Spinal stenosis is characterized by the narrowing of the central spinal canal, intervertebral foramen, and/or lateral recess within the cervical spine, thoracic spine, or lumbar spine, resulting in progressive nerve root compression.
Epidemiology
Etiology
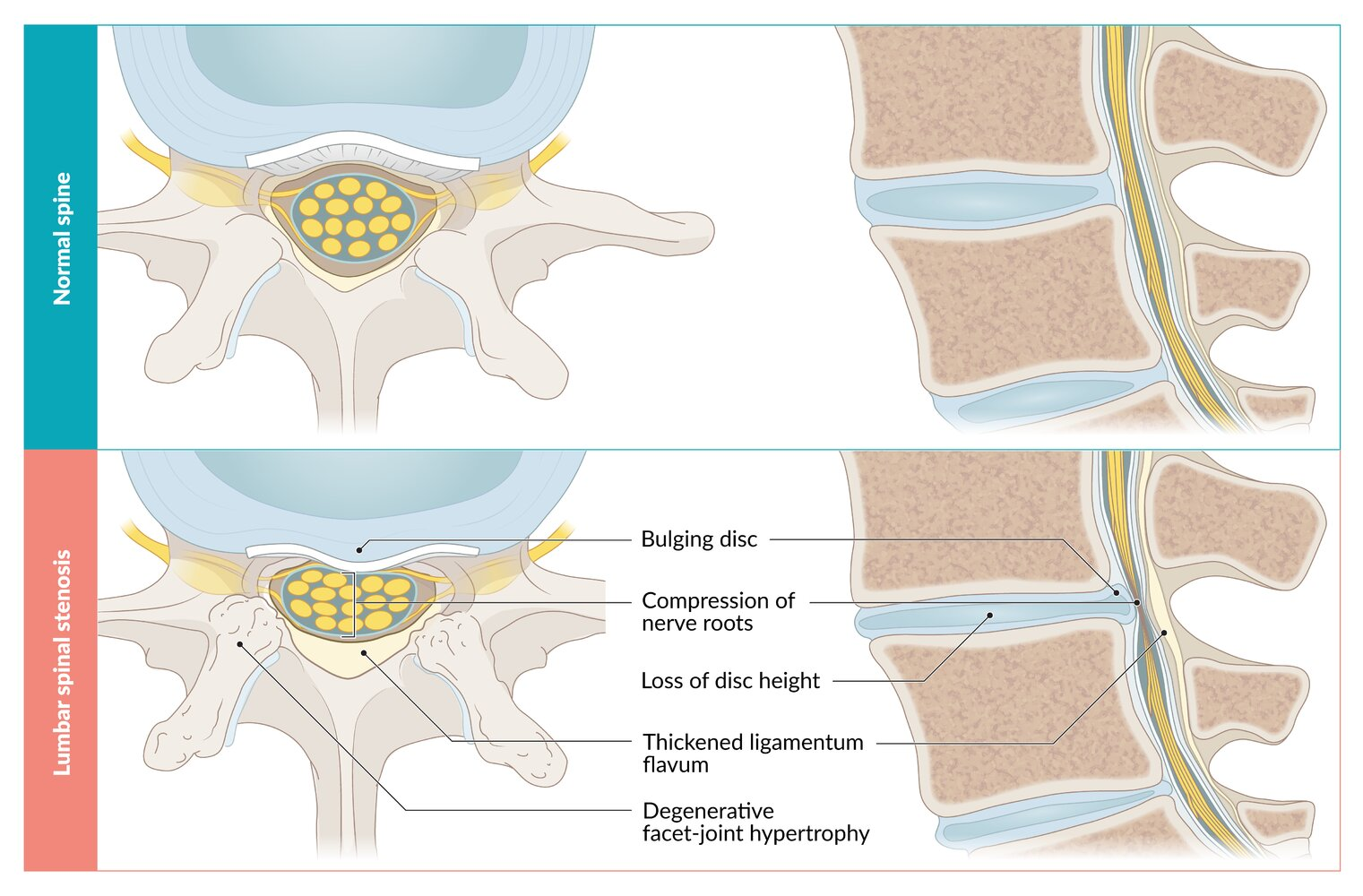
- Degenerative joint disease (most common)
- Spondylolisthesis (anterior or posterior)
- Disk space narrowing (e.g., due to osteoarthritis and/or degenerative disk disease)
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Load-dependent lower back pain that worsens with walking
- Neuropathic claudication: a group of neuropathic symptoms affected by postural changes
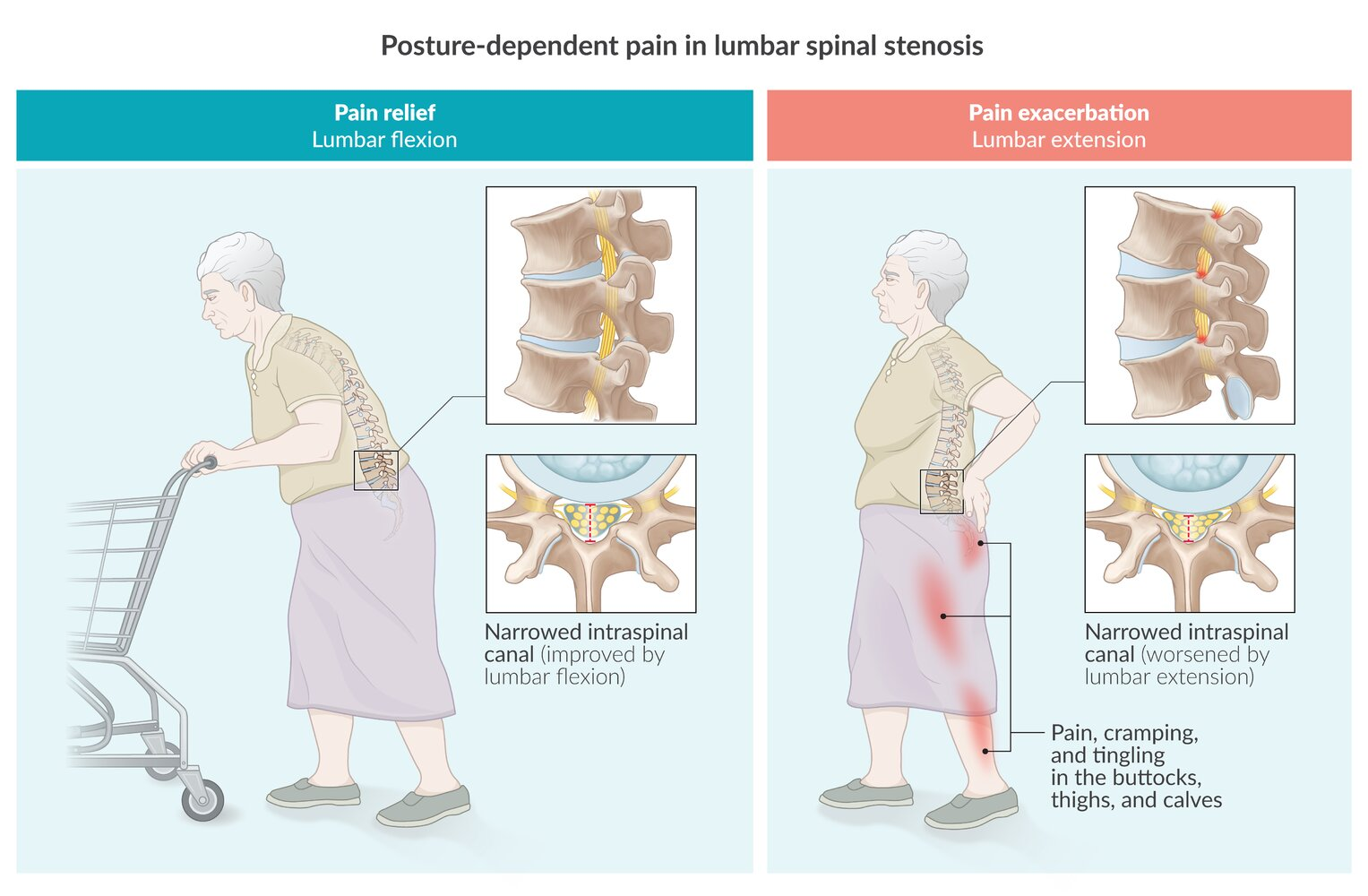
- Worsens with lumbar extension (e.g., walking, prolonged standing)
- Relieved by lumbar flexion (e.g., sitting, laying down, cycling)