Epidemiology
- More common in adults than children
-
Since introduction of the Hib vaccine, incidence in children has significantly decreased and incidence in adults has risen via other causal pathogens.
-
- Peak incidence in children: 6–12 years
Etiology
- Traditionally: Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- Most cases now involve:
Pathophysiology
Mnemonic
The hallmarks of epiglottitis are the three Ds: Dysphagia, Drooling, and Distress.
- Drooling is due to pain in swallowing.
Clinical features
- Respiratory distress (inspiratory retractions, cyanosis)
- Inspiratory stridor
- Tripod position: eases respiration as the airway diameter is increased by leaning forward and extending the neck in a seated position
- Sore throat
- Dysphagia and odynophagia
- Drooling
- Muffled voice (i.e., resembling a “hot-potato” voice) with painful speech
- Acute onset of high fever (39–40°C; 102–104°F)
- Toxic appearance
- Restlessness and/or anxiety
Diagnostics
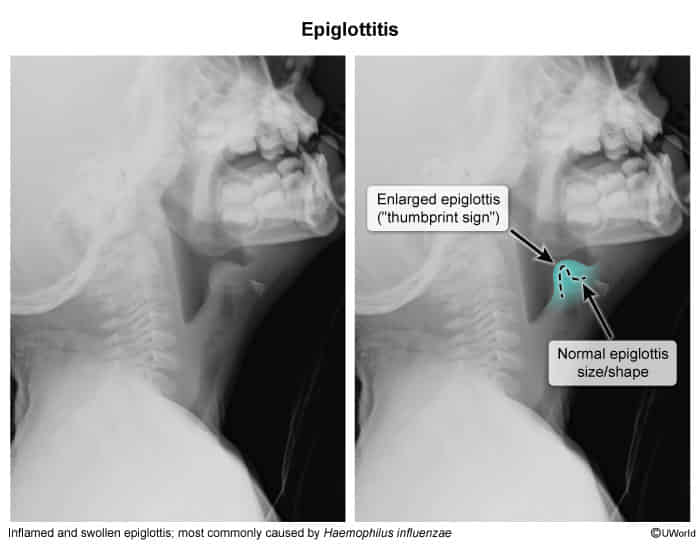
Soft-tissue lateral neck x-ray
- Thumb sign (also referred to as thumbprint sign): enlarged epiglottis and supraglottic narrowing