Epidemiology
Etiology
Autosomal recessive defect in the SLC12A3 gene on chromosome 16p → impaired function of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter in the distal convoluted tubule → impaired Na+ and Cl- reabsorption → mild natriuresis → mild volume depletion → mild RAAS activation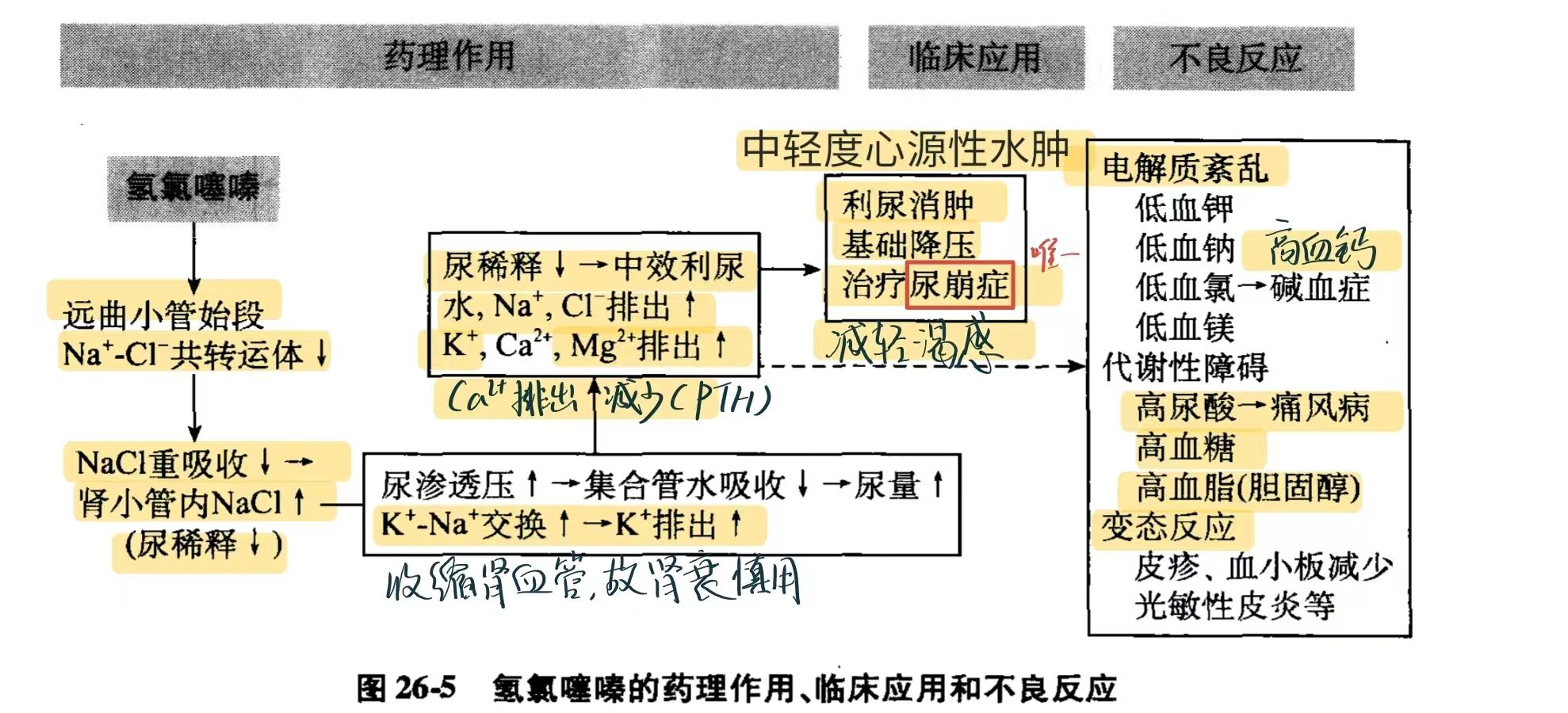
Clinical features
Clinical features are similar to those of chronic thiazide diuretic use:
- Fatigue, muscle weakness
- Muscle cramps and/or tetany
- Mild polyuria
Diagnostics
- Metabolic alkalosis
- increasing Na+ absorption in exchange for K+ and H+ secretion.
- Severe hypokalemia
- Hypercalcemia and hypocalciuria
- Decreased intracellular sodium levels increase the activity of the basolateral Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in the cells of the distal convoluted tubule. Sodium is transported into, and calcium out of, the cell, resulting in decreased intracellular calcium concentration that leads to increased reabsorption from the lumen via luminal Ca2+ channels. Calcium reabsorption may also be increased because of increased uptake of sodium and calcium in the proximal tubule as a result of sodium depletion.
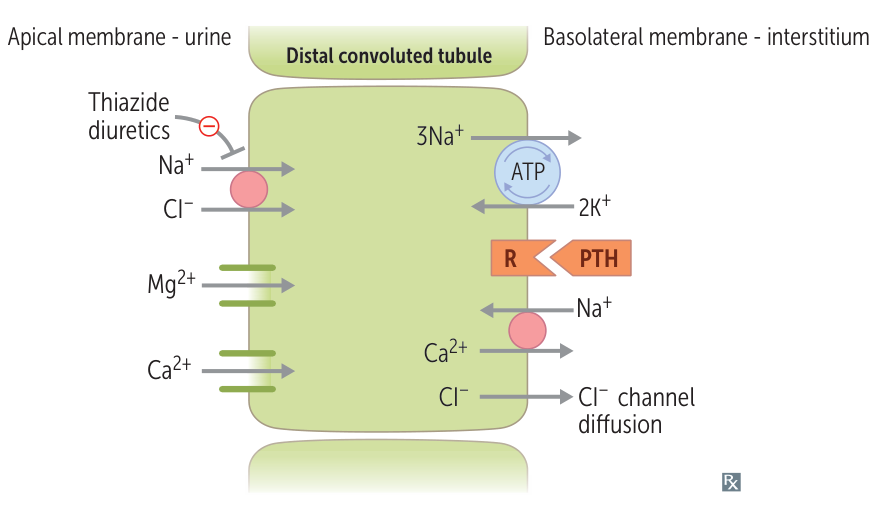
- Decreased intracellular sodium levels increase the activity of the basolateral Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in the cells of the distal convoluted tubule. Sodium is transported into, and calcium out of, the cell, resulting in decreased intracellular calcium concentration that leads to increased reabsorption from the lumen via luminal Ca2+ channels. Calcium reabsorption may also be increased because of increased uptake of sodium and calcium in the proximal tubule as a result of sodium depletion.
- Hypomagnesemia