Epidemiology
Most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults, especially in African American and Hispanic populations
Etiology
- Heroin use
- HIV infection
- Sickle cell disease
- Massive obesity
- Interferon treatment
- Congenital malformations (e.g., Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome)
Pathophysiology
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: sclerosis of glomeruli → damage and loss of podocytes
Clinical features
Diagnostics
- LM: segmental sclerosis and hyalinosis
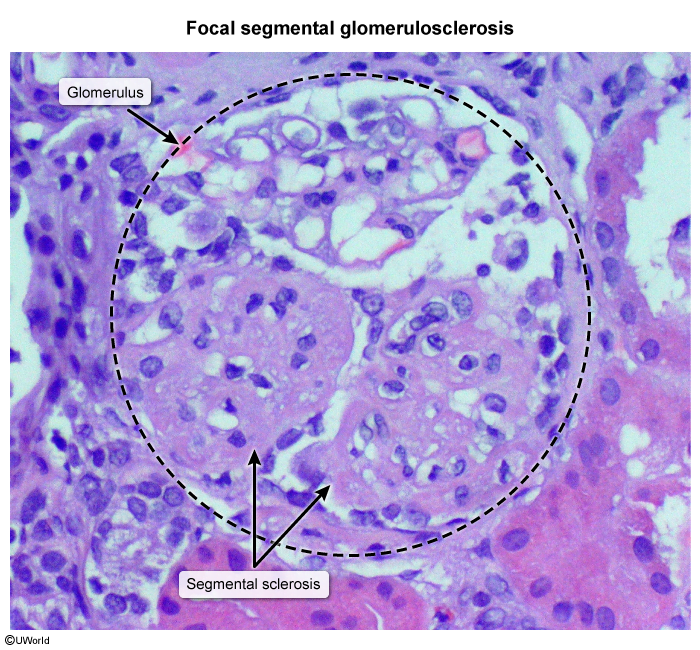
- EM: effacement of podocyte foot processes (similar to minimal change disease)
Treatment
- Initial management: supportive therapy including an RAAS inhibitor (i.e., ACEI or ARB).
- Consider immunosuppressive therapy for all patients with nephrotic syndrome due to FSGS.
- Prednisone