Epidemiology
Etiology
Melanocyte is in the stratum basale of the skin, i.e. the dermoepidermal junction
Risk factors for cutaneous melanoma
- UV radiation exposure
- Light skin types
- Genetic mutations, including:
- BRAF gene mutations
- Seen in 50% of melanomas
- V600E mutation (most common): an activating mutation in the BRAF gene that substitutes glutamic acid for valine at amino acid position 600
- CDKN2A gene mutations
- BRAF gene mutations
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
ABCDE criteria
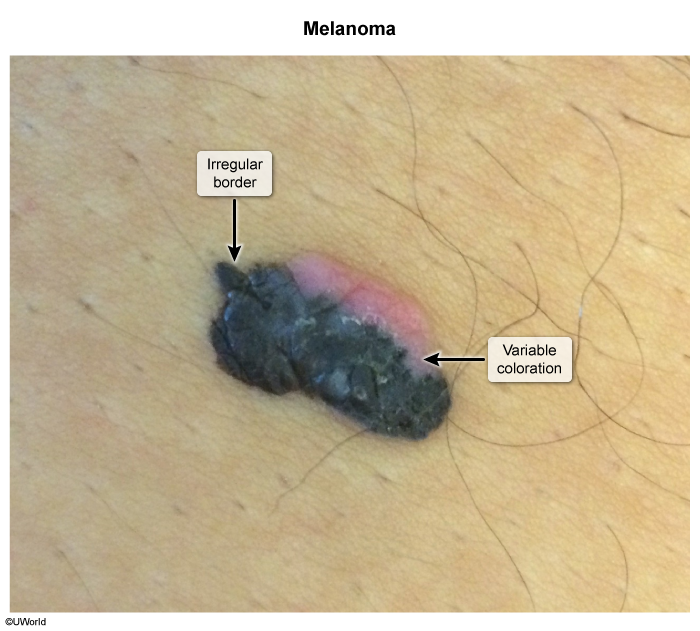
- A = Asymmetry
- B = Border (irregular border with indistinct margins)
- C = Color (variegated pigmentation within the same lesion)
- Red areas are due to vessel ectasia (dilation) and local inflammation.
- Brown or black, flared areas along the border are due to advancing, neoplastic melanocytes.
- White and gray areas appear when cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize tumor antigens (eg, melan-A) and induce apoptosis, leading to malignant melanocyte regression (cleared patches).
- D = Diameter > 6 mm
- E = Evolving (a lesion that changes in size, shape, or color over time)
Subtypes
- Superficial Spreading: Most common type (~70%). It has a prolonged radial (horizontal) growth phase before invading vertically.
- Nodular: Second most common type (~15%). It is aggressive with early vertical growth, presenting as a dark, dome-shaped papule or nodule.
- Lentigo Maligna: Occurs in chronically sun-exposed areas, typically in the elderly. It has a long radial growth phase.
- Acral Lentiginous: Most common type in dark-skinned individuals. It appears on the palms, soles, and under the nails (subungual). This subtype is aggressive.
Lentigo maligna
- Core Concept: Melanoma in situ on chronically sun-damaged skin.
- Characterized by a prolonged radial (horizontal) growth phase, where atypical melanocytes are confined to the epidermis and contiguous adnexal structures.
- Can progress to invasive lentigo maligna melanoma when neoplastic cells breach the basement membrane and enter the dermis (vertical growth phase).
- Patient Profile: Elderly pt with a Hx of extensive sun exposure.
- Classic Location: Face, neck, scalp, dorsal forearms.
- Clinical Presentation: A large, flat (macule/patch), slow-growing lesion with irregular borders and variegated color (tan, brown, black).
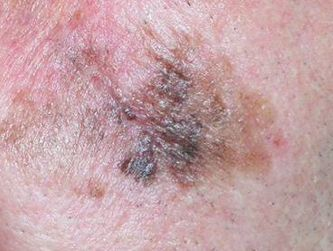
- High-Yield Sign of Progression: The development of a nodule or papule within the flat lesion signifies transformation into invasive lentigo maligna melanoma.
- Diagnosis & Tx:
- Dx: Biopsy (excisional preferred).
- Tx: Surgical excision.
- Prognosis: Excellent if treated as in situ disease. Prognosis worsens with invasion, determined by Breslow depth.
Diagnostics
- Histopathology revealed poorly differentiated cells with abundant mitotic activity and necrosis.
- Breslow depth: Distance from stratum granulosum to deepest tumor cells

- Breslow depth: Distance from stratum granulosum to deepest tumor cells
- Immunostaining was positive for S-100 (a protein expressed in cells derived from the neural crest such as melanocytes) and HMB-45 (a marker for immature melanosomes found in melanocytic tumors) indicating melanoma.
- S-100 is also expressed in Schwannoma