Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Chromosomal nondisjunction → chromosome X monosomy/mosaicism → impaired ovarian development → malfunctioning streak gonads with connective tissue instead of normal germ cells → estrogen and progesterone deficiencies
- Karyotype
- Meiotic nondisjunction (most often in paternal gametes) → complete sex chromosomal monosomy (45,XO; no Barr body)
- Barr body: The inactive X chromosome present in all female somatic cells. Appears as a small, dark-staining spot at the periphery of the nucleus. Consists of tightly-packed, transcriptionally-inactive, heterochromatin.
- Mitotic nondisjunction of an embryonic cell → sex chromosomal mosaicism (45,XO/46,XX) → mild phenotypic expression
- Meiotic nondisjunction (most often in paternal gametes) → complete sex chromosomal monosomy (45,XO; no Barr body)
Clinical features
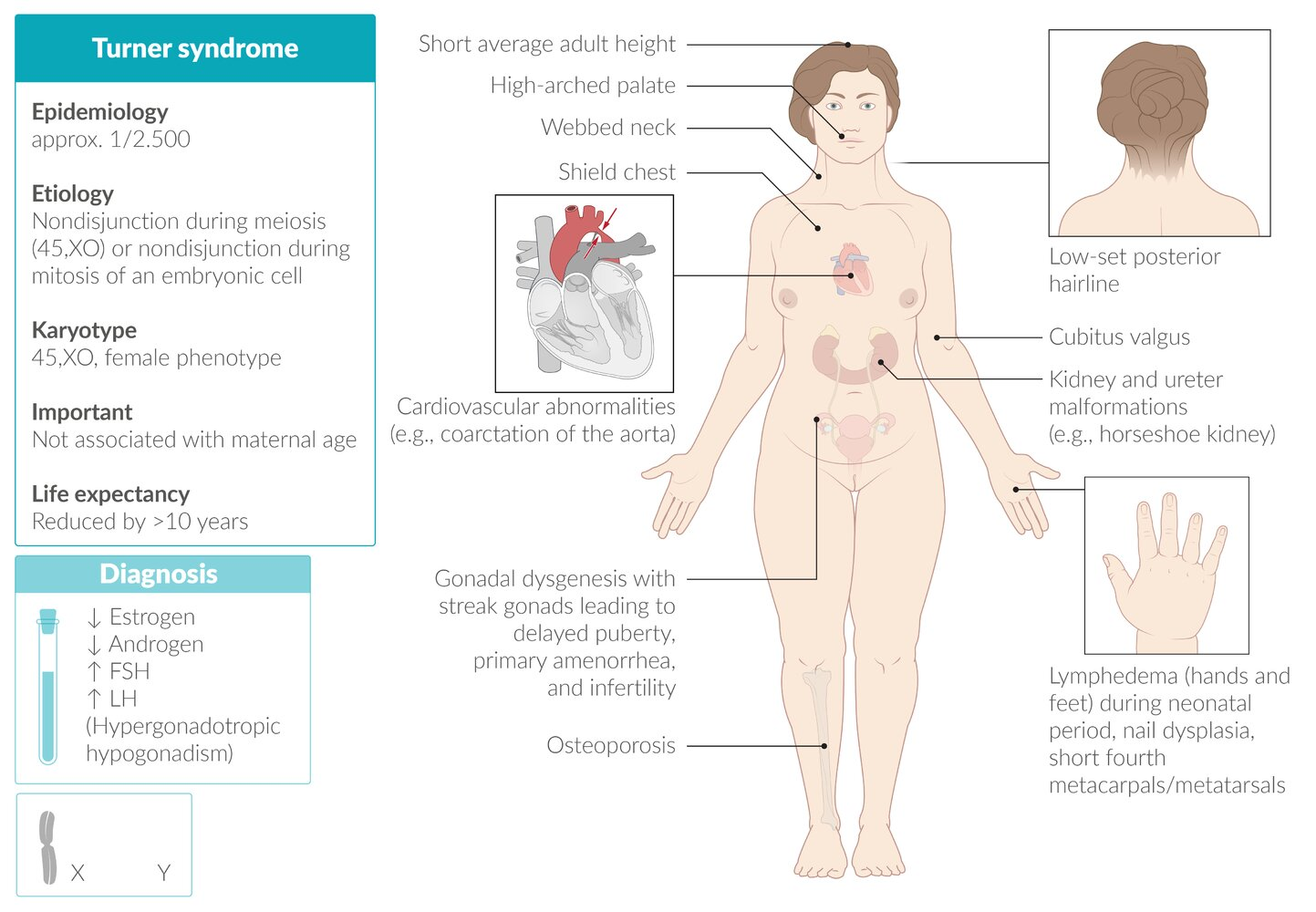
- Lymphatic system abnormalities
- Cystic hygroma
- a congenital lymphatic cyst (macrocystic lymphangioma) in the posterior triangle of the neck caused by malformation and obstruction of the fetal lymphatic system
- Present at birth as a soft, compressible, painless, posterior triangle neck mass
- Can cause dysphagia or airway compromise
- Lymphedema of the hands and feet in the neonatal period
- Cystic hygroma
- Musculoskeletal findings
- Short stature: due to the presence of only one copy of the SHOX (short stature homeobox) gene, normally located on the X chromosome
- Scoliosis are common
- Shield chest: broad chest with widely spaced nipples
- Webbed neck: skin folds along the side of the neck between the mastoid process and the acromion
- Cubitus valgus
- Short fourth metacarpals/metatarsals, nail dysplasia
- High arched palate
- Low-set posterior hairline
- Osteoporosis and pathologic fractures
- Cardiovascular abnormalities
- Bicuspid aortic valve: increased risk of premature aortic stenosis and/or insufficiency
- As a result of valve calcification.
- Coarctation of the aorta with brachial-femoral delay
- Aortic dissection and rupture
- Hypertension (even in children)
- Bicuspid aortic valve: increased risk of premature aortic stenosis and/or insufficiency
- Other disorders
- Gonadoblastoma (especially in patients with 45,XO/46,XY mosaicism)
- Malformations of the kidney and ureters (especially horseshoe kidney)
- Hashimoto thyroiditis
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Tip
Most patients with Turner syndrome have normal intelligence.