Etiology
- Primary MDS (90% of cases)
- Tends to occur in elderly patients
- Secondary MDS (10% of cases): caused by exogenous bone marrow damage
Pathophysiology
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of hematological cancers in which malfunctioning pluripotent stem cells lead to hypercellularity and dysplasia of the bone marrow. This, in turn, leads to cytopenia of one or more cell lines (thrombocytopenia, erythrocytopenia, leukocytopenia).
Clinical features
- Depending on the affected cell line:
- Erythrocytopenia (70% of cases) → symptoms of anemia
- Leukocytopenia with increased susceptibility to bacterial infections, especially of the skin
- Thrombocytopenia with impaired primary hemostasis → petechial bleeding
- Hepatosplenomegaly (uncommon)
Diagnostics
Tip
MDS is marked by the following:
- ≥1 cytopenias: normal hematopoiesis is impaired due to neoplastic cell replication in the bone marrow; therefore, patients usually present with symptoms of ≥1 cytopenia such as fatigue/dyspnea on exertion (anemia), bleeding/bruising (thrombocytopenia), or infections (leukopenia). Because erythrocyte production is impaired, reticulocyte count will be low despite significant anemia. However, significant extramedullary hematopoiesis does not occur, so hepatosplenomegaly is rare.
- Dysplasia of erythrocytes and neutrophils: peripheral blood smear usually shows normocytic or macrocytic erythrocytes with a variety of abnormalities (eg, oval macrocytes). Neutrophils are typically hypolobulated and hypogranular.
- Normocytic or macrocytic anemia (rarely microcytic) of refractory type (refractory anemia)
- Leukocytopenia and/or thrombocytopenia
- Nucleated RBCs
- Pseudo-Pelger-Huet anomaly
- Neutrophils with hyposegmented nuclei (usually bilobed)
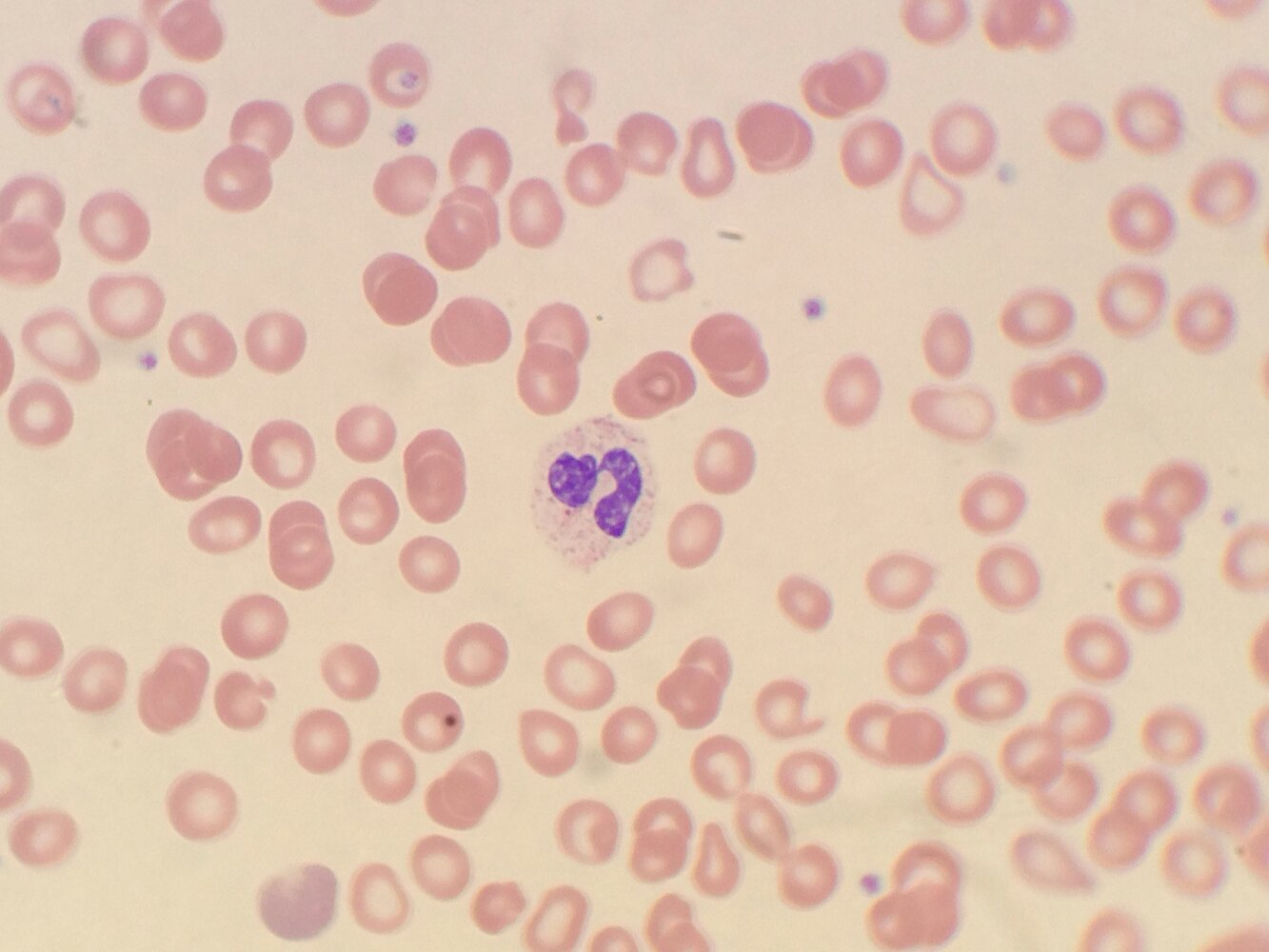
- Seen in peripheral blood smears of patients undergoing chemotherapy
- Neutrophils with hyposegmented nuclei (usually bilobed)
- Bone marrow biopsy: hypercellular, dysplastic bone marrow
- Ringed sideroblasts
- Chromosome analysis: In > 50% of patients, chromosomal aberrations can be detected at the time of diagnosis