Epidemiology
Etiology
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- INO is common in individuals with MS between 20–50 years of age
- Typically bilateral
- Hemorrhage (common cause in older patients)
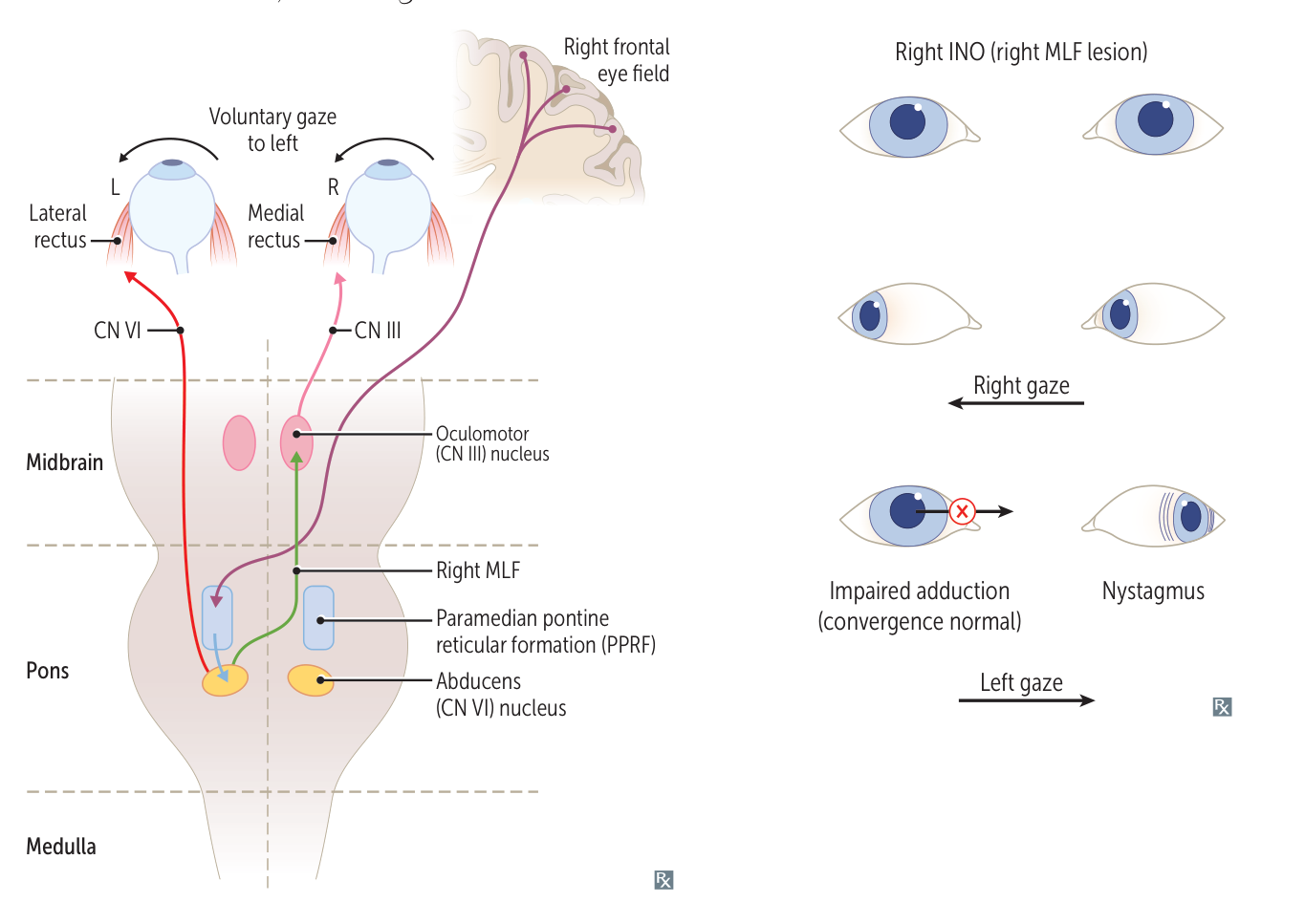
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Mnemonic
- INO = Ipsilateral adduction failure, Nystagmus Opposite.
- The paramedian pontine reticular formation in the pons helps to coordinate horizontal eye movements. A lesion here produces a contralateral gaze deviation known as a gaze palsy in which the eyes are fixed to the opposite side as the lesion.
- Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation = PeePers Run From the lesion.