Epidemiology
Etiology
- Taenia solium (pork tapeworm)
- Fecal-oral: eggs are ingested from contaminated water or vegetables
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Often asymptomatic
- Symptoms caused by cysticerci accumulation in subcutaneous tissue, muscles, brain, spinal cord, and eyes
- Palpable subcutaneous cysts
- Myalgia
- Neurocysticercosis (cysticerci-containing cysts in the CNS): increased intracranial pressure, neurological deficits, seizures
- Ocular cysticercosis: eye pain, loss of visual acuity or vision in one eye
Diagnostics
- Initial test: CBC may show eosinophilia
- Additional testing
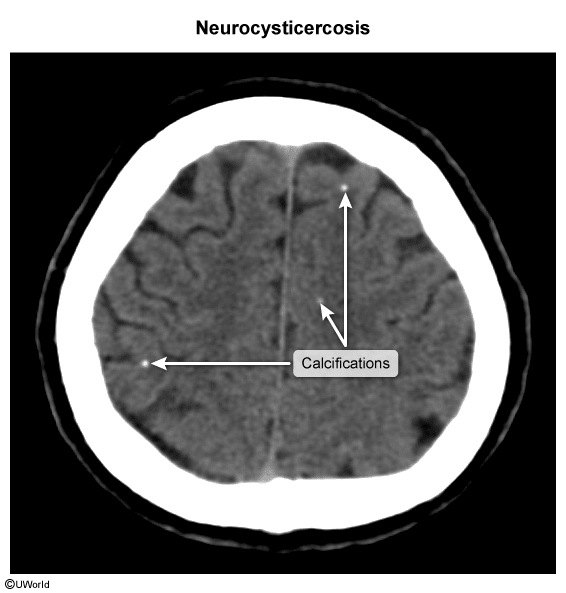
- Imaging: cerebral MRI/CT showing multiple, small (< 1 cm) cystic lesions with a membranous wall and an invaginated scolex (“dot sign”)
- Viable cysts: round, hypodense ± scolex
- Nonviable cysts: calcified nodules
- Lumbar puncture: ↑ protein, ↓ glucose, mononuclear pleocytosis
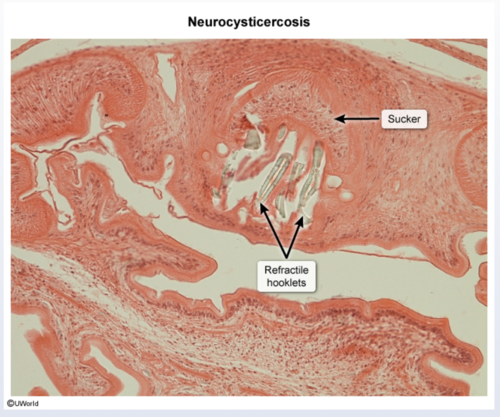
- Biopsy: Cysts with an invaginated scolex during earlier stages
Treatment

