Epidemiology
Most common viable autosomal chromosome aberration (∼ 1:700 live births) and most common genetic cause of cognitive impairment
The risk of a Down syndrome pregnancy increases with maternal age.
Incidence at 20 years: ∼ 1:2000
Incidence at 45 years: ∼ 1:30
Etiology
Full trisomy 21 (∼ 95% of cases)
Definition: three complete copies of chromosome 21 are present in all cells, with a total of 47 chromosomes
Pathogenesis: meiotic nondisjunction
Karyotype: ♀: 47,XX,+21 or ♂: 47,XY,+21
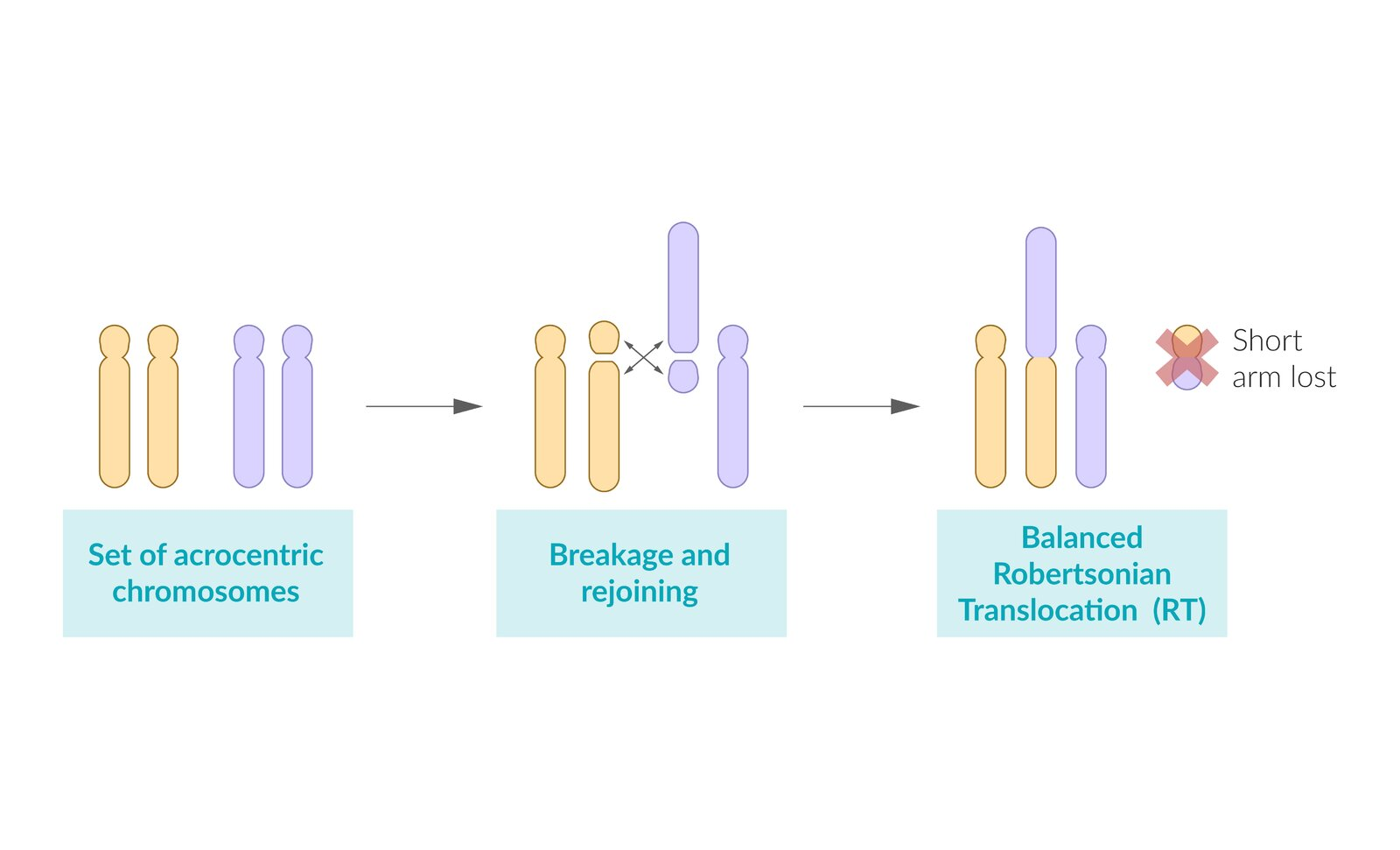
Translocation trisomy 21 (3–4% of cases)
Definition: three copies of chromosome 21 are present, one of which is attached to another chromosome, usually chromosome 14 (less likely attached to chromosomes 13, 15, or 22)
Pathogenesis and karyotype
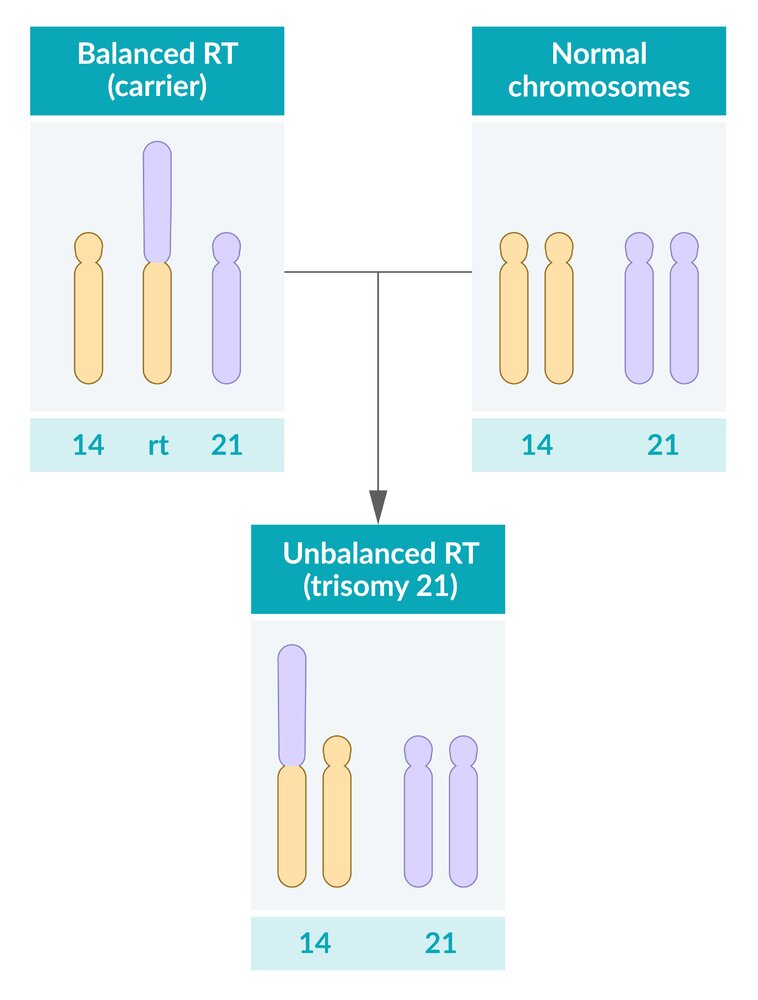
Balanced Robertsonian translocation: translocation of the long arm of chromosome 21 to the long arm of chromosome 14. Not symptomatic, but can affect future generations
Unbalanced Robertsonian translocation: clinical features of trisomy 21 caused by inheritance of a translocation chromosome and a normal chromosome
Mosaic trisomy 21 (1–2% of cases)
Definition: two cell lines are present , the trisomy 21 cell line and the normal cell line
Phenotypic expression varies according to the ratio of healthy to trisomic cells.
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Facial and cranial features (craniofacial dysmorphia)
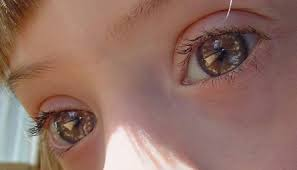
Eyes
Upward-slanting palpebral fissures
Epicanthal folds Ocular hypertelorism: a distance between the eyes greater than the 95th percentile
Brushfield spots: an aggregation of connective tissue in the periphery of the iris, visible as white or grayish-brown spots.
Hypoplastic nasal bones, broad and flat nasal bridge
Extremities, soft tissue, and skeletal features
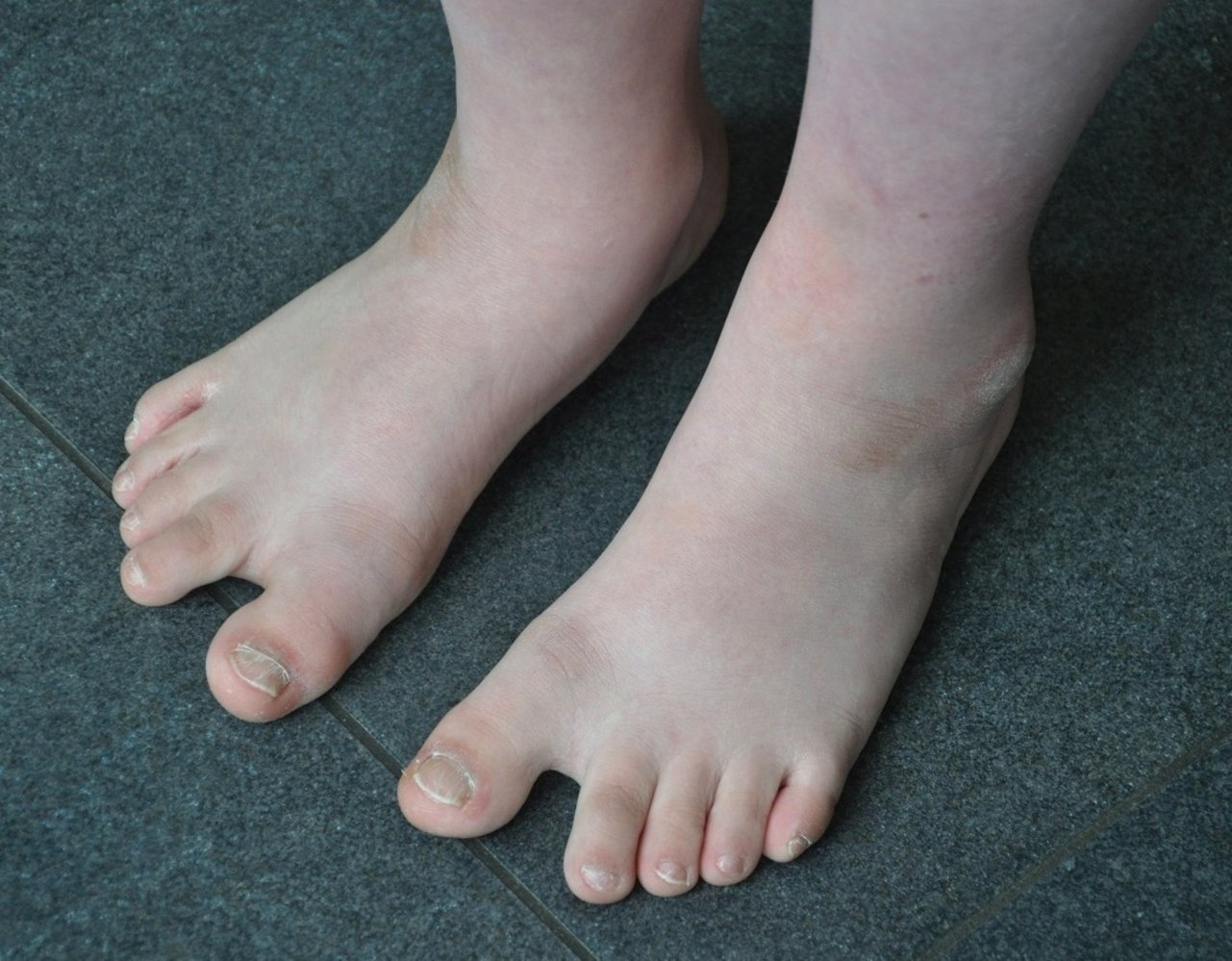
Extremities
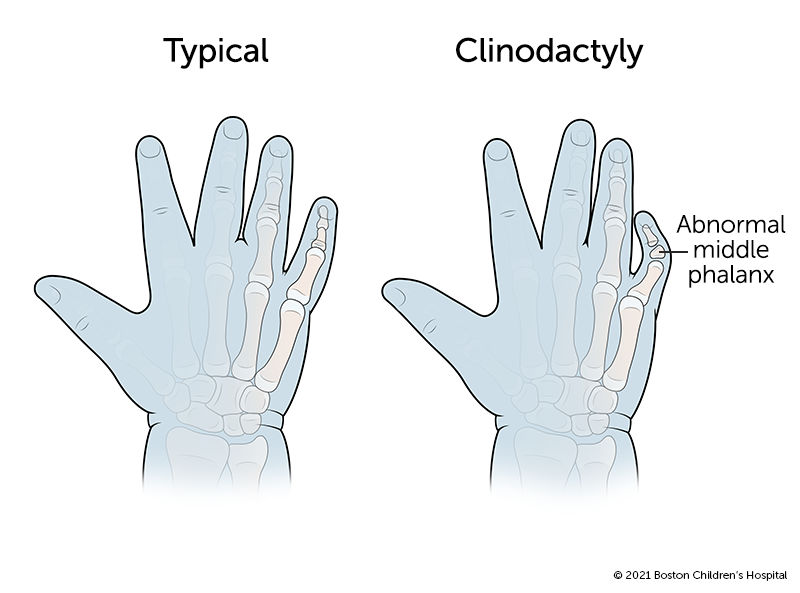
Transverse palmar crease: single crease that runs across the palm, along the metacarpophalangeal joints perpendicular to the fingers Sandal gap : a medial displacement of the first toe leading to a large space between the first and second toes Clinodactyly: abnormal curvature of a finger (typically refers to inward curvature of the 5th finger)
Skeletal features
Atlantoaxial instability
Short stature
Heart: congenital heart defects in ∼ 50% of cases
Atrioventricular septal defect (endocardial cushion defect) is the most common heart defect in individuals with Down syndrome. Ventricular septal defect Atrial septal defects
Gastrointestinal tract
Early-onset Alzheimer disease (The amyloid precursor protein, which generates amyloid beta, is located on chromosome 21.)
Diagnostics
Treatment