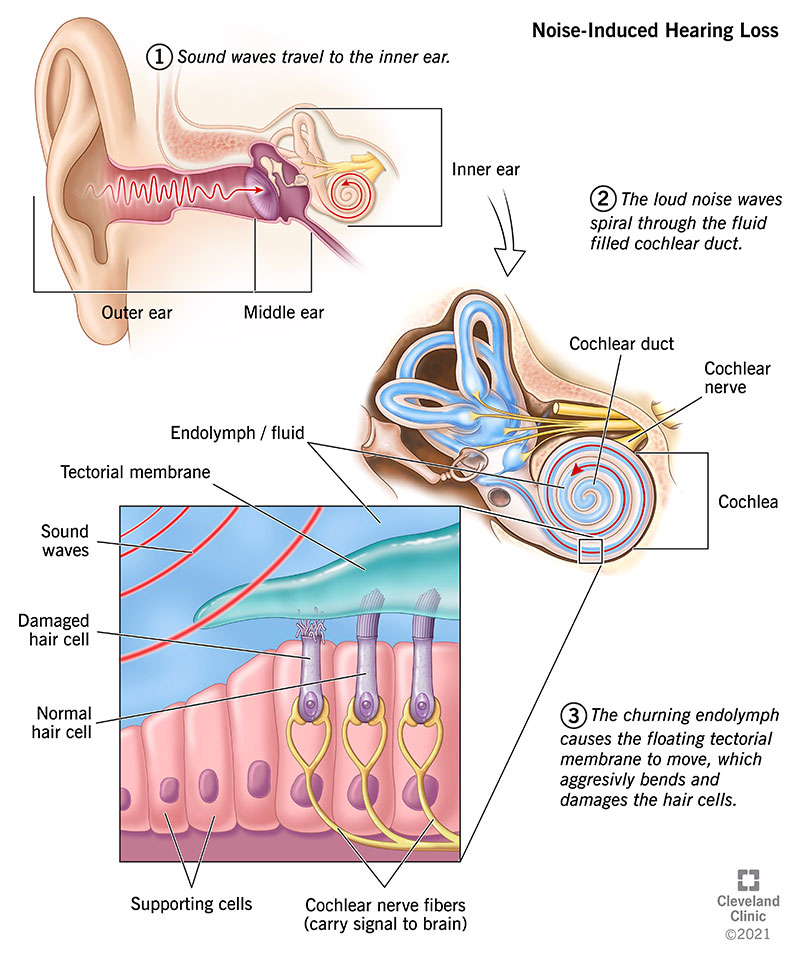
- Sudden noise > 120 dB → tympanic membrane rupture → conductive hearing loss
- Repeated or constant exposure to noise > 85 dB → cumulative microtrauma and irreversible damage to the stereocilia of hair cells of the organ of Corti → sensorineural hearing loss
- Clinical features
- Slowly progressive hearing loss, beginning with loss of high-frequency hearing
- Difficulty hearing in noisy, crowded environments
- Difficulty hearing high-pitched voices (e.g., children’s) occurs as the condition progresses.
- Treatment
- There is no definitive treatment.
- Hearing aids or cochlear implants
- Prevention: hearing protection (i.e., earplugs or earmuffs)