- Overview
- Network of proteins and polysaccharides secreted by cells.
- Provides structural support, regulates cell signaling, adhesion, migration, and proliferation.
- Composed of:
- Structural Proteins (Collagen, Elastin)
- Adhesive Glycoproteins (Fibronectin, Laminin)
- Proteoglycans & Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Structural Proteins
1. Collagen
Structure
- A collagen molecule is a protein with a repeating amino acid sequence (Gly-X-Y)n.
- The first amino acid of this triplet is glycine (collagen is comprised of ⅓ glycine).
- Position X: most commonly proline (also common: lysine, hydroxylysine)
- Position Y: most commonly hydroxyproline (also common: hydroxylysine, lysine)
Collagen Synthesis & Processing
- 1. Synthesis (in RER):
- Synthesis of preprocollagen (α-chains).
- 2. Hydroxylation (in RER): t
- Hydroxylation of specific proline and lysine residues.
- Requires prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase.
- Cofactor: Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Deficiency → Scurvy.
- Purpose: To add hydroxyl (-OH) groups to proline and lysine. These groups are essential for forming the hydrogen bonds that stabilize the triple helix structure in the next step. Without hydroxylation, the helix is unstable.
- 3. Glycosylation (in RER):
- Glycosylation of hydroxylysine residues.
- Formation of procollagen (triple helix) from 3 α-chains. Problems with triple helix formation → Osteogenesis Imperfecta.
- Purpose: Glycosylation helps correctly align the three α-chains. The subsequent formation of the procollagen triple helix creates a stable, soluble, and transportable precursor molecule ready for secretion.
- 4. Exocytosis (to Extracellular Space):
- Procollagen is transported out of the cell.
- 5. Proteolytic Processing (Extracellular):
- Cleavage of disulfide-rich terminal regions of procollagen by procollagen peptidases.
- Forms insoluble tropocollagen. Problems with cleavage → a form of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.
- Purpose: To cleave the terminal propeptides, converting soluble procollagen into insoluble tropocollagen. This insolubility is crucial, as it allows the tropocollagen molecules to self-assemble into fibrils. The propeptides prevent this aggregation from happening inside the cell.
- 6. Cross-linking (Extracellular):
- Reinforcement of multiple tropocollagen molecules by covalent lysine-hydroxylysine cross-linkage.
- Catalyzed by lysyl oxidase.
- Cofactor: Copper (Cu2+). Deficiency or problems with lysyl oxidase → Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Menkes Disease.
Drawing 2026-01-15 21.36.00.excalidraw
⚠ Switch to EXCALIDRAW VIEW in the MORE OPTIONS menu of this document. ⚠ You can decompress Drawing data with the command palette: ‘Decompress current Excalidraw file’. For more info check in plugin settings under ‘Saving’
Excalidraw Data
Text Elements
Vitamin C Deficiency
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Ehlers-Danlos
Menkes Disease
Embedded Files
58c7f467e25b3598403f962e309bd81ecd1fe2c6: Pasted Image 20260115213631_102.png
Link to original
Types
- Type I (Mnemonic: b”one”)
- Location: Bone, Skin, Tendon, dentin, fascia, cornea, late wound repair. Scar tissue.
- Function: Most abundant type. Provides high tensile strength.
- Pathology: Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Characterized by brittle bones (“brittle bone disease”), blue sclerae, hearing loss, and dental imperfections.
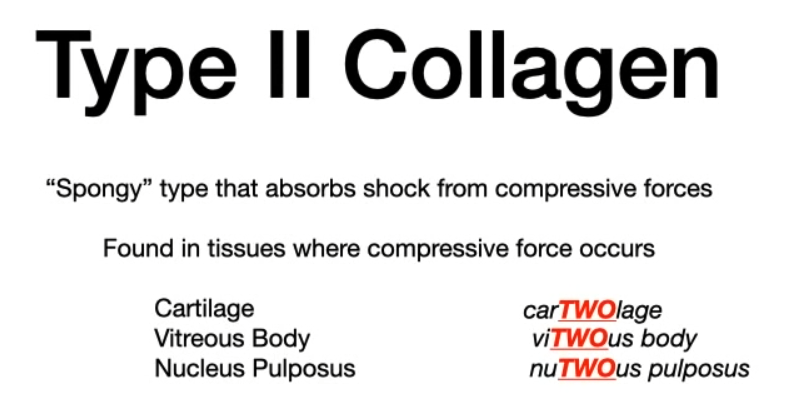
- Type II (Mnemonic: car”two”lage)
- Location: Cartilage (hyaline, elastic), vitreous body, nucleus pulposus.
- Function: Provides resistance to compression.
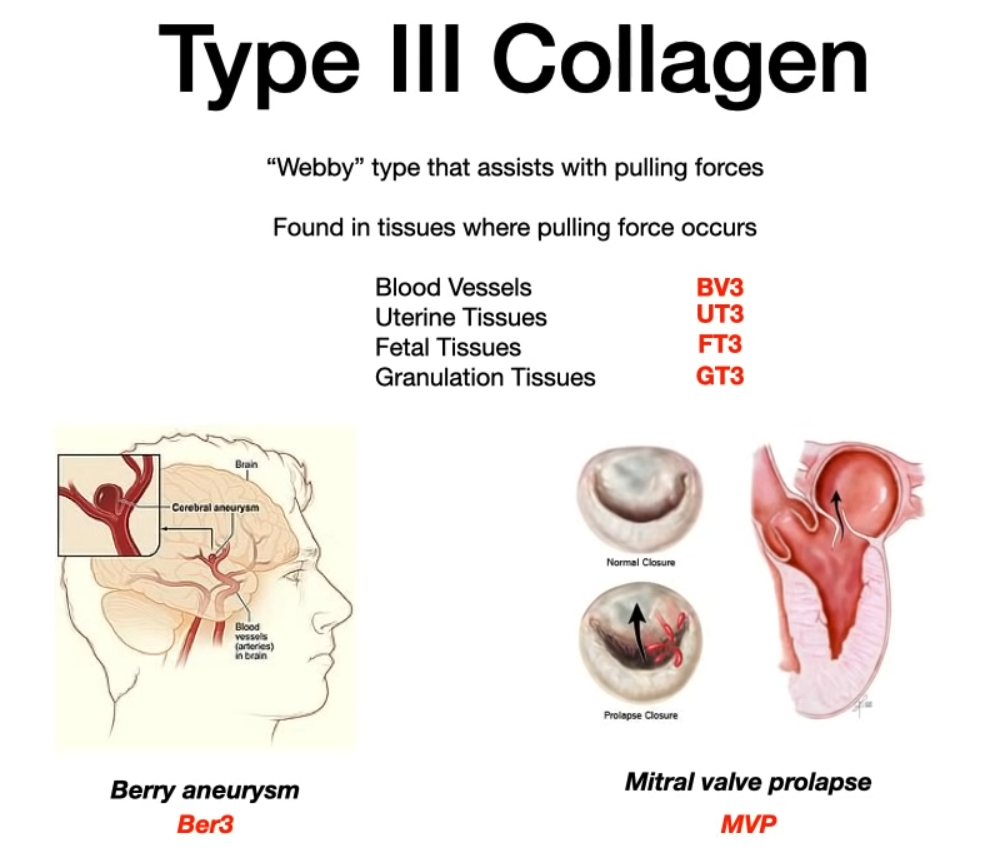
- Type III (Mnemonic: “ThreE D” for Ehlers-Danlos)
- Location: Reticulin fibers. Found in skin, blood vessels, uterus, fetal tissue, granulation tissue (early wound repair).
- Function: Provides pliable, distensible support.
- Pathology: Deficient in the vascular type of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Presents with fragile tissues, easy bruising, and risk of arterial or organ rupture.
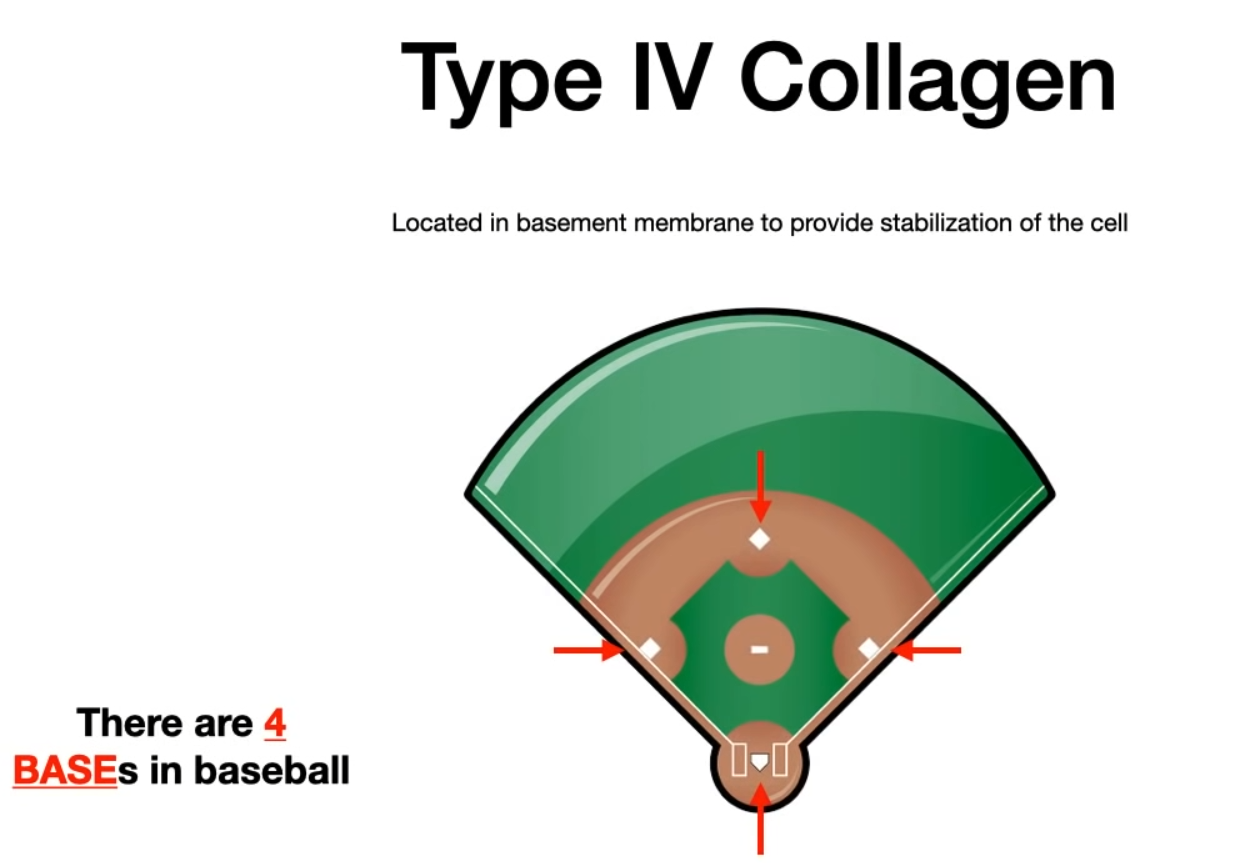
- Type IV (Mnemonic: “Four on the Floor”)
- Location: Basement membrane, basal lamina, lens.
- Function: Forms a sheet-like network for support and filtration.
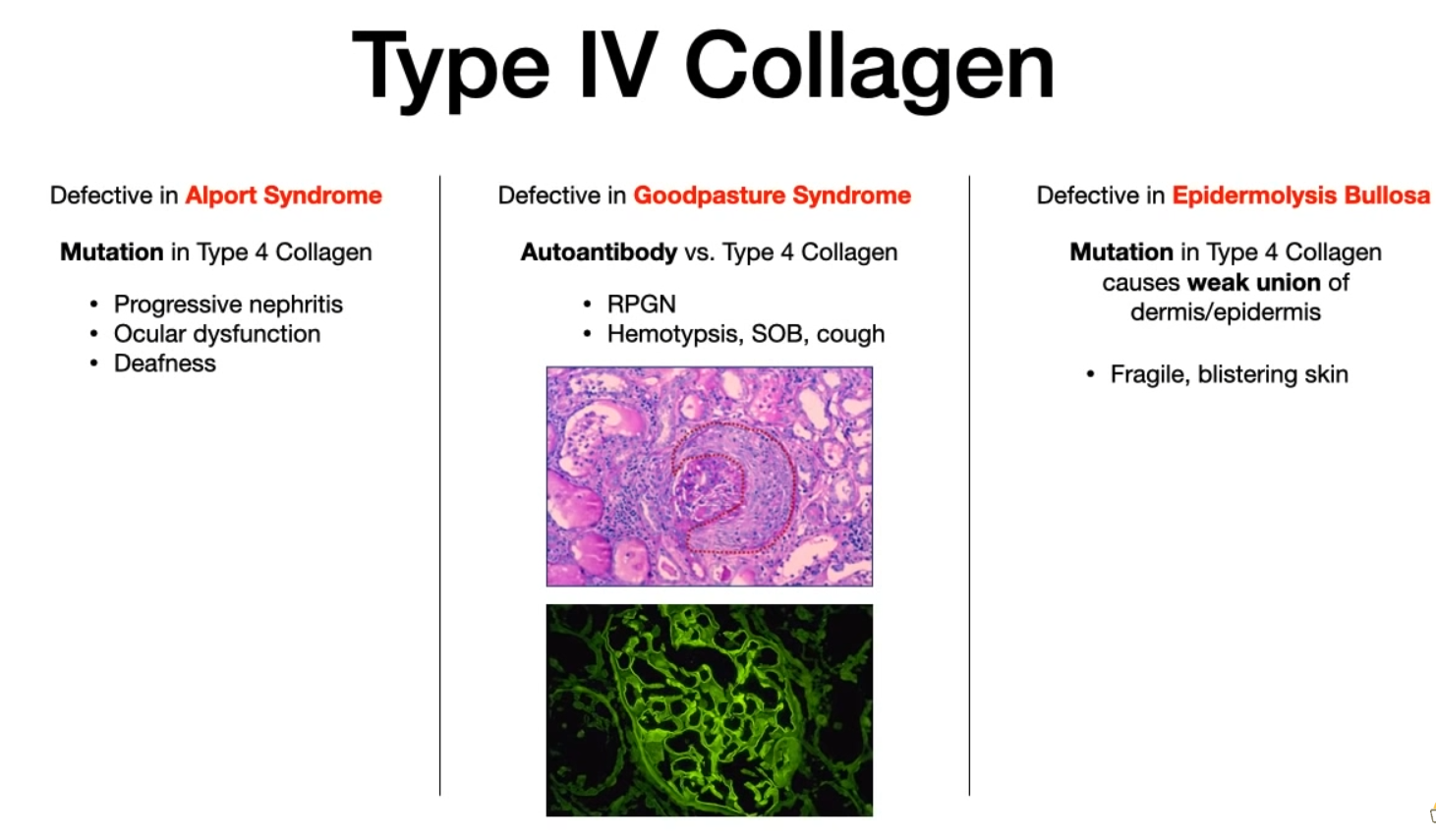
- Pathology:
- Alport Syndrome: X-linked dominant disorder. Classic triad of sensorineural hearing loss, ocular abnormalities, and progressive glomerulonephritis (hematuria). “Can’t see, can’t pee, can’t hear a bee.”
- Targeted by autoantibodies in Goodpasture Syndrome.

Tip
- Compare with ligaments, which are made of elastin.
- Ligaments attach bone to bone, and tendons attach muscle to bone.
- Connect presence of elastin with Marfan syndrome
- FBN1 can disrupt the normal regulation of TGF-β → Tall stature
- Skin → Skin hyperextensibility
- Large arteries → aortic dilation, aneurysms, or dissection
- Elastic ligaments → Joint hypermobility
- Lung → Increased risk of spontaneous pneumothorax
2. Elastin
- Function: Provides stretch and recoil to tissues.
- Location: Skin, lungs, large arteries (aorta), elastic ligaments.
- Structure: Rich in non-hydroxylated proline, glycine, and lysine.
- Synthesis: Tropoelastin is secreted and cross-linked by lysyl oxidase (requires copper) to form elastin.
- Key Associations:
- Fibrillin-1 acts as a scaffold for elastin deposition. A defect in fibrillin-1 causes Marfan syndrome.
- Elastin is broken down by elastase. Elastase is inhibited by α1-antitrypsin.
- Deficiency of α1-antitrypsin → excessive elastase activity → destruction of elastic fibers in the lungs → emphysema.
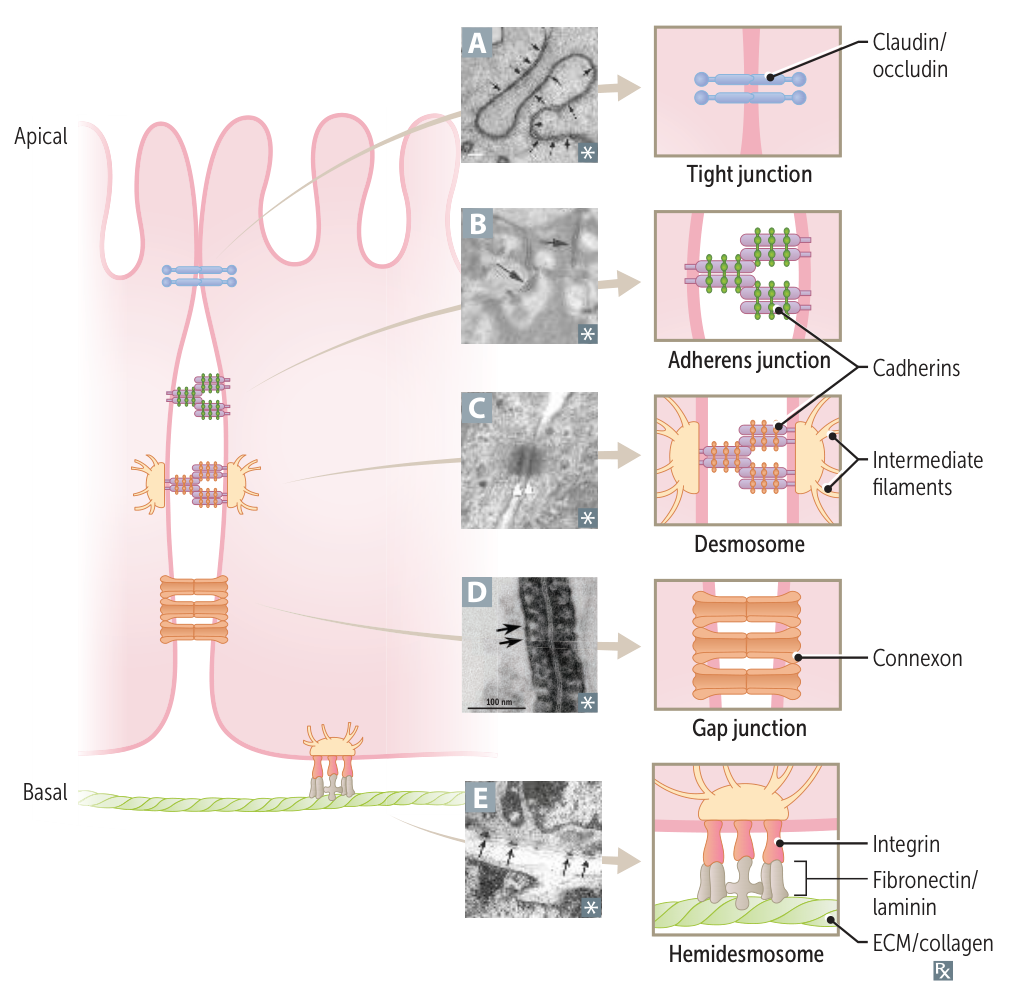
Adhesive Glycoproteins
- Function: Connect cells to the ECM.
- Laminin:
- Key component of the basement membrane.
- Binds Type IV collagen, heparan sulfate, and integrins on the cell surface.
- Fibronectin:
- Binds integrins, collagen, and heparin.
- Mediates cell adhesion and migration. Important in wound healing. t
Proteoglycans & Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
- Function: Form a hydrated, gel-like matrix that resists compressive forces. Binds growth factors.
- Structure:
- Proteoglycan: Core protein + covalently attached GAGs.
- GAGs: Long, unbranched polysaccharides of repeating disaccharide units. Highly negatively charged (sulfate and carboxyl groups) which attracts Na⁺ and water, creating the gel-like consistency.
- Major GAGs:
- Hyaluronic acid (Hyaluronan): Unique. Not sulfated and not attached to a core protein. Found in synovial fluid, vitreous humor.
- Chondroitin sulfate: Most abundant GAG. In cartilage, bone, tendons.
- Heparan sulfate: In basement membrane, on cell surfaces.
- Dermatan sulfate: Skin, blood vessels, heart valves.
- Keratan sulfate: Cornea, cartilage.
- Pathology:
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (e.g., Hurler syndrome, Hunter syndrome) are lysosomal storage diseases caused by a deficiency of enzymes needed to degrade GAGs.