Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory disease of unknown origin, which most commonly affects individuals between 30–60 years of age and is characterized by different types of lesions involving the skin and mucosa.
Epidemiology
Etiology
- Associated with hepatitis C infections
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Cutaneous lichen planus
- 5 “Ps”: pruritic, purple/pink, polygonal, papules & plaques
- Lesions
- Purple, well-demarcated papules or plaques
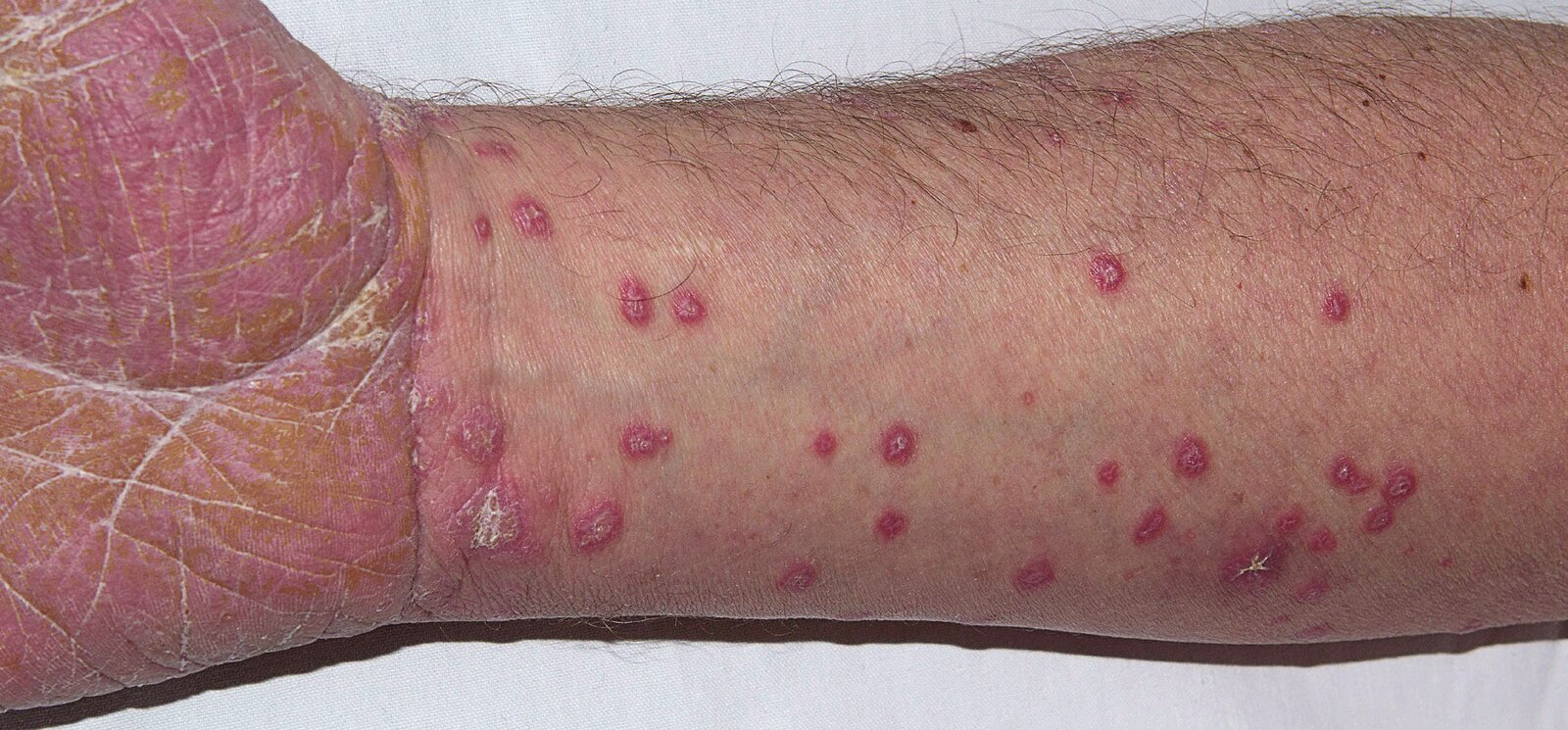
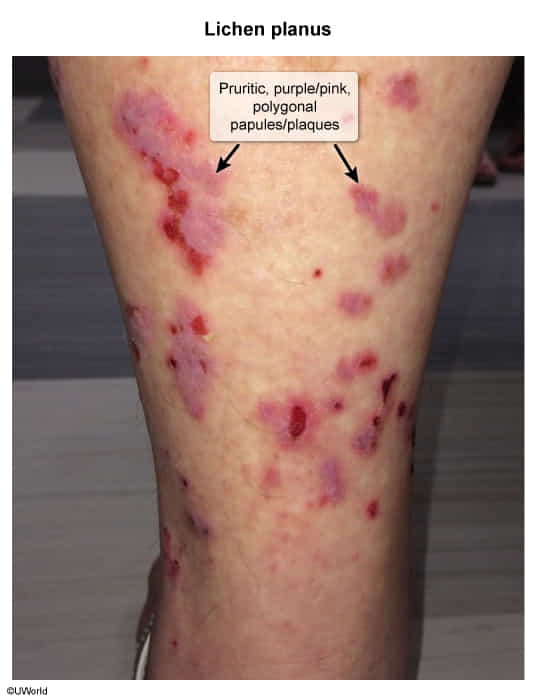
- Planar (flat-topped)
- Polygonal, irregular borders
- Pruritic, often severe
- Wickham striae: white, reticular lines on the surface of mucosal lesions
- Purple, well-demarcated papules or plaques
- Distribution pattern
- Affects the extremities, especially the ankles and flexor wrists, as well as the trunk
- Bilateral, symmetrical distribution
Oral lichen planus
Diagnostics
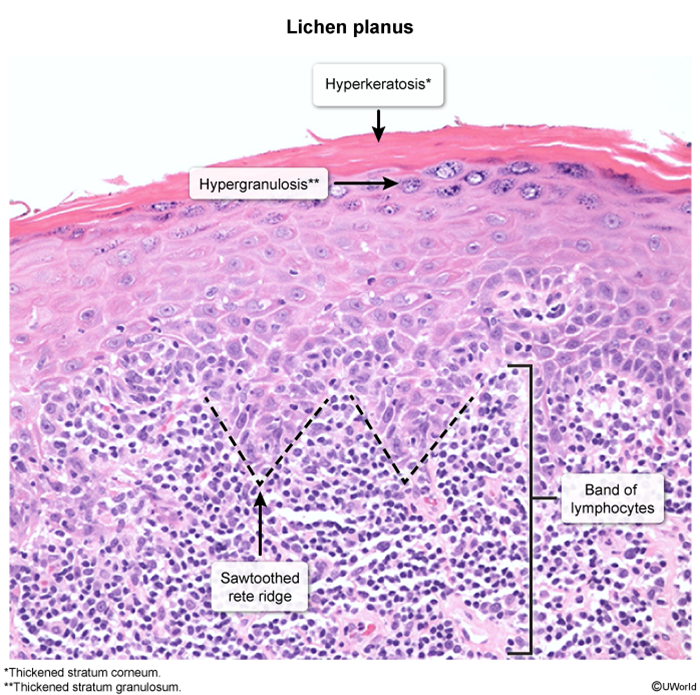
Pathology
- Hyperkeratosis
- Wedge-shaped hypergranulosis
- Irregular acanthosis (saw-tooth appearance)
- Band-like lymphocytic infiltrate at the dermal-epidermal junction
Differential Diagnostics
Psoriasis vs Lichen planus
- Immune Mechanism:
- Lichen Planus primarily involves CD8+ T cells targeting basal keratinocytes, creating a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate at the dermo-epidermal junction and interface dermatitis
- Psoriasis is driven by Th17/Th1 cells and involves complex cytokine cascades (IL-17, IL-22, TNF-α), affecting the entire epidermis and leading to neutrophil recruitment
- Keratinocyte Response:
- Lichen Planus shows normal to slow keratinocyte turnover, allowing time for proper differentiation, resulting in hypergranulosis (increased keratohyalin granules)
- Because of immune stress?
- Psoriasis exhibits extremely rapid keratinocyte turnover (3-5 days vs normal 28-30 days), preventing proper differentiation, leading to loss of granular layer and parakeratosis

| Feature | Psoriasis | Lichen Planus |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Red plaques with silvery scales | Flat-topped, purple papules with white lines |
| Common Sites | Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, nails | Wrists, ankles, oral/genital mucosa |
| Itchiness | Often mild or absent | Frequently intense |
| Nail Involvement | Common (pitting, onycholysis) | Possible (thinning, ridging) |
| Mucosal Involvement | Rare | Common, especially mouth |
| Auspitz Sign | Present | Absent |
| Histopathology | Acanthosis, parakeratosis, Munro abscesses | Saw-tooth lymphocytes, Civatte bodies |
| Associated Conditions | Psoriatic arthritis, metabolic syndrome | Hepatitis C, other autoimmune diseases |