Physiologic anticoagulants
- Inhibit intrinsic pathway:
- Antithrombin (with heparin): inhibit factor 2(thrombin), 9, 10, 11, 12
- Protein C: inhibit 5, 8; need VitK to synthesize
- Inhibit extrinsic pathway:
- TFPI(Tissue factor pathway inhibitor): combine factor 10 to inhibit factor 7a
Tip
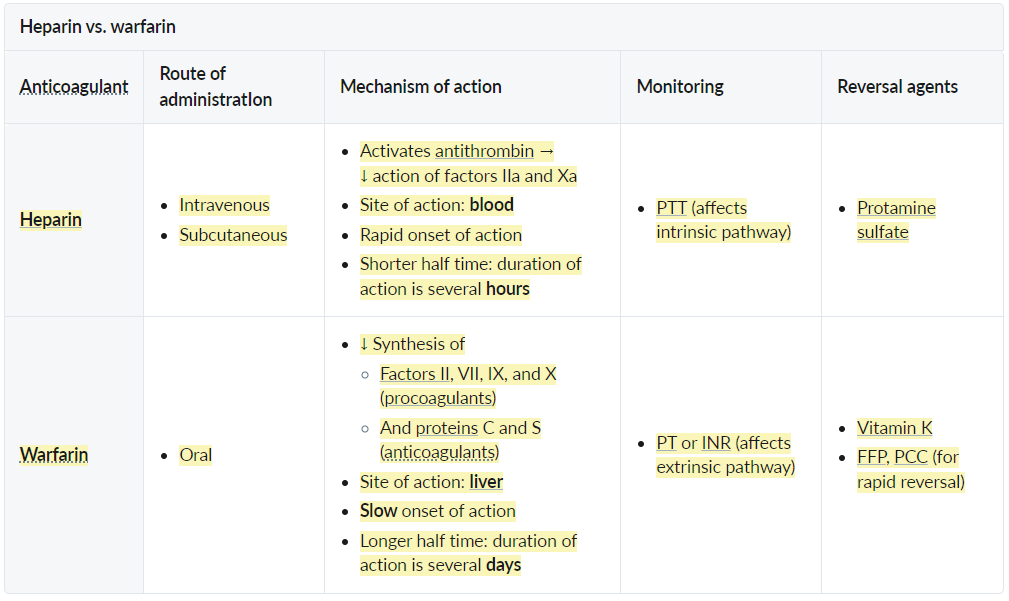
- Heparin: also affects VIII and IX → intrinsic pathway → PTT
- Warfarin: affects both intrinsic and extrinsic pathway, but VII has shorter half life → extrinsic pathway → PT
- The half-lives of the procoagulants are ∼ 2–4 days (except for factor VII, which has a short half-life), while the anticoagulants only have half-lives of 6–10 hours.
- Intrinsic pathway remains active another 2–3 days, while extrinsic pathway and protein C are already inactive.
- Direct thrombin inhibitors: prolonged thrombin time (TT), no change to PTT or PT (not routinely monitored)
- Direct factor Xa inhibitors: prolonged PT and PTT, unchanged thrombin time (not routinely monitored)
Tip
Anticoagulants cause thrombosis, this can also be seen in HIT.
Heparins (Unfractionated & LMWH)
- Unfractionated Heparin (UFH)
- Mechanism: Binds Antithrombin III irreversibly inactivates Thrombin (IIa) and Factor Xa. t
- Clinical Use: Immediate anticoagulation (PE, ACS, DVT), safe in pregnancy.
- Monitoring: Follow PTT.
- Adverse Effects: Bleeding, Osteoporosis (long-term), Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT).
- Pathophysiology: IgG antibodies form against Heparin-Platelet Factor 4 (PF4) complex. Immune complex activates platelets thrombosis + thrombocytopenia.
- Reversal: Antidote: protamine sulfate (a positively-charged protein that can neutralize negatively-charged heparin by forming inactive complexes)
- Can’t give fresh frozen plasma (FFP), since it contains antithrombin III → enhances heparin effect
- Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH)
- Drugs: Enoxaparin, Dalteparin.
- Mechanism: Acts more on Factor Xa than Thrombin. Better bioavailability and longer half-life than UFH.
- Clinical Use: DVT prophylaxis/treatment, Acute Coronary Syndrome. Safe in pregnancy. t
- Monitoring: None usually required (can monitor anti-Xa levels in renal failure or obesity).
- Contraindications: Renal insufficiency (renally cleared).
Vitamin K Antagonist (Warfarin)
- Mechanism
- Clinical Use
- Chronic anticoagulation (e.g., venous thromboembolism prophylaxis, prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation).
- “Bridge” therapy: to prevent transient hypercoagulable state and Warfarin Skin Necrosis
- Start Heparin + Warfarin simultaneously. Discontinue Heparin once INR is therapeutic for >24 hrs (usually takes days due to long half-life of Factor II).
- Monitoring
- Adverse Effects
- Bleeding.
- Teratogenic (bone/cartilage defects) Avoid in pregnancy (Use LMWH).
- Warfarin Skin Necrosis: Rare complication in pts with underlying Protein C deficiency. t
Warfarin reversal
| Warfarin overdose | Heparin overdose | |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin K | • Effective (takes days) | • Ineffective |
| FFP | • Effective (contains all blood clotting factors & proteins) | • Ineffective (contains antithrombin III → enhances heparin effect) |
| Protamine | • Ineffective | • Effective (heparin-specific antidote) t |
- Stop warfarin.
- Administer IV vitamin K PLUS 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC)
- If PCC is unavailable, give fresh frozen plasma (FFP)
- Monitor INR every 6 hours until warfarin has been fully reversed (INR ≤ 1.1)
Warfarin interactions
Warfarin is metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes.
- Decrease of anticoagulant effect
- Rifampicin, carbamazepine, St. John’s wort, ginger, licorice: induce metabolic breakdown of warfarin via induction of cytochrome P450
- Foods rich in vitamin K (e.g., kale, spinach): counter effect of warfarin
- Gastric acid inhibition (PPI use), cholestyramine treatment: impaired uptake of warfarin
- Increase of anticoagulant effect
- Several antidepressants and antibiotics, PPIs, amiodarone, grapefruit: impair metabolic breakdown via inhibition of cytochrome P450
- Acetaminophen: metabolite of acetaminophen interrupts vitamin K cycle via inhibition of vitamin K-dependent carboxylase
- Sulfonamides, sulfonylureas: competitively block or displace warfarin at plasma protein binding sites
- Damage to gut flora (e.g., antibiotic therapy): impaired bacterial vitamin K synthesis
Direct Factor Xa Inhibitors (“-xabans”)
- Drugs: Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Edoxaban.
- Mechanism: Bind to and directly inhibit Factor Xa. t
- Not blocking conversion from X to Xa
- Clinical Use: DVT/PE treatment and prophylaxis, Stroke prophylaxis in non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
- Advantages: Fixed oral dosing, no monitoring required.
- Adverse Effects: Bleeding.
- Reversal: Andexanet alfa.
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (DTIs)
- Act independently from antithrombin
- The effect of most parenteral anticoagulants (except for direct thrombin inhibitors) works by enhancing native antithrombin III.
- Intravenous DTIs
- Drugs: Bivalirudin, Argatroban.
- Mechanism: Directly inhibit thrombin (Factor IIa).
- Clinical Use: Anticoagulation in patients with HIT (Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia).
- Oral DTIs
- Drugs: Dabigatran.
- Mechanism: Directly inhibits thrombin.
- Clinical Use: Venous thromboembolism, Atrial fibrillation.
- Reversal: Idarucizumab (monoclonal antibody fragment).