Reservoir
Water and humid conditions (e.g., hot tubs, contaminated contact lens solution)
Characteristics
- Lophotrichous flagella (motile)
- Aerobic
- Catalase positive
- Oxidase positive
- Produces pyocyanin (blue-green pigment) → formation of blue‑green pus in infection
- Sweet odor when grown in culture
- Nonlactose fermenting
Virulence factors and resistances
- Mucoid polysaccharide capsule → biofilm formation
- Conversion to a mucoid phenotype that produces an alginate polysaccharide, which strengthens biofilm structure and aids in the inhibition of opsonization and phagocytosis
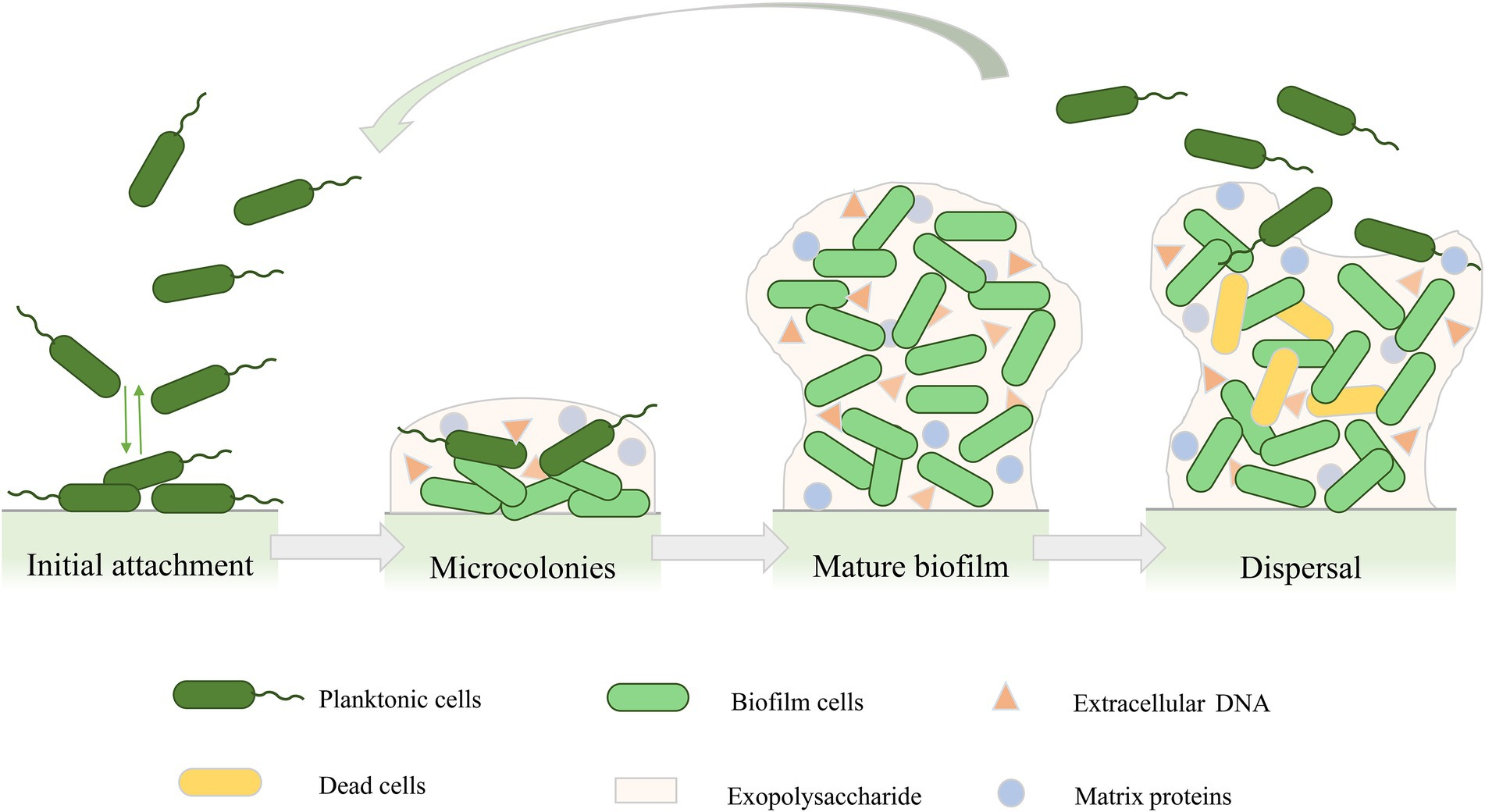
- Conversion to a mucoid phenotype that produces an alginate polysaccharide, which strengthens biofilm structure and aids in the inhibition of opsonization and phagocytosis
- Endotoxin → fever, shock
- Exotoxin A: inactivates EF-2 → inhibition of protein synthesis → death of host cells
- Phospholipase C: degrades cell membranes
Diseases
- Upper respiratory infections
- Nosocomial pneumonia (e.g., ventilator associated pneumonia)
- Chronic pneumonia in individuals with cystic fibrosis
- Skin infections
- Nosocomial burn wound infections
- Hot tub folliculitis
- Ecthyma gangrenosum in immunocompromised individuals
- Corneal ulcers and/or keratitis in contact lens wearers or after eye injuries
- Malignant otitis externa in elderly individuals with diabetes
- Endocarditis or osteomyelitis in individuals who use IV drugs
- Nosocomial UTI
- Sepsis
Diseases in immunocompetent people
- Respiratory tract infections in people with underlying conditions:
- Cystic fibrosis patients (most common)
- Bronchiectasis
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- External ear infections:
- Swimmer’s ear (otitis externa), especially in frequent swimmers
- Hot tub folliculitis
- Eye infections:
- Contact lens-related keratitis
- Corneal infections after trauma or surgery
- Skin and soft tissue infections:
- Burns
- Deep puncture wounds, especially if contaminated with water
- Infections after surgery in moist areas
- Healthcare-associated infections:
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia
- Catheter-associated urinary tract infections
- Post-surgical wound infections